Abstract
Purpose
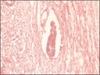
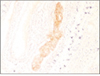
Clinicopathologic factors associated with prognosis in breast cancer patients have varied. Among clinicopathologic factors, lymphovascular invasion (LVI) has been suggested to be a significant prognostic indicator for breast cancer. LVI means that cancer cells were found invading the lymphatics in the breast parenchyma adjacent to or well beyond the margin of the invasive tumor, and this can be an indicator of an increased chance that cancer could spread, as is demonstrated by the positive lymph nodes. The objective of this study was to determine whether LVI are associated with other clinicopathologic factors in breast cancer.
Methods
The expression of HER-2, Ki-67, P53, estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor was determined immunohistochemically in 120 breast cancer patients, including 77 patients that demonstrated the absent of LVI and 43 patients with the present of LVI.
Results
LVI was noted in 43 patients (35.8%) of the 120 breast cancer patients. Of the 77 patients with absent of LVI, the number of stage III patients (13 patients, 16.9%) was lower than the number of stage I (25 patients, 32.5%) and stage II breast cancer patients (39 patients, 50.6%). Of the 43 patients with absent of LVI, 5 patients (11.6%), 13 patients (30.2%), and 25 patients (58.2%) were in stage I, II, and III, respectively. There was a significant correlation between LVI and the stage (P=0.000). The strong expression (+3) of HER-2 was seen in 17 (39.5%) of the 43 patients in whom LVI was seen and in 15 (19.5%) of the 77 patients in whom LVI was not seen. Overexpression of Ki-67 was noted in 42 (97.7%) of the 43 patients in whom LVI was seen and in 64 (83.1%) of the 77 in whom LVI was not seen. HER-2 and Ki-67 overexpression was significantly associated with LVI (p=0.027 and p=0.018, respectively). LVI did not correlate with the expression of P53, the estrogen receptor status and the progesterone receptor status. There was a strong association of LVI and the lymph node status (p=0.000). Finally, LVI was associated with tumor size (p=0.014) and with the nuclear grade (p=0.022).
Figures and Tables
References
1. Shin HR, Jung KW, Won YJ, Park JG. 2002 Annual report of the Korea Central Cancer Registry: Based on registered data from 139 Hospitals. Cancer Res Treat. 2004. 36:103–114.

2. Gusterson BA, Gelber RD, Goldhirsch A, Price KN, Save-Soderborgh J, Anbazhagan R, et al. Prognostic importance of c-erbB-2 expression in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1992. 10:1049–1056.
3. Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, Levin WJ, Ullrich A, McGuire WL. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987. 235:177–182.

4. Ross JS, Fletcher JA, Bloom KJ, Linette GP, Stec J, Symmans WF, et al. Targeted therapy in breast cancer: the HER-2/neu gene and protein. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2004. 3:379–398.
5. Slamon DJ, Leyland-Jones B, Shak S, Fuchs H, Paton V, Bajamonde A, et al. Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N Engl J Med. 2001. 344:783–792.

6. Lauria R, Perrone F, Carlomagno C, De Laurentiis M, Morabito A, Gallo C, et al. The prognostic value of lymphatic and blood vessel invasion in operable breast cancer. Cancer. 1995. 76:1772–1778.

7. Truong PT, Yong CM, Abnousi F, Lee J, Kader HA, Hayashi A, et al. Lymphovascular invasion is associated with reduced locoregional control and survival in women with node-negative breast cancer treated with mastectomy and systemic therapy. J Am Coll Surg. 2005. 200:912–921.

8. Sundquist M, Thorstenson S, Klintenberg C, Brudin L, Nordenskjold B. Indicators of loco-regional recurrence in breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2000. 26:357–362.

9. Schoppmann SF, Bayer G, Aumayr K, Taucher S, Geleff S, Rudas M, et al. Prognostic value of lymphangiogenesis and lymphovascular invasion in invasive breast cancer. Ann Surg. 2004. 240:306–312.

10. Elston CW, Ellis IO. Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological grade in breast cancer: experience from a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology. 1991. 19:403–410.

11. Goldhirsch A, Glick JH, Wood WC, Gelber RD, Coates AS, Thurlimann B, Senn HJ. Meeting highlights: international expert consensus on the primary therapy of early breast cancer 2005. Ann Oncol. 2005. 16:1569–1583.

12. Lee AH, Pinder SE, Macmillan RD, Mitchell M, Ellis IO, Elston CW, et al. Prognostic value of lymphovascular invasion in women with lymph node negative invasive breast carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 2006. 42:357–362.

13. de Mascarel I, Bonichon F, Durand M, Mauriac L, MacGrogan G, Soubeyran I, et al. Obvious peritumoral emboli: an elusive prognostic factor reappraised. Multivariate analysis of 1320 node-negative breast cancers. Eur J Cancer. 1998. 34:58–65.

14. Trihia H, Murray S, Price K, Gelber RD, Golouh R, Goldhirsch A, et al. Ki-67 expression in breast carcinoma. Cancer. 2003. 97:1321–1331.

15. Pinto AE, Andre S, Pereira T, Nobrega S, Soares J. Prognostic comparative study of S-phase fraction and Ki-67 index in breast carcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 2001. 54:543–549.

16. Jung SY, Han WS, Shin HJ, Lee JE, Hwang KT, Hwang SE, et al. Usefulness of Ki-67 as a prognostic factor in lymph node-negative breast cancer. J Breast Cancer. 2006. 9:31–35.

17. Ariga R, Zarif A, Korasick J, Reddy V, Siziopikou K, Gattuso P. Correlation of her-2/neu gene amplification with other prognostic and predictive factors in female breast carcinoma. Breast J. 2005. 11:278–280.

18. Prati R, Apple SK, He J, Gornbein JA, Chang HR. Histopathologic characteristics predicting HER-2/neu amplification in breast cancer. Breast J. 2005. 11:433–439.

19. Bilous M, Ades C, Armes J, Bishop J, Brown R, Cooke B, et al. Predicting the HER2 status of breast cancer from basic histopathology data: an analysis of 1500 breast cancers as part of the HER2000 International Study. Breast. 2003. 12:92–98.

20. Riou G, Mathieu MC, Barrois M, Le Bihan ML, Ahomadegbe JC, Benard J, et al. c-erbB-2 (HER-2/neu) gene amplification is a better indicator of poor prognosis than protein over-expression in operable breast-cancer patients. Int J Cancer. 2001. 95:266–270.

21. Bianchi S, Palli D, Falchetti M, Saieva C, Masala G, Mancini B, et al. ErbB-receptors expression and survival in breast carcinoma: a 15-year follow-up study. J Cell Physiol. 2006. 206:702–708.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download