Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the short term outcome of internal fixation using 2.4 mm volar locking compression plate for the treatment of unstable distal radius fractures.
Materials and Methods
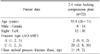
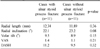
We retrospectively analyzed the results in 22 cases, which were treated with 2.4 mm volar locking compression plate. We evaluated the radiologic results and the clinical results according to Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand (DASH) score and visual analogue scale.
Figures and Tables
 | Fig. 13.5 mm T-LCP (A), 2.4 mm volar extra-articular (B) and juxta-articular distal radius T-LCP (C). 2.4 mm volar distal radius T-LCPs have five smaller holes than 3.5 mm T-LCP on the head. |
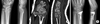 | Fig. 2
(A) Complex intra-articular fracture in a 52-year-old woman. Computed tomography scans demonstrate the intra-articular fracture.
(B) Anteroposterior and lateral radiographs are made ten months after volar fixation with 2.4 mm juxta-articular T-shaped locking compression plate.
|
References
1. Amadio PC, Silverstein MD, Ilstrup DM, Schleck CD, Jensen LM. Outcome after Colles fracture: the relative responsiveness of three questionnaires and physical examination measures. J Hand Surg Am. 1996; 21:781–787.

2. Arora R, Lutz M, Fritz D, Zimmermann R, Oberladstätter J, Gabl M. Palmar locking plate for treatment of unstable dorsal dislocated distal radius fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2005; 125:399–404.

3. Cho CH, Bae KC, Kwon DH. Volar T-locking compression plate for treatment of unstable distal radius fractures. J Korean Fract Soc. 2008; 21:220–224.

4. Chung KC, Watt AJ, Kotsis SV, Margaliot Z, Haase SC, Kim HM. Treatment of unstable distal radial fractures with volar locking plating system. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88:2687–2694.

5. Constantine KJ, Clawson MC, Stern PJ. Volar neutralization plate fixation of dorsally displaced distal radius fractures. Orthopedics. 2002; 25:125–128.

6. Dowrick AS, Gabbe BJ, Williamson OD, Cameron PA. Does the disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand (DASH) scoring system only measure disability due to injuries to the upper limb? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006; 88:524–527.

7. Drobetz H, Kutscha-Lissberg E. Osteosynthesis of distal radial fractures with a volar locking screw plate system. Int Orthop. 2003; 27:1–6.

8. Gummesson C, Ward MM, Atroshi I. The shortened disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand questionnaire (QuickDASH): validity and reliability based on responses within the full-length DASH. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2006; 7:44.
9. Haidukewych GJ. Innovations in locking plate technology. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2004; 12:205–212.

10. Jupiter JB, Marent-Huber M. LCP Stud Group. Operative management of distal radial factures with 2.4-millimeter locking plates. A multicenter prospective case series. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009; 91:55–65.

11. Koval KJ, Hoehl JJ, Kummer FJ, Simon JA. Distal femoral fixation: a biomechanical comparison of the standard condylar buttress plate, a locking buttress plate and the 95-degree blade plat. J Orthop Trauma. 1997; 11:521–524.

14. Matheson LN, Melhorn JM, Mayer TG, Theodore BR, Gatchel RJ. Reliability of a visual analog version of QuickDASH. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88:1782–1787.
15. Musgrave DS, Idler RS. Volar fixation of dorsally displaced distal radius fractures using the 2.4-mm locking compression plates. J Hand Surg Am. 2005; 30:743–749.

16. Orbay JL. The treatment of unstable distal radius fractures with volar fixation. Hand Surg. 2000; 5:103–112.

18. Orbay JL, Fernandez DL. Volar fixed-angle plate fixation for unstable distal radius fractures in the elderly patient. J Hand Surg Am. 2004; 29:96–102.

19. Pichon H, Chergaoui A, Jager S, et al. Volar fixed angle plate LCP 3.5 for dorsally distal radius fracture. About 24 cases. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2008; 94:152–159.
20. Scheck M. Long-term follow-up of treatment of comminuted fractures of the distal end of the radius by transfixation with kirschner wires and cast. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1962; 44:337–351.

21. Strohm PC, Müller CA, Helwig P, Mohr B, Südkamp NP. Is the locking, 3.5 mm Palmar T-Plate the implant of choice for displaced distal radius fractures? Z Orthop Unfall. 2007; 145:331–337.

22. Tejwani NC, Wolinsky P. The changing face of orthopaedic trauma: locked plating and minimally invasive techniques. Instr Course Lect. 2008; 57:3–9.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download