Abstract
Purpose
This study was done to identify and compare factors associated with intention to receive Human Papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine between male and female undergraduate students.
Methods
In the fall of 2010, 479 students responded to self-administered questionnaires about their intention to receive HPV vaccine, HPV knowledges, HPV related involvements and optimistic bias, subject's characteristics including opinion about HPV vaccine. Mann-Whitney U test, uni-variate and multi-variate logistic regression were used for data analysis with SPSS/WIN.
Results
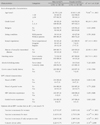
Intention to receive vaccine were 22.0% of men and 25.0% of women. There were significantly different in HPV knowledge (Z=-2.74, p=.006), optimistic bias (Z=-4.60, p<.001), vaccine is necessary for women (Z=-4,30, p<.001), vaccine is necessary for men (Z=-4.37, p<.001), vaccine is necessary if only symptom exist (Z=-4.52, p<.001), but there were not different in intention to receive vaccine, involvement between men and women. Concern about vaccine safety (OR=3.19, 95% CI 1.63~6.23) was determinant of intention to receive HPV vaccine for men.
Figures and Tables
Table 1
Socio-demographic, HPV related Characteristics and Opinions about HPV Vaccine: Gender Differences (N=479)
References
1. Allen J.D., Mohlajee A.P., Shelton R.C., Othus M.K.D., Fontenot H.B., Hanna R. Stage of adoption of the human papillomavorus vaccine among college women. Preventive Medicine. 2009. 48:420–425. doi; 10.1016/j.ypmed.2008.12.005.
2. Human papillomavirus. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2011. 2011, September, 20. Retrieved. Author;from, http://www.cdc.gov/.
3. Cha D.P. Self serving bias for HIV/AIDS infection among college students. Journal of Public Relations Research. 2004. 8:137–160.
4. Denny-Smith T., Bairan A., Page M.C. A survey of female nursing students’knowledge, health beliefs, perceptions of risk, and risk behaviors regarding human papillomavirus and cervical cancer. Journal of the American Academy of Nurse practitioners. 2006. 18:62–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7599.2006.00100.x.
5. Dunne E.F., Neilson C.M., Stone K.M., Markowitz L.E., Giuliano A.R. Prevalence of HPV infection among men: A systematic review of the literature. Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2006. 194:1044–1057. doi: 10.1086/507432.
6. Ferris D.G., Waller J.L., Miller J., Patel P., Price G.A., Jackson L., et al. Variables associated with Human Papillomavirus(HPV) vaccine acceptance by Men. The Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine: JABFM. 2009. 22:34–42. doi: 10.3122/jabfm.2009.01.080008.
7. Franceschi S., Herrero R., Clifford G.M., Snijder P.J.G., Arslan A., Anh P.T.H., et al. Variations in the age-specific curves of human papillomavirus prevalence in women worldwide. International Journal of Cancer. Journal International du Cancer. 2006. 119:2677–2684. doi; 10.1002/ijc.22241.
8. Kang H.S., Moneyham L. Attitudes toward and intention to receive the human papilloma virus (HPV) vaccination and intention to use condoms among female Korean college students. Vaccine. 2010. 28:811–816. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.10.052.
9. Katz M.L., Krieger J.L., Roberto A.J. Human papillomavirus(HPV): College male's knowledge, perceived risk, sources of information, vaccine barriers and communication. Journal of Men's Health. 2011. 8:175–184. doi: 10.1016/j.jomh.2011.04.002.
10. Kim H.W. Effects of prevention education on Human Papillomavirus linked to cervix cancer for unmarried female university students. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2009. 39:490–498. doi: 10.4040/jkan.2009.39.4.490.
11. Kim H.W., Ahn H.Y. Study on the knowledge of human papillomavirus in female university students. Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing. 2007. 13:13–20.
12. Kim H.W. Factors influencing mothers' acceptance of Human Papillomavirus vaccination to prevent cervical cancer in their daughters. Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing. 2011. 17:137–147. doi: 10.4069/kjwhn.2011.17.2.137.
13. Kuitto K., Pickel S., Neumann H., Jahn D., Metelmann H.-R. Attitudinal and socio-structural determinants of cervical cancer screening and HPV vaccination uptake: A quantitative multivariate analysis. Journal of Public Health. 2010. 18:179–188. 10.1007/s10389-009-0308-z.
14. Lee E.J., Park J.S. Knowledge about cervical cancer, health beliefs and human papillomavirus vaccination rate in female university students. Journal of Korean Oncology Nursing. 2011. 11:65–73. doi: 10.5388/jkon.2011.11.1.65.
15. Lee S.H. The relationship between the optimistic bias about cancer and the cancer-preventive behaviors of the Korean, Chinese, American, and Japanese adults residing in Korea. 2009. Seoul: Konkuk University;Unpublished master's thesis.
16. Liddon N., Hood J., Wynn B.A., Markowitz L.E. Acceptability of human papillomavirus vaccine for males: A review of the literature. Journal of Adolescent Health. 2010. 46:113–123. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2009.11.199.
17. Marlow L.A., Waller J., Wardle J. The impact of HPV information on perceived risk of cervical cancer. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers and Prevention. 2009. 18:373–376. doi; 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-08-0357.
18. Peres J. Who should get the HPV vaccine? Usage expands amid debate. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 2010. 102:838–839.
19. Shin H.R., Franceschi S., Vaccarella S., Roh J.-W., Ju Y.-H., Oh J.-K., et al. Prevalence and determinants of genital infection with Papillomavirus, in female and male university students in Busan, South Korea. The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2004. 190:468–476. doi; 10.1086/421279.
20. Sohn A., Tabang F., Moon C.-S., Ki S.-D. Optimistic bias on HIV/AIDS among high school students in Seoul. Korea. Health and Social Science. 2009. 25:57–78.
21. Wheldon C.W., Daley E.M., Buhi E.R., Nyitray A.G., Giuliano A.R. Health beliefs and attitudes associated with HPV vaccine intention among young gay and bisexual men in the southeastern United States. Vaccine. 2011. 29:8060–8065. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.08.045.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download