Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate clinical and radiological results using 3.5 mm & 2.4 mm volar locking compression plate (LCP) in distal radius fractures.
Materials and Methods
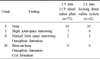
This study reviewed the results of 115 cases of distal radius fractures treated with 3.5 mm volar LCP (73 cases) & 2.4 mm volar LCP (42 cases) from September 2003 to June 2009. The radiographic results were evaluated by radiographic assessment, and the clinical results were evaluated by Knirk and Jupiter's criteria, Modified Mayo wrist scoring system and DASH score.
Results
Radiological evaluation of the radial length, radial inclination, volar tilt and intraarticular step off were improved both 3.5 mm volar LCP and 2.4 mm volar LCP. Nine cases of arthritis occured in 3.5 mm volar LCP and 7 cases in 2.4 mm volar by using the Knirk and Jupiter's criteria. The mean score evaluated by Modified Mayo was 86.7 in 3.5 mm volar LCP and 84.8 in 2.4 mm volar LCP. DASH score was 11.2 point in 3.5 mm volar LCP, 10.9 point in 2.4 mm volar LCP. All cases showed bone union showing no evidence of malunion, nounion, nor metal failure.
Figures and Tables
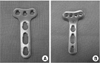 | Fig. 1
(A) Photograph shows 3.5 mm LCP distal radius plate.
(B) Photograph shows 2.4 mm locking distal radius system.
|
 | Fig. 2
(A) 52 year old female patient presented with distal radius fracture as AO classification C1.
(B) Postoperative radiographs show acceptable reduction with 3.5 mm LCP distal radius plate.
(C) Postoperative 17 months radiographs show complete bone union.
|
 | Fig. 3
(A) 64 year old male patient presented with distal radius fracture as AO classification C2.
(B) Postoperative radiographs show volar fixation using 2.4 mm locking distal radius system.
(C) Postoperative 12 months radiographs show locking compression screws are involved on the artricular surface. The patient had limitation in range of motion as flexion, extension because of wrist pain.
|
References
1. Arora R, Lutz M, Hennerbichler A, Krappinger D, Espen D, Gabl M. Complications following internal fixation of unstable distal radius fracture with a palmar locking-plate. J Orthop Trauma. 2007. 21:316–322.

2. Choi JY, Kim KC, Kim KH. Analysis of result of operative treatment for distal radius fracture. J Korean Soc Fract. 2000. 13:338–342.

3. Constantine KJ, Clawson MC, Stern PJ. Volar neutralization plate fixation of dorsally displaced distal radius fractures. Orthopedics. 2002. 25:125–128.

4. Cooney WP, Bussey R, Dobyns JH, Linscheid RL. Difficult wrist fractures. Perilunate fracture-dislocations of the wrist. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987. 214:136–147.
5. Fernandez DL, Geissler WB. Treatment of displaced articular fractures of the radius. J Hand Surg Am. 1991. 16:375–384.

6. Haidukewych GJ. Innovations in locking plate technology. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2004. 12:205–214.

7. Jupiter JB, Lipton H. The operative treatment of intraarticular fractures of the distal radius. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993. 292:48–61.

8. Knirk JL, Jupiter JB. Intra-articular fractures of the distal end of the radius in young adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986. 68:647–659.

9. Koval KJ, Hoehl JJ, Kummer FJ, Simon JA. Distal femoral fixation: a biomechanical comparison of the standard condylar buttress plate, a locked buttress plate, and the 95-degree blade plate. J Orthop Trauma. 1997. 11:521–524.

11. Lee LW, Putnam MD. Unstable fractures of the distal radius: an algorithmic method of treatment. Orthop Trans. 1988. 12:537–541.
12. Leung F, Zhu L, Ho H, Lu WW, Chow SP. Palmar plate fixation of AO type C2 fracture of distal radius using a locking compression plate--a biomechanical study in a cadaveric model. J Hand Surg Br. 2003. 28:263–266.

13. Lim JY, Lee HY, Song JH, Kang JW, Lee JY. Evaluation of the reliability, construct validity, and responsiveness of the. Korean version of the DASH. J Korean Soc Surg Hand. 2005. 10:192–198.
14. Lipton HA, Wollstein R. Operative treatment of intraarticular distal radial fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996. 327:110–124.

15. Musgrave DS, Idler RS. Volar fixation of dorsally displaced distal raiuds fractures using the 2.4-mm locking compression plates. J Hand Surg Am. 2005. 30:743–749.

16. Perren SM. Evolution and rationale of locked internal fixator technology. Introductory remarks. Injury. 2001. 32:Suppl 2. B3–B9.
17. Pichon H, Chergaoui A, Jager S, et al. Volar fixed angle plate LCP 3.5 for dorsally distal radius fracture. About 24 cases. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2008. 94:152–159.
19. Schuind F, Donkerwolcke M, Rasquin C, Burny F. External fixation of fractures of the distal radius: a study of 225 cases. J Hand Surg Am. 1989. 14:404–407.

20. Stover M. Distal femoral fractures: current treatment, results and problems. Injury. 2001. 32:Suppl 3. SC3–SC13.

21. Strohm PC, Müller CA, Helwig P, Mohr B, Südkamp NP. Is the locking, 3.5 mm Palmar T-Plate the implant of choice for displaced distal radius fractures? Z Orthop Unfall. 2007. 145:331–337.

22. Trumble TE, Culp R, Hanel DP, Geissler WB, Berger RA. Intra-articular fractures of the distal aspect of the radius. Instr Course Lect. 1999. 48:465–480.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download