Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the incidence of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in trauma patients with pelvic or acetabular fracture and determine high risk factors.
Materials and Methods
Twenty-three patients who had a pelvic or acetabular fracture were enrolled between March 2011 and February 2012. All patients had mechanical and chemical prophylaxis and underwent deep vein thrombosis (DVT) computed tomography around 2 weeks after injury for evaluation of VTE. The relationships between VTE and each of sex, age, body mass index, injury severity score, intensive care unit stay, transfusion, operation time, coagulopathy, and associated injury were analyzed.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
A 21-year-old female with injury severity score 29.
(A) Three-dimensional computed tomography (CT) image of the pelvis showing pelvic ring injury (jumper's fracture) and right acetabular fracture (both column).
(B) Sagittal reconstruction image of the lumbar-spine showing an L1 bursting fracture with neurologic deficit.
(C) Postoperative X-ray of lumbar-spine.
(D) Chest CT image showing a filling defect in the posterobasal segmental pulmonary artery right with vital sign 142/88-37.7-120-22 at postoperative 6 days.
(E) Inferior vena cava filter insertion.
(F) Postoperative X-ray after definitive surgery.
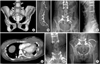
Fig. 2
Comparison of the rate of venous thromboembolism between subgroup with risk scores of 13 or less and 14 or more. VTE: Venous thromboembolism.
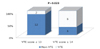
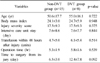
Table 3
Clinical Features of Patients who Experienced a Venous Thromboembolism

BMI: Body mass index, ISS: Injury severity score, DVT: Deep vein thrombosis, F: Female, M: Male, Post.: Posterior, fx.: Fracture, Postop.: Postoperative, Preop.: Preoperative, PE: Pulmonary embolism, EIV: External iliac vein, FV: Femoral vein, PV: Popliteal vein, PeV: Peroneal vein, PTV: Posterior tibial vein, CIV: Common iliac vein, AC: Anticoagulants, IVC: Inferior vena cava.
References
1. Abelseth G, Buckley RE, Pineo GE, Hull R, Rose MS. Incidence of deep-vein thrombosis in patients with fractures of the lower extremity distal to the hip. J Orthop Trauma. 1996. 10:230–235.

2. Cham MD, Yankelevitz DF, Shaham D, et al. The Pulmonary Angiography-Indirect CT Venography Cooperative Group. Deep venous thrombosis: detection by using indirect CT venography. Radiology. 2000. 216:744–751.

3. Geerts WH, Bergqvist D, Pineo GF, et al. American College of Chest Physicians. Prevention of venous thromboembolism: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest. 2008. 133:6 Suppl. 381S–453S.

4. Geerts WH, Code KI, Jay RM, Chen E, Szalai JP. A prospective study of venous thromboembolism after major trauma. N Engl J Med. 1994. 331:1601–1606.

5. Greenfield LJ, Proctor MC, Rodriguez JL, Luchette FA, Cipolle MD, Cho J. Posttrauma thromboembolism prophylaxis. J Trauma. 1997. 42:100–103.

6. Hak DJ. Prevention of venous thromboembolism in trauma and long bone fractures. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2001. 7:338–343.

7. Helfet D. Magnetic resonance venography to evaluate deep venous thrombosis in patients with pelvic and acetabular trauma. J Trauma. 2001. 51:178.
8. Knudson MM, Morabito D, Paiement GD, Shackleford S. Use of low molecular weight heparin in preventing thromboembolism in trauma patients. J Trauma. 1996. 41:446–459.
9. Loud PA, Grossman ZD, Klippenstein DL, Ray CE. Combined CT venography and pulmonary angiography: a new diagnostic technique for suspected thromboembolic disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998. 170:951–954.

10. Loud PA, Katz DS, Bruce DA, Klippenstein DL, Grossman ZD. Deep venous thrombosis with suspected pulmonary embolism: detection with combined CT venography and pulmonary angiography. Radiology. 2001. 219:498–502.

11. Loud PA, Katz DS, Klippenstein DL, Shah RD, Grossman ZD. Combined CT venography and pulmonary angiography in suspected thromboembolic disease: diagnostic accuracy for deep venous evaluation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000. 174:61–65.

12. Montgomery KD, Geerts WH, Potter HG, Helfet DL. Thromboembolic complications in patients with pelvic trauma. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996. (329):68–87.

13. Montgomery KD, Geerts WH, Potter HG, Helfet DL. Practical management of venous thromboembolism following pelvic fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 1997. 28:397–404.

14. Moser KM, LeMoine JR. Is embolic risk conditioned by location of deep venous thrombosis? Ann Intern Med. 1981. 94:439–444.

15. Napolitano LM, Garlapati VS, Heard SO, et al. Asymptomatic deep venous thrombosis in the trauma patient: is an aggressive screening protocol justified? J Trauma. 1995. 39:651–657.

16. Russell GV Jr, Nork SE, Chip Routt ML Jr. Perioperative complications associated with operative treatment of acetabular fractures. J Trauma. 2001. 51:1098–1103.

17. Sen RK, Kumar A, Tripathy SK, Aggarwal S, Khandelwal N, Manoharan SR. Risk of postoperative venous thromboembolism in Indian patients sustaining pelvi-acetabular injury. Int Orthop. 2011. 35:1057–1063.
18. Stannard JP, Riley RS, McClenney MD, Lopez-Ben RR, Volgas DA, Alonso JE. Mechanical prophylaxis against deep-vein thrombosis after pelvic and acetabular fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001. 83-A:1047–1051.
19. Stannard JP, Singhania AK, Lopez-Ben RR, et al. Deep-vein thrombosis in high-energy skeletal trauma despite thromboprophylaxis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005. 87:965–968.

20. Steele N, Dodenhoff RM, Ward AJ, Morse MH. Thromboprophylaxis in pelvic and acetabular trauma surgery. The role of early treatment with low-molecular-weight heparin. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005. 87:209–212.

21. Stein PD, Fowler SE, Goodman LR, et al. PIOPED II Investigators. Multidetector computed tomography for acute pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med. 2006. 354:2317–2327.
22. White RH, Goulet JA, Bray TJ, Daschbach MM, McGahan JP, Hartling RP. Deep-vein thrombosis after fracture of the pelvis: assessment with serial duplex-ultrasound screening. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1990. 72:495–500.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download