Abstract
Purpose
To report the results of patients treated by minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) for proximal tibial shaft fractures.
Materials and Methods
From September 2003 to June 2008, thirty-two patients with proximal tibial shaft fractures weretreated by MIPO. There were 22 men and 10 women and mean age was 43.8 years (range; 21~72 years). Follow-up was available for all patients and the mean follow-up period was 19.5 months (range; 12~40 months). Duration of union, range of knee motion and postoperative complications were evaluated.
Results
Twenty-nine patients (90.6%) healed after the MIPO technique. The mean duration of radiographic union was 18.3 weeks (range; 10~28 weeks). The mean range of knee motion was 134 degrees at the last follow-up. There were 1 non-union, 2 delayed unions, 1 superficial infection, 1 deep infection, 2 malunions with more than 5 degrees of malalignment and 14 cases of skin irritation by plate.
Figures and Tables
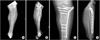 | Fig. 1
(A, B) A 68-year old man with severe communited proximal tibial fracture.
(C, D) The fracture was healed 20 weeks after surgery.
|
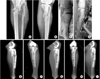 | Fig. 2
(A, B, C) A 69-year-old man with severe communited, open proximal tibial fracture by traffic acident.
(D) Clinical photograph after application of external fixator.
(E) Follow-up radiograph after 16 weeks shows metal failure.
(F, G) The dual plating was performed after removal of internal devices.
(H, I) Bone union with satisfactory functional results was achieved at 6 months after second operation.
|
References
1. Boldin C, Fankhauser F, Hofer HP, Szyszkowitz R. Three-year results of proximal tibia fractures treated with the LISS. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006. 445:222–229.

2. Böstman O, Hänninen A. The fibular reciprocal fracture in tibial shaft fractures caused by indirect violence. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1982. 100:115–121.

3. Cole PA, Zlowodzki M, Kregor PJ. Treatment of proximal tibia fractures using the less invasive stabilization system: surgical experience and early clinical results in 77 fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2004. 18:528–535.

4. Collinge C, Sanders R, DiPasquale T. Treatment of complex tibial periarticular fractures using percutaneous techniques. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000. 375:69–77.

5. D'Aubigne RM, Maurer P, Zucman J, Masse Y. Blind intramedullary nailing for tibial fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1974. 105:267–275.
6. Egol KA, Tejwani NC, Capla EL, Wolinsky PL, Koval KJ. Staged management of high-energy proximal tibia fractures (OTA types 41): the results of a prospective, standardized protocol. J Orthop Trauma. 2005. 19:448–455.
7. Gerber A, Ganz R. Combined internal and external osteosynthesis a biological approach to the treatment of complex fractures of the proximal tibia. Injury. 1998. 29:Suppl 3. C22–C28.

8. Helfet DL, Suk M. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis of fractures of the distal tibia. Instr Course Lect. 2004. 53:471–475.
9. Kim JW, Oh CW, Oh JK, et al. Staged minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of proximal tibial fracture. J Korean Fract Soc. 2009. 22:6–12.

10. Lachiewicz PF, Funcik T. Factors influencing the results of open reduction and internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990. 259:210–215.

11. Laflamme GY, Heimlich D, Stephen D, Kreder HJ, Whyne CM. Proximal tibial fracture stability with intramedullary nail fixation using oblique interlocking screws. J Orthop Trauma. 2003. 17:496–502.

12. Lang GJ, Cohen BE, Bosse MJ, Kellam JF. Proximal third tibial shaft fractures. Should they be nailed? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995. 315:64–74.
13. Littenberg B, Weinstein LP, McCarren M, et al. Closed fractures of the tibial shaft. A meta-analysis of three methods of treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998. 80:174–183.
14. Oh CW, Oh JK, Jeon IH, et al. Double plating of proximal tibial fractures using minimally invasive percutaneous osteosynthesis technique. J Korean Fract Soc. 2005. 18:250–255.

15. Oh CW, Oh JK, Jeon IH, et al. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate stabilization of proximal tibial fractures. J Korean Fract Soc. 2004. 17:224–229.

16. Peindl RD, Zura RD, Vincent A, Coley ER, Bosse MJ, Sims SH. Unstable proximal extraarticular tibia fractures: a biomechanical evaluation of four methods of fixation. J Orthop Trauma. 2004. 18:540–545.
17. Perren SM. Evolution of the internal fixation of long bone fractures. The scientific basis of biological internal fixation: choosing a new balance between stability and biology. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002. 84:1093–1110.
18. Phisitkul P, McKinley TO, Nepola JV, Marsh JL. Complications of locking plate fixation in complex proximal tibia injuries. J Orthop Trauma. 2007. 21:83–91.

19. Sarmiento A, Gersten LM, Sobol PA, Shankwiler JA, Vangsness CT. Tibial shaft fractures treated with functional braces. Experience with 780 fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1989. 71:602–609.

20. Schatzker J, Lambert DC. Supracondylar fractures of the femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979. 138:77–83.

21. Schatzker J, McBroom R, Bruce D. The tibial plateau fracture. The Toronto experience 1968--1975. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979. 138:94–104.
22. Tejwani NC, Achan P. Staged management of high-energy proximal tibia fractures. Bull Hosp Jt Dis. 2004. 62:62–66.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download