Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
(A) A 54 year-old man had a comminuted subtrochanteric femur.
(B) The surgical darping was done for both legs to have a better evaluation of postoperative alignment.
(C) After the insertion of a flexible nail from the distal segment, a preliminary reduction was achieved.
(D, E) Then, half-pins were fixed on the anterior aspect of proximal and distal segments, with assembling with an external
fixator. A LCP-DF was inserted through the proximal submuscular tunnel.
(F, G, H) A butterfly fragment was fixed with a lag screw by the help of collinear clamp.
(I, J) Satisfactory alignment was achieved postoperatively and a bridging callus was seen at 6 months postoperatively.
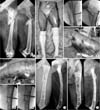
Fig. 2
(A) A 34 year-old woman with a comminuted subtrochanteric femur.
(B) Initially, the proximal segment was internally rotated with the help of half-pin.
(C) This makes a better idea to have a preliminary reduction. The flexible nail technique was used.
(D) A locking plate was inserted through the proximal submuscular tunnel (arrow).
(E, F, G) A fine tuning of remained displacement was done by pulling the distal segment with a half-pin (arrows).
(H, I) Postoperatively, satisfactory alignment was achieved without touching the middle fragment.
(J) A successful union with a good bridging callus at 8 months postoperatively.
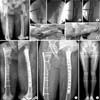
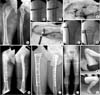
Fig. 3
(A) A 40 year-old man with a spiral fracture of subtrochanteric femur.
(B) The patient had multiple rib fractures with lung contusion, which made the choice of plating rather than nailing. Colinear
clamp made a successful reduction, (C, D) followed by the percutaneous lag screws.
(E) After insertion of a locking plate through the submuscular tunnel, (F, G) screws were fixed percutaneouosly.
(H) Postoperatively, good alignment was achieved.
(I, J, K, L) Union occurred at 6 months postoperatively, with a good functional outcome.
References
2. Celebi L, Can M, Muratli HH, Yagmurlu MF, Yuksel HY, Bicimoğlu A. Indirect reduction and biological internal fixation of comminuted subtrochanteric fractures of the femur. Injury. 2006; 37:740–750.

3. Garnavos C, Peterman A, Howard PW. The treatment of difficult proximal femoral fractures with the Russell-Taylor reconstruction nail. Injury. 1999; 30:407–415.

4. Haidukewych GJ, Berry DJ. Nonunion of fractures of the subtrochanteric region of the femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004; 419:185–188.

5. Higgins TF, Pittman G, Hines J, Bachus KN. Biomechanical analysis of distal femur fracture fixation: fixed-angle screw-plate construct versus condylar blade plate. J Orthop Trauma. 2007; 21:43–46.

6. Kang S, McAndrew MP, Johnson KD. The reconstruction locked nail for complex fractures of the proximal femur. J Orthop Trauma. 1995; 9:453–463.

7. Krettek C, Miclau T, Grün O, Schandelmaier O, Tscherne H. Intraoperative control of axes, rotation and length in femoral and tibial fractures-technical note. Injury. 1998; 29:Suppl 3. C29–C39.
8. Krettek C, Schandelmaier P, Miclau T, Tscherne H. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) using the DCS in proximal and distal femoral fractures. Injury. 1997; 28:Suppl 1. A20–A30.

9. Kulkarni SS, Moran CG. Results of dynamic condylar screw for subtrochanteric fractures. Injury. 2003; 34:117–122.

10. Nungu KS, Olerud C, Rehnberg L. Treatment of subtrochanteric fractures with the AO dynamic condylar screw. Injury. 1993; 24:90–92.

11. Oh CW, Oh JK, Kim SJ, et al. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for comminuted subtrochanteric fracture of the femur. J Korean Fract Soc. 2006; 19:407–411.

12. Oh CW, Song HR, Jeon IH, Min WK, Park BC. Nail-assisted percutaneous plating of pediatric femoral fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007; 456:176–181.

13. Pai CH. Dynamic condylar screw for subtrochanteric fractures with greater trochanteric extension. J Orthop Trauma. 1996; 10:317–322.

14. Pakuts AJ. Unstable subtrochanteric fractures-gamma nail versus dynamic condylar screw. Int Orthop. 2004; 28:21–24.

15. Perren SM. Evolution of the internal fixation of long bone fractures. The scientific basis of biological internal fixation: choosing a new balance between stability and biology. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002; 84:1093–1110.
16. Pryce Lewis JR, Ashcroft GP. Reverse LISS plating for proximal segmental femoral fractures in the polytrauma patient: a case report. Injury. 2007; 38:235–239.

17. Saarenpää I, Heikkinen T, Jalovaara P. Treatment of subtrochanteric fractures. A comparison of the gamma nail and the dynamic hip screw: short-term outcome in 58 patients. Int Orthop. 2007; 31:65–70.

18. Siebenrock KA, Muller U, Ganz R. Indirect reduction with a condylar blade plate for osteosynthesis of subtrochanteric femoral fractures. Injury. 1998; 29:Suppl 3. C7–C15.

20. Sohn OJ, Kim SD, Kim IW, Byun SJ. A comparative study of trochanteric fractures treated with the intertrochanteric/subtrochanteric fixation or the proximal femoral nail. J Korean Fract Soc. 2006; 19:303–308.

21. Vaidya SV, Dholakia DB, Chatterjee A. The use of a dynamic condylar screw and biological reduction techniques for subtrochanteric femur fracture. Injury. 2003; 34:123–128.

22. Valverde JA, Alonso MG, Porro JG, Rueda D, Larrauri PM, Soler JJ. Use of the gamma nail in the treatment of fractures of the proximal femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998; 350:56–61.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download