Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify differences in Health Locus of Control (HLOC), depression, wellbeing, and Health Promoting Lifestyle Profile II (HPLP) between middle aged Korean and Korean-American women.
Methods
Data from 80 Korean-American women living in Los Angeles, USA and 82 Korean women living in W-city, Korea, were collected using a self administered questionnaire including items on HLOC, HPLP, a Wellbeing Index and Major Depression Inventory.
Results
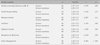
There were statistically significant differences between the middle aged Koreans and Korean-Americans on mean age, education, religion, and current health insurance. Significant differences were found on HLOC (F=2.504, p=.033) and Wellbeing (F=2.451, p=.036). The results also showed significant differences on HPLP (total HPLP, F=4.655, p=.001; physical activity, F=2.967, p=.014; nutrition, F=4.250, p=.001; spiritual growth, F=4.398, p=.001; interpersonal relations, F=2.648, p=.025; and stress management, F=5.201, p<.001) using ANCOVA. However, there were no significant differences on depression, or health responsibility in HPLP between the groups.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Andrews M.M., Boyle J. Transcultural concepts in nursing care. 2008. Lippincotts, Williams & Wilkins.
2. Bech P., Rasmussen N.-A., Olsen L.R., Neorholm V., Abildgaard W. The sensitivity and specificity of the Major Depression Inventory, using the present state examination as the index of diagnostic validity. Journal of Affective Disorders. 2001. 66:159–164.
3. Berstein K.S. Mental health issues among urban Korean American immigrants. Journal of Transcultural nursing. 2007. 18(2):175–180.
4. Choe M.A., Im E.O. Difference in needs for physical activity among healthy women, women with physical limitations and Korean immigrant women. Asian Nursing Research. 2007. 1(1):48–60.
5. Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 1998. 2nd ed. NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Inc.
6. Figueras J., McKee M., Lessof S., Duran A., Menabde N. Health systems, health and wealth: Assessing the case for investing in health system. 2008. WHO.
7. Glanz K., Rimer B.K., Lewis F.M. Health Behaviors and Health Education. 2002. Josse-Bass A Wiley Imprint.
8. Han K.S. A study of stress reaction, symptoms of stress, health promoting behavior, and quality of life in Korean immigrant middle aged women. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2000. 30(3):606–618.
9. Im E.O., Meleis A.I., Lee K.A. Cultural competence of measurement scales of menopausal symptoms: Use in research among Korean women. International Journal of Nursing Studies. 1999. 36:455–463.
10. Jang Y., Kim G., Chiriboga D., King-Kallimanis B. A bidimensional model of acculturation for Korean American older adults. Journal of Aging and Studies. 2007. 21:267–275.
11. Kong E.H. The influence of culture on the experiences of Korean, Korean American, and Caucasian-American family caregivers of frail older adults: A literature review. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2007. 37(2):213–220.
12. Lee K.J., Chang C.J., Yoo J.H., Yi Y.J. Factors effecting health promoting behaviors in middle-aged women. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2005. 35(3):494–502.
13. Lee E.E., Farren C.J. Depression among Korean, Korean American, and Caucasian American family caregivers. Journal of Transcultural Nursing. 2004. 15(1):18–25.
14. Lee E.O., Im N.Y., Park H.A., Lee I.S., Kim J.I., Bae J.I. Nursing Research and statistical analysis. 2009. Seoul:
15. Lee S.J., Park E.S., Park Y.J. Determinants of health promoting behavior of middle aged women in Korea. The Journal of Nurses Academic Society. 1996. 26(2):320–336.
16. Oh B.J. A predicting model of Health promoting behaviors and quality of life in patients with stomach cancer. 1995. Seoul: The Seoul National University;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
17. Park G.J., Lee K.H. A structural model for depression in middle-aged women. Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing. 2002. 8(1):69–84.
18. Park H.S., Kim S.K., Cho G.Y. A study on climatric symptoms, depression and quality of life in middle-aged women. Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing. 2003. 9(4):479–488.
19. Park S.Y., Bernstein K.S. Depression and Korean American immigrants. Archives of Psychiatric Nursing. 2008. 22(1):12–19.
20. Rock D.L., Meyerowitz B.E., Maisto S.A., Wallston K.A. The derivation and validation of six multidimensional health locus of control scale clusters. Research in Nursing & Health. 1987. 10:185–195.
21. Seo H.M., Hah Y.S. A study of factors influencing on health promoting lifestyle in the elderly-Application of Pender's Health Promotion Model-. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2004. 34(7):1288–1297.
22. Shin H.S., Han H.R., Kim M.T. Predictors of psychological well-being amongst Korean immigrants to the United States: A structured interview survey. International Journal of Nursing Studies. 2007. 44:415–426.
23. Shin K.R., Shin C. The lived experience of Korean Immigrant women acculturating into the United States. Health Care Women International. 1999. 20(6):603–617.
24. Sohn L., Harada N.D. Knowledge and use of preventive health practice among Korean women in Los Angele county. Preventive Medicine. 2005. 41:167–178.
25. Song M.S., Kim S.M., Kim J.I., Cho N.O. Measurement in gerontology research. 2007. Seoul: KoonJa.
26. Sung M.H. An analysis of the relationship between climatric symptoms and depression of muddle-aged women. Journal of Korean Academy of Women's Health Nursing. 2000. 6(4):465–476.
27. Tommey A.M., Allgood M.R. Nursing theorist and their work. 2006. 6th ed. Mosby.
28. Walker S.N., Hill-Polerecky D.M. Psychometric evaluation of the Health-promoting lifestyles profile II. Unpublished manuscript, University of Nebraska Medical Center. 1996. Retrieved from http://app1.unmc.edu/nursing/conweb/view_profile.cfm?lev1=facstf&lev2=fac&lev3=facswalker&PubStat=(none)&web=pub.
29. Wallston K.A., Wallston B.S., DeVelis R. Development of the multidimensional health locus of control(MHLC) scales. Health Education Monographs. 1978. 6:160–170. Retrieved from http://www.vanderbilt.edu/nursing/kwallston/mhlcscales.htm.
30. Wallston K.A. The validity of the multidimensional health locus of control scales. Journal of Health Psychology. 2005. 10(4):623–631. Retrieved from http://www.vanderbilt.edu/nursing/kwallston/mhlcscales.htm.
31. Women's Health Nursing Curriculum Inquiry Group. Women's health nursing care. 2010. Seoul: Soomoonsa.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download