Abstract
Purpose
To compare information about fracture type in MRI with simple radiograph in tibial plateau fractures and evaluate tibial plateau fractures type and accompanying soft tissue injury, and evaluate usefulness of MRI in tibial plateau fractures.
Materials and Methods
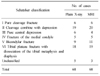
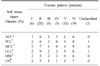
Compared MRI with simple radiograph about Schatzker classification, depression of articular surface and displacement of bone fragment from the 68 examples who checked MRI and we evaluated soft tissue injury around knee joint.
Results
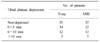
There were 7 examples of Schatzker type change after MRI check. Average depression of articular surface in simple radiograph was 2.93 mm and 4.28 mm in MRI. It increased by 1.35 mm and it was meaningful statistically (p<0.05). There was no significant difference between MRI and simple radiograph of displaced bone fragment (p=0.168). There were 58 (85.3%) cases of soft tissue injury in MRI.
Conclusion
MRI can find additional fracture line or articular depression that can't be found in simple radiograph and gives more information about articular depression and soft tissue that is useful in surgical plans. I think preoperative MRI is necessary to better treatment of fracture & treatment of periarticular soft tissue injury in tibial plateau fracture.
Figures and Tables
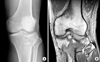
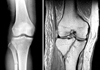
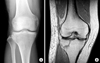 | Fig. 1(A) Plain X-ray doesn't reveal fracture lines.
(B) MRI reveals new fracture lines (pure cleavage fracture).
|
References
1. Barrow BA, Fajman WA, Parker LM, Albert MJ, Drvaric DM, Hudson TM. Tibial plateau fractures: evaluation with MR imaging. Radiographics. 1994; 14:553–559.

2. Bennett WF, Browner B. Tibial plateau fractures: a study of associated soft tissue injuries. J Orthop Trauma. 1994; 8:183–188.
3. Brophy DP, O'malley M, Lui D, Denison B, Eustace S. MR imaging of tibial plateau fractures. Clin Radiol. 1996; 51:873–878.

4. Chan PS, Klimkiewicz JJ, Luchetti WT, et al. Impact of CT scan on treatment plan and fracture classification of tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 1997; 11:484–489.

5. Chang SH, Kang JD, Ha PS, Lee JH. Knee ligamentous Injuries combined with tibial condyle fracture: clinical study of 30 patients. J Korean Surg Soc. 1988; 23:722–732.

6. Cho HO, Kwak KD, Lim DH, Ahn SM, Kang KK. The efficacy of MRI in tibial plateau fractures. J Korean Fract Soc. 2004; 17:122–132.

7. Colletti P, Greenberg H, Terk MR. MR findings in patients with acute tibial plateau fractures. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 1996; 20:389–394.

8. Dias JJ, Stirling AJ, Finlay DB, Gregg PJ. Computerized axial tomography for tibial plateau fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1987; 69:84–88.
9. Han SH, Yang BG, Kim CH, Ahn TW, Jeong ST. Treatment of the tibial condyle fracture. J Korean Soc Fract. 1998; 11:214–225.

10. Holt MD, Williams LA, Dent CM. MRI in the management of tibial plateau fractures. Injury. 1995; 26:595–599.

11. Kearns . Radiologic view and quality in the assessment of tibial plateau fracture: Are we missing something? J Orthop Trauma. 1989; 3:167.
12. Kettelkamp DB, Hillberry BM, Murrish DE, Heck DA. Degenerative arthritis of the knee secondary to fracture malunion. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988; 234:159–169.

13. Kim JY, Cho WS, Kim RS, Kang BK. Application of computed tomography for tibial condylar fractures. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1987; 22:260–268.

14. Kode L, Lieberman JM, Motta AO, Wilber JH, Vasen A, Yagan R. Evaluation of tibial plateau fractures: Efficacy of MR imaging compared with CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994; 163:141–147.

15. Lansinger O, Bergman B, Korner L, Andersson GB. Tibial condylar fractures: A twenty-year-follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986; 68:13–19.
16. Mink JH, Deutsch AL. Occult cartilage and bone injuries of the knee: detection, classification and assessment with MR imaging. Radiology. 1989; 170:823–829.

17. Moon MS, Woo YK, Shim SS. Tibial plateau fracture. An analysis of the results of treatment in 37 patients. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1989; 24:8–14.

18. Moore TM, Harvey JP Jr. Reontgenographic measurement of the tibial plateau depression due to fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974; 56:155–160.

19. Rafii M, Firooznia H, Golimbu C, Bonamo J. Computed tomography of tibial plateau fracture. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1984; 142:1181–1186.
20. Rosen MA, Jackson DW, Berger PE. Occult Osseous Lesions documented by MRI associated with anterior cruciate ligament ruptures. Arthroscopy. 1991; 7:45–51.

21. Ruth JT. Fractures of the tibial plateau. Am J Knee Surg. 2001; 14:125–128.
22. Schatzker J, McBroom R, Bruce D. The tibial plateau fracture. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979; 138:94–104.
23. Tscherne H, Lobenhoffer P. Tibial plateau fractures: Management and expected results. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993; 292:87–100.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download