Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the amount and related factors of reduction loss in distal radius fracture after treatment by Kapandji technique.
Materials and Methods
From September 2004 to May 2006, 44 cases (43 patients) of distal radius fractures were treated by Kapandji technique. Fracture were classified with AO classification and volar tilt, radial inclination, and radial length were measured in preoperative, immediate, postoperative radiographs. Also the amount and related risk factors of reduction loss were analyzed. In addition, the radiological results at last follow up were evaluated using modified Lidstrom scoring system.
Results
There was significantly more reduction loss of volar tilt in the patients with AO type C comparing with other fracture types, but the patients who were treated using three k-wire fixations including intrafocal K-wires showed significantly more reduction loss of volar tilt also. Overall radiological results at last follow up showed that excellent was 50% in cases with dorsal comminution, but, the other cases 90%. In addition, excellent was 70% in type A cases, but, in type C 44%.
Conclusion
Kapandji technique percutaneous pinning is the one of effective treatment options for distal radius fracture. But, type of fracture, total number of K-wires, and presence of dorsal cortical comminution showed the significant relation with postoperative reduction loss of volar tilt and overall radiological results at last follow up.
Figures and Tables
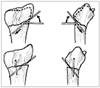 | Fig. 1Intrafocal pin technique of Kapandji. The two K-wires are inserted into the fracture site rather than through the distal fracture fragment both radially and dorsally. The K-wires are then levered up to reduce the fracture and advanced through the opposite proximal intact far cortex to prevent redisplacement of the distal fragments. These intrafocal pinnings of K-wires buttress the distal fragments and allow the maintenance of radial inclination and palmar tilt, respectively. |
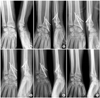 | Fig. 222-year-old man of extraarticular distal radius fracture without dorsal comminution was treated by Kapandji technique percutaneous pinning.
(A) Preoperative radiographs show AO classification A2 fracture.
(B) Immediate postoperative radiographs show that radial length, volar tilt and radial inclination are well restored.
(C, D, E) Radiographs at postoperative 1, 2, 4 weeks show the maintenance of reduction well.
(F) Radiographs at last follow up show excellent radiological result without significant reduction loss.
|
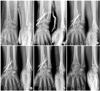 | Fig. 355-year-old woman of intraarticular distal radius fracture with dorsal comminution was treated by Kapandji technique percutaneous pinning.
(A) Preoperative radiographs show AO classification C2 fracture.
(B) Immediate postoperative radiographs show that radial length, volar tilt and radial inclination are relatively well restored.
(C, D, E) But, radiographs at postoperative 1, 2, 4 weeks show the progressive development of reduction loss in all radiological
parameters.
(F) Radiographs at last follow up show fair radiological result with significant reduction loss.
|
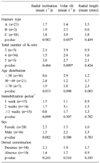
Table 1
The overall amount of reduction loss according to various radiographic parameters at each postoperative period

References
1. Axelrod T, Paley D, Green J, McMurtry RY. Limited open reduction of the lunate facet in comminuted intra- articular fractures of the distal radius. J Hand Surg Am. 1988; 13:372–377.

2. Bradway JK, Amadio PC, Cooney WP. Open reduction and internal fixation of displaced, comminuted intra-articular fractures of the distal end of the radius. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1989; 71:839–847.

3. Clancey GJ. Percutaneous Kirschner-wire fixation of Colles fractures. A prospective study of thirty cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984; 66:1008–1014.

4. Colles A. On the fracture of the carpal extremity of the radius (Reprinted from the original 1814 article). Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006; 445:5–7.
5. Cooney WP 3rd, Dobyns JH, Linscheid RL. Complications of Colles' fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1980; 62:613–619.

6. Dupytren B. One the injuries and disease of bones. London: The Sydenham Society;1847.
7. Epinette JA, Lehut JM, Cavenaile M, Bouretz JC, Decoulx J. Pouteau-Colles fracture: double-closed "basket- like" pinning according to Kapandji. Apropos of a homogeneous series of no cases. Ann Chir Main. 1982; 1:71–83.
8. Falch JA. Epidemiology of fractures of the distal forearm in Oslo, Norway. Acta Orthop Scand. 1983; 54:291–295.

9. Greatting MD, Bishop AT. Intrafocal (Kapandji) pinning of unstable fractures of the distal radius. Orthop Clin North Am. 1993; 24:301–307.

10. Green DP, O'Brien ET. Open reduction of carpal dislocations: indications and operative techniques. J Hand Surg Am. 1978; 3:250–265.

11. Gurd FB. The Colles-Pouteau fracture of the lower end of the radius. Am J Surg. 1937; 38:526–538.

12. Jenkins NH, Jones DG, Johnson SR, Mintowt-Czyz WJ. External fixation of Colles' fractures. An anatomical study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1987; 69:207–211.

13. Kapandji A. Internal fixation by double intrafocal plate. Functional treatment of non articular fractures of the lower end of the radius. Ann Chir. 1976; 30:903–908.
14. Kapandji A. Intra-focal pinning of fractures of the distal end of the radius 10 years later. Ann Chir Main. 1987; 6:57–63.
15. Kapoor H, Agarwal A, Dhaon BK. Displaced intra-articular fractures of distal radius: a comparative evaluation of results following closed reduction, external fixation and open reduction with internal fixation. Injury. 2000; 31:75–79.

16. Kim JH, Lee KH, Hwang KT. The factors of reduction loss in Kapandji technique for distal radius fractures. J Korean Soc Surg Hand. 2004; 9:250–256.
17. Knirk JL, Jupiter JB. Intra-articular fractures of the distal end of the radius in young adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986; 68:647–659.

18. Lee LW, Putnam MD. Algorithmic management of unstable distal radius fractures. Orthop Trans. 1988; 12:357–542.
19. Lidstrom A. Fractures of the distal end of the radius A clinical and statistical study of end results. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl. 1959; 41:1–118.
20. Lucas GL, Sachtjen KM. An analysis of hand function in patients with Colles' fracture treated by Rush rod fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1981; 155:172–179.

22. Owen RA, Melton LJ 3rd, Johnson KA, Ilstrup DM, Riggs BL. Incidence of Colles' fracture in a North American community. Am J Public Health. 1982; 72:605–607.

23. Palmer AK. Fractures of the distal radius. In : Green DP, editor. Operative hand surgery. 2nd ed. New York: Churchill Livingstone;1988. p. 991–1026.
24. Palmer AK, Werner FW. Biomechanics of the distal radioulnar joint. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984; 187:26–35.

25. Rubinovich RM, Rennie WR. Colles' fracture: end results in relation to radiologic parameters. Can J Surg. 1983; 26:361–363.
26. Peltier LF. Eponymic fractures: Abraham Colles and Colles' fracture. Surgery. 1954; 35:322–328.
27. Peltier LF. Fractures of the distal end of the radius. An historical account. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984; 187:18–22.
28. Sarmiento A, Zagorski JB, Sinclair WF. Functional bracing of Colle's fractures: a prospective study of immobilization in supination vs pronation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1980; 146:175–183.
29. Shiota E. Intra-focal fixation for treating distal radius fracture: results of 104 cases. J Orthop Sci. 1999; 4:106–114.

30. Taleisnik J, Watson HK. Midcarpal instability caused by malunited fractures of the distal radius. J Hand Surg Am. 1984; 9:350–357.

31. Zagorski JB. Comminuted fractures of the distal radius. Instr Course Lect. 1990; 39:255–258.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download