Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the effectiveness of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for the diagnosis and usefulness of vertebroplasty in osteoporotic occult vertebral fractures.
Materials and Methods
Of 472 osteoporotic vertebral fractures treated from May 2003 to July 2009, 45 patients were diagnosed with occult osteoporotic vertebral fracture. Their medical charts and radiographs were reviewed. The degree of vertebral body collapse was graded by a semiquantitative method. In order to increase the reliability, interpretation was based on radiographic diagnoses from 3 orthopedic surgeons. Vertebroplasty was performed at 31 of the 45 patients, for whom conservative treatment failed. Pre-operatively and post-operatively, pain was evaluated using a visual analog scale (VAS).
Results
We observed 55 occult fractures in 45 patients. Forty vertebrae (72.7%) among the 55 vertebrae were just adjacent to an old vertebral fracture with deformation of the vertebral body. The rediagnosis rate of occult fracture attempted without MRI was only 21.8%. The average pre-operative VAS score of 8.07 (6~9) was improved to 2.43 after surgery and showed no delayed vertebral body collapse.
Conclusion
Gadolinium enhancement of MRI is critical to the diagnosis of occult vertebral fractures, which are 9% of whole osteoporotic vertebral fractures. Seventy-two point seven percent of occult vertebral fractures were just adjacent to an old vertebral fracture with collapse of the vertebral body. This means that if vertebroplasty is performed without thorough MRI examination, it may fail.
Figures and Tables
 | Fig. 1The Genant semiquantitative scale, one of the vertebral fracture assessment tools, is classified into 4 grades according to the degree of collapse. |
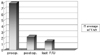 | Fig. 2The mean of the preop. VAS was 8.07, and that was improved to a VAS of 2.43 after vertebroplasty. VAS: Visual analogue scale, Preop.: Pre-operative, Postop.: Post-operative, F/U: Follow-up. |
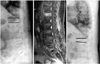 | Fig. 3This patient was proven by magnetic resonance imaging, to have a T12 occult fracture, and this occult fracture developed into delayed body collapse during conservative treatment. |
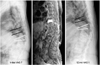 | Fig. 4This patient had a T9 occult fracture adjacent to an old fracture with severe body collapse. Delayed collapse was found even after successful conservative therapy. VAS: Visual analogue scale. |
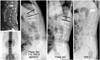
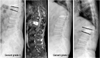 | Fig. 5This patient had L1 occult fracture and underwent vertebroplasty. A radiograph 1 year after the operation shows no further collapse. The visual analogue scale score was improved from 8 to 1 after vertebroplasty. Note that the occult fracture was just adjacent to the old one with severe body collapse. |
References
1. Black DM, Cummings SR, Stone K, Hudes E, Palermo L, Steiger P. A new approach to defining normal vertebral dimensions. J Bone Miner Res. 1991. 6:883–892.

2. Cho YS, Cho SD, Kim BS, Park TW, Lew S, Hwang SY. Kummell's disease managed by percutaneous vertebroplasty. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2001. 8:226–234.

3. Chou LH, Knight RQ. Idiopathic avascular necrosis of a vertebral body. Case report and literature review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997. 22:1928–1932.
4. Dasgupta B, Shah N, Brown H, Gordon TE, Tanqueray AB, Mellor JA. Sacral insufficiency fractures: an unsuspected cause of low back pain. Br J Rheumatol. 1998. 37:789–793.
5. Deramond H, Depriester C, Galibert P, Le Gars D. Percutaneous vertebroplasty with polymethylmethacrylate. Technique, indications, and results. Radiol Clin North Am. 1998. 36:533–546.
6. Deutsch AL, Mink JH, Waxman AD. Occult fractures of the proximal femur: MR imaging. Radiology. 1989. 170:113–116.

7. Genant HK, Wu CY, van Kuijk C, Nevitt MC. Vertebral fracture assessment using a semiquantitative technique. J Bone Miner Res. 1993. 8:1137–1148.

8. Grasland A, Pouchot J, Mathieu A, Paycha F, Vinceneux P. Sacral insufficiency fractures: an easily overlooked cause of back pain in elderly women. Arch Intern Med. 1996. 156:668–674.

9. Hwang J, Kim C, Kim J. Vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic compression fracture: more than 1 year follow up. J Korean Fract Soc. 2004. 17:368–373.

10. Kanchiku T, Taguchi T, Kawai S. Magnetic resonance imaging diagnosis and new classification of the osteoporotic vertebral fracture. J Orthop Sci. 2003. 8:463–466.

11. Kim C, Choi Y, Baek S, et al. Vertebroplasty on osteoporotic compression fracture. J Korean Soc Fract. 2002. 15:123–126.

12. Kleerekoper M, Nelson DA, Peterson EL, Tilley BC. Outcome variables in osteoporosis trials. Bone. 1992. 13:Suppl 1. S29–S34.

13. Lichtenstein L. Diseases of bone and joints. 1975. 2nd ed. St. Louis: Mosby;244.
14. Moulopoulos LA, Yoshimitsu K, Johnston DA, Leeds NE, Libshitz HI. MR prediction of benign and malignant vertebral compression fractures. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1996. 6:667–674.

15. Osterhouse MD, Kettner NW. Delayed posttraumatic vertebral collapse with intravertebral vacuum cleft. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2002. 25:270–275.

16. Peh WC, Khong PL, Yin Y, et al. Imaging of pelvic insufficiency fractures. Radiographics. 1996. 16:335–348.

17. Pham T, Azulay-Parrado J, Champsaur P, Chagnaud C, Legré V, Lafforgue P, et al. "Occult" osteoporotic vertebral fractures: vertebral body fractures without radiologic collapse. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005. 30:2430–2435.
18. Ross PD, Davis JW, Epstein RS, Wasnich RD. Ability of vertebral dimensions from a single radiograph to identify fractures. Calcif Tissue Int. 1992. 51:95–99.

19. Schinz HR, Baensch WE, Friedl E, Uehlinger E. Roentgen diagnostics. 1952. vol. II:1st ed. New York: Grune & Stratton;1554–1556.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download