Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the clinical efficacy of F-plate in displaced intra-articular fractures of calcaneus.
Materials and Methods
Total 43 cases treated with F-plate and followed up at least six months postoperatively were reviewed. Radiographically, Böhler angle was measured and all cases were subdivided by Sanders classification. Each case was reviewed for the presence of local infection, traumatic arthritis, nonunion, and any breakage of plate or screw. Maryland foot score was used for clinical assessment and factors influencing on clinical results were determined.
Results
The mean Böhler angle was improved from 0.5° (range: -24.7~35.5°) preoperatively to 25.8° (range: 14.2~38.6°) postoperatively and the angle at last follow-up was 23.5° (range: 10.2~37.5°), showing about 2.3 degree decline compared to postoperative Böhler angle. There were two cases of F-plate breakage and two cases of screw breakage but the metal breakage did not affect any change in Böhler angle. Other complications were; five cases of traumatic arthritis, one case of varus malunion and one case of deep wound infection. According to Maryland foot score, there were 10 excellent, 22 good, 10 fair and 1 poor result. Furthermore, Age, pre-operative Böhler angle and the patient's expectation on financial compensation had significant influences upon the clinical result.
Figures and Tables
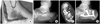 | Fig. 1A 45-year-old male patient sustained intra-articular calcaneus fracture by fall down from 2 meter height.
(A) Intraoperative photograph shows extensile lateral approach.
(B) Preoperative X-ray shows joint depression type intra-articular calcaneal fracture with negative Böhler angle.
(C) Preoperative semicoronal CT scan shows Sanders IIA calcaneal fracture.
(D) Postoperative X-ray shows restoration of Böhler angle and stable fixation.
|
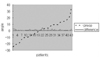 | Fig. 2Correlation of Böhler angle at initial and postoperative six months. The immediate postoperative Böhler angle was maintained to postoperative six months.preop: Preoperative Böhler angle (broken line), patient: Each patient was ordered according to the degree of Böhler angle, difference: Between imediate postoperative state and postoperative six months in Böhler angle (solid line).
|
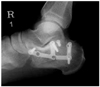 | Fig. 3A 40-year-old-male patient was treated using a F-plate. Postoperative 20 months X-ray shows breakage of plate but metal breakage did not affect any change in Böhler angle. |
References
1. Benirschke SK, Sangeozan BJ. Extensive intraarticular fractures of the foot. Surgical management of calcaneal fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993; 292:128–134.
2. Borrelli J Jr, Lashgari C. Vascularity of the lateral calcaneal flap: a cadeveric injection study. J Orthop Trauma. 1999; 13:73–77.
3. Burdeaux BD. Reduction of calcaneal fractures by the Mc-Reynolds medial approach technique and its experimental basis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983; 177:87–103.

4. Essex-Lopresti P. The mechanism, reduction technique, and results in fractures of the os calcis. Br J Surg. 1952; 39:395–419.

5. Hutchinson F 3rd, Huebner MK. Treatment of os calcis fractures by open reduction and internal fixation. Foot Ankle Int. 1994; 15:225–232.

6. Lee HJ, Kang SY, Kim JW. Surgical treatment of displaced intra-articular fracture of the calcaneus using a Y-plate. J Korean Soc Fract. 2002; 15:433–438.

7. Letournel E. Open reduction and internal fixation of calcaneus fractures. In : Spiege PG, editor. Topics in orthopedic trauma. 1st ed. Baltimore: University Parkpress;1984. p. 173–192.
8. Letournel E. Open treatment of acute calcaneal fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993; (290):60–67.

10. Sanders R, Fortin P, DiPasquale T, Walling A. Operative treatment in 120 displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures. Results using a prognostic computed tomography scan classification. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993; 290:87–95.
11. Sanders R, Sigvard T, Hansen ST, McReynold JS. Trauma to the calcaneus and its tendon. Disorders of the foot and ankle. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Co;1991.
12. Segal D, Marsh JL, Leiter B. Clinical application of computerized axial tomography (CAT) scanning of calcaneus fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985; 199:114–123.

13. Tornetta P. Open reduction and internal fixation of the calcaneus using minifragment plates. J Orthop Trauma. 1996; 10:63–67.

14. Yang KH, Park YH, Won JH, Kim DY. Mechanical properties of F plate in intraarticular calcaneal fractures. J Korean Fract Soc. 2004; 17:167–172.

15. Zwipp H, Tscherne H, Thermann H, Weber T. Osteosynthesis of displaced intraarticular fractures of the calcaneus. Results in 123 cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993; 290:76–86.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print






 XML Download
XML Download