Abstract
High-energy injury, as traffic accident or fall down, can cause fracture of femur head and posterior dislocation of hip joint which is accompanied with ipsilateral acetabulum fracture or femur neck fracture. But the case that femur head fracture and posterior dislocation of the hip joint coincide with ipsilateral intertrochanteric fracture of proximal femur is so uncommon that reports of the case is very rare. We hereby are to report the experienced and treated-cases of femur head fracture and posterior dislocation of the hip joint that is accompanied with ipsilateral intertrochanteric fracture.
Figures and Tables
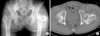 | Fig. 1
(A) Anteroposterior Hip radiograph shows left femoral head fracture and combined ipsilateral intertrochanteric fracture. (B) Axial CT image shows large fracture fragment of femoral head and posterior hip dislocation in the left hip joint. |
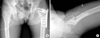 | Fig. 2
(A, B) Immediate postoperative anteroposterior and axial Hip radiographs show that left femoral head fracture was fixated with standard Acutrak screw and ipsilateral intertrochanteric fracture was fixated with LCP-DF. |
References
1. Ganz R, Gill TJ, Gautier E, Ganz K, Krügel N, Berlemann U. Surgical dislocation of the adult hip a technique with full access to the femoral head and acetabulum without the risk of avascular necrosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001. 83:1119–1124.
2. Henle P, Kloen P, Siebenrock KA. Femoral head injuries: which treatment strategy can be recommended? Injury. 2007. 38:478–488.

3. Hunter GA. Posterior dislocation and fracture-dislocation of the hip. A review of fifty-seven patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1969. 51:38–44.
4. Jaskulka RA, Fischer G, Fenzl G. Dislocation and fracture-dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991. 73:465–469.

5. Khan MH, Wright VJ, Prayson MJ. Ipsilateral intertrochanteric and pipkin fractures: an unusual case. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2007. 36:E53–E55.
6. Klasen HJ, Binnendijk B. Fracture of the neck of the femur associated with posterior dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1984. 66:45–48.

8. Paul Tornetta III. Bucholz R, Heckman J, Charles CB, editors. Hip Dislocations and fracture of the femoral head. Rockwood and Green's Fractures in adults. 2005. 6th. ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Co;1715–1752.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download