Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the results of using minimally invasive reduction techniques in patients with femoral subtrochanteric fracture.
Materials and Methods
We retrospectively analyzed 40 patients (41 cases) with subtrochanteric fracture who underwent using minimally invasive reduction techniques. The mean age was 61.4 years (15-89 years), and the mean follow-up period was 32.7 months (12-66 months). Clinical results were assessed using the Parker-Palmer mobility score and the Salvati-Wilson hip functional score. Radiographic results were evaluated using bone union time and femur neck-shaft angle.
Results
No significant difference was observed in the pre- and postoperative Parker-Palmer mobility score. Salvati-Wilson hip functional score showed more than good grade in 37 cases (90%) at the last follow-up. Union was achieved in all 41 cases at an average of 22.5 weeks (18-30 weeks). The mean femoral neck-shaft angle immediately postoperatively was 128.8 degrees (120-140 degrees), and the mean difference versus contralateral sides was 2.5 degrees varus (-6-13 degrees).
Figures and Tables
 | Fig. 1Reduction technique.
(A, B) Reduction was performed with a Hohmann retractor and a long tonsil in the proximal thigh.
(C) Reduction was maintained with a bone hook.
|
 | Fig. 2
(A, B, C) Fractures of the oblique pattern were temporally reduced by a collinear clamp and fixed with a cerclage wiring. |
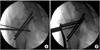 | Fig. 3
(A) A bone hook was maintained in place until the lag screws were inserted at the proper position of the femoral head.
(B) A locking compressing plate-distal femur (LCP-DF) was inserted through the proximal submuscular tunnel and fixed with locking screws.
|
References
1. Afsari A, Liporace F, Lindvall E, Infante A Jr, Sagi HC, Haidukewych GJ. Clamp-assisted reduction of high subtrochanteric fractures of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009. 91:1913–1918.

2. Barquet A, Francescoli L, Rienzi D, López L. Intertrochanteric-subtrochanteric fractures: treatment with the long Gamma nail. J Orthop Trauma. 2000. 14:324–328.

4. Carr JB. The anterior and medial reduction of intertrochanteric fractures: a simple method to obtain a stable reduction. J Orthop Trauma. 2007. 21:485–489.

5. Choi JS, Moon DH, Noh YT. The treatment of subtrochanteric fracture with cephallomedually nail: minimal incision and lowman clamp assisted reduction. J Korean Fract Soc. 2011. 24:301–306.

6. Craig NJ, Maffulli N. Subtrochanteric fractures: current management options. Disabil Rehabil. 2005. 27:1181–1190.

7. Gadegone WM, Salphale YS. Proximal femoral nail - an analysis of 100 cases of proximal femoral fractures with an average follow up of 1 year. Int Orthop. 2007. 31:403–408.

8. Holt G, Nunag P, Duncan K, Gregori A. Outcome after short intramedullary nail fixation of unstable proximal femoral fractures. Acta Orthop Belg. 2010. 76:347–355.
9. Hwang CS, Chung PH, Kang S, et al. Treatment of subtrochanteric femur fractures using intramedullary devices. J Korean Fract Soc. 2008. 21:13–18.

10. Kim JJ, Kim JW. Subtrochanteric Fracture: Intramedullary Nailing. J Korean Fract Soc. 2009. 22:114–122.

11. Li F, Sang W, Wang Q, Huang J, Lu H. Subtrochanteric fracture treatment: a retrospective study of 46 patients. Med Princ Pract. 2011. 20:519–524.

12. Oh CW. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of subtrochanteric femoral fractures. J Korean Fract Soc. 2009. 22:123–129.

13. Oh CW, Kim JJ, Byun YS, et al. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of subtrochanteric femur fractures with a locking plate: a prospective series of 20 fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009. 129:1659–1665.

14. Oh CW, Oh JK, Kim SJ, et al. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for comminuted subtrochanteric fracture of the femur. J Korean Fract Soc. 2006. 19:407–411.

15. Park J, Yang KH. Correction of malalignment in proximal femoral nailing--Reduction technique of displaced proximal fragment. Injury. 2010. 41:634–638.

16. Park SY, Yang KH, Yoo JH, Yoon HK, Park HW. The treatment of reverse obliquity intertrochanteric fractures with the intramedullary hip nail. J Trauma. 2008. 65:852–857.

17. Parker MJ, Maheshwer CB. The use of a hip score in assessing the results of treatment of proximal femoral fractures. Int Orthop. 1997. 21:262–264.

18. Robinson CM, Houshian S, Khan LA. Trochanteric-entry long cephalomedullary nailing of subtrochanteric fractures caused by low-energy trauma. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005. 87:2217–2226.

19. Russel TA, Taylor JC. Browner BD, Jupiter JB, Levine AM, Trafton PG, editors. Subtrochanteric fractures of femur. Skeletal trauma. 1992. Philadelphia: Saunders;1490–1492.
20. Salvati EA, Wilson PD Jr. Long-term results of femoral-head replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973. 55:516–524.

21. Sanders R, Regazzoni P. Treatment of subtrochanteric femur fractures using the dynamic condylar screw. J Orthop Trauma. 1989. 3:206–213.

23. Shukla S, Johnston P, Ahmad MA, Wynn-Jones H, Patel AD, Walton NP. Outcome of traumatic subtrochanteric femoral fractures fixed using cephalo-medullary nails. Injury. 2007. 38:1286–1293.

24. Siebenrock KA, Müller U, Ganz R. Indirect reduction with a condylar blade plate for osteosynthesis of subtrochanteric femoral fractures. Injury. 1998. 29:Suppl 3. C7–C15.

25. Sims SH. Subtrochanteric femur fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 2002. 33:113–126.
26. Webb LX. Proximal femoral fractures. J South Orthop Assoc. 2002. 11:203–212.
27. Wu CC. Locked nailing for shortened subtrochanteric nonunions: a one-stage treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009. 467:254–259.

28. Yoon HK. Treatment of subtrochanteric fracture. J Korean Hip Soc. 2007. 19:283–291.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download