Abstract
Materials and Methods
A retrospective study of 23 patients among 30 patients with pilon fractures from March 2006 to November 2008, who underwent two-stage treatment of pilon fractures with a minimum of 24 months follow-up. The mean follow-up period was 28 months (24~41 months). In the first stage of the operation, open reduction of the articular surface and external fixation were performed after minimal incision. As the soft tissue healed, locking compression plate fixation was performed with the Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis. Radiographic evaluation was graded by the criteria of Burwell and Charnley, and functional assessment of the ankle was evaluated by the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) ankle-hindfoot score.
Figures and Tables
 | Fig. 1Twenty-three patients were classified by pre-operative simple X-ray and computed tomography scan using the Rüedi-Allgöwer16) classification in this study. |
 | Fig. 2Distribution of soft tissue injury patterns is shown in this figure using the Tscherne and Goetzen20) classification in this study. |
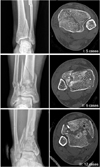
 | Fig. 3
(A) This 47-year-old male had a fall injury and sustained a Rüedi-Allgöwer type III pilon fracture. The fracture was treated by external fixation with three screw fixation using anteromedial approach (arrow) to the tibial plafond.
(B) This 41-year-old male had a motor vehicle accident and sustained a Rüedi-Allgöwer type III pilon fracture. The axial computed tomography scanning demonstrate a communited articular injury that is composed of three major articular components and central impacted fragment (black arrow). The fracture is treated by external fixation with three screw fixation using anterolateral approach (white arrow) to tibial plafond.
(C) As in the first stage treatment, the pilon fracture was realigned and stabilized by an external mono fixator, with the fibular fracture being fixed with a plate and screw.
|
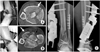
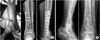 | Fig. 4
(A) Two weeks after the first operation, closed reduction and internal fixation with locking compression plate (Synthes, Oberdorf, Switzerland) were performed.
(B) At post-operative 36 months, the patient underwent the removal of the implant. The post-operative radiographs show good alignment and good ankle articulation.
|
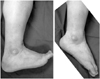 | Fig. 5Last follow-up photographs show good ankle range of motion in 41-year-old male patients who underwent two stage treatment of pilon fracture. |
References
1. Baumgaertel F, Buhl M, Rahn BA. Fracture healing in biological plate osteosynthesis. Injury. 1998. 29:Suppl 3. C3–C6.

2. Blauth M, Bastian L, Krettek C, Knop C, Evans S. Surgical options for the treatment of severe tibial pilon fractures: a study of three techniques. J Orthop Trauma. 2001. 15:153–160.

3. Bone LB. Fractures of the tibial plafond. The pilon fracture. Orthop Clin North Am. 1987. 18:95–104.

4. Bone L, Stegemann P, McNamara K, Seibel R. External fixation of severely comminuted and open tibial pilon fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993. (292):101–107.

5. Borens O, Kloen P, Richmond J, Roederer G, Levine DS, Helfet DL. Minimally invasive treatment of pilon fractures with a low profile plate: preliminary results in 17 cases. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009. 129:649–659.

7. Burwell HN, Charnley AD. The treatment of displaced fractures at the ankle by rigid internal fixation and early joint movement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1965. 47:634–660.

8. Coonrad RW. Fracture-dislocations of the ankle joint with impaction injury of the lateral weight-bearing surface of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1970. 52:1337–1344.

9. Destot E. Traumatismes du pied et rayons: X. Malleles, astragale, calcaneum, avant-pied. 1911. Paris: Masson;1–10.
10. Mast JW, Spiegel PG, Pappas JN. Fractures of the tibial pilon. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988. (230):68–82.
11. Mast JW, Teipner WA. A reproducible approach to the internal fixation of adult ankle fractures: rationale, technique, and early results. Orthop Clin North Am. 1980. 11:661–679.

13. Patterson MJ, Cole JD. Two-staged delayed open reduction and internal fixation of severe pilon fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 1999. 13:85–91.
14. Pierce RO Jr, Heinrich JH. Comminuted intra-articular fractures of the distal tibia. J Trauma. 1979. 19:828–832.
15. Rommens PM, Claes P, De Boodt P, Stappaerts KH, Broos PL. Therapeutic procedure and long-term results in tibial pilon fracture in relation to primary soft tissue damage. Unfallchirurg. 1994. 97:39–46.

16. Rüedi TP, Allgöwer M. The operative treatment of intra-articular fractures of the lower end of the tibia. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979. (138):105–110.

17. Shin HK, Choi JY, Lee JW. Treatment of the pilon fracture involving tibial shaft using two staged MIPO technique. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2006. 10:184–189.
18. Takakura Y, Tanaka Y, Kumai T, Tamai S. Low tibial osteotomy for osteoarthritis of the ankle. Results of a new operation in 18 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995. 77:50–54.
19. Teeny SM, Wiss DA. Open reduction and internal fixation of tibial plafond fractures. Variables contributing to poor results and complications. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993. (292):108–117.
20. Tscherne H, Gotzen L. Tscherne H, Gotzen L, editors. External articular transfixation of joint injuries with severe soft tissue damage. Fractures with soft tissue injuries. 1984. Berlin: Springer-Verlag;103–117.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download