4. Halsted WS. I. The results of radical operations for the cure of carcinoma of the breast. Ann Surg. 1907; 46:1–19.
5. Sleeman J, Schmid A, Thiele W. Tumor lymphatics. Semin Cancer Biol. 2009; 19:285–297. PMID:
19482087.

6. Nemoto T, Vana J, Bedwani RN, Baker HW, McGregor FH, Murphy GP. Management and survival of female breast cancer: results of a national survey by the American College of Surgeons. Cancer. 1980; 45:2917–2924. PMID:
7388735.

7. Carter CL, Allen C, Henson DE. Relation of tumor size, lymph node status, and survival in 24,740 breast cancer cases. Cancer. 1989; 63:181–187. PMID:
2910416.

8. Kim T, Giuliano AE, Lyman GH. Lymphatic mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy in early-stage breast carcinoma: a metaanalysis. Cancer. 2006; 106:4–16. PMID:
16329134.
9. Fisher B, Montague E, Redmond C, Barton B, Borland D, Fisher ER, et al. Comparison of radical mastectomy with alternative treatments for primary breast cancer: a first report of results from a prospective randomized clinical trial. Cancer. 1977; 39(6 Suppl):2827–2839. PMID:
326381.
10. Cancer Research Campaign Working Party. Cancer Research Campaign (King's/Cambridge) trial for early breast
cancer: a detailed update at the tenth year. Lancet. 1980; 2:55–60. PMID:
6105244.
11. Sacre RA. Clinical evaluation of axillar lymph nodes compared to surgical and pathological findings. Eur J Surg Oncol. 1986; 12:169–173. PMID:
3709822.
12. Cooper KL, Meng Y, Harnan S, Ward SE, Fitzgerald P, Papaioannou D, et al. Positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for the assessment of axillary lymph node metastases in early breast cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess. 2011; 15:iii–iiv. 1–134.

13. Hwang SO, Lee SW, Kim HJ, Kim WW, Park HY, Jung JH. The comparative study of ultrasonography, contrast-enhanced MRI, and (18) F-FDG PET/CT for detecting axillary lymph node metastasis in T1 breast cancer. J Breast Cancer. 2013; 16:315–321. PMID:
24155761.
14. Caudle AS, Cupp JA, Kuerer HM. Management of axillary disease. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2014; 23:473–486. PMID:
24882346.

15. Gilchrist RK. Fundamental factors governing lymphatic spread of carcinoma. Ann Surg. 1940; 111:630–639. PMID:
17857569.

16. Zeidman I, Buss JM. Experimental studies on the spread of cancer in the lymphatic system: I. effectiveness of the lymph node as a barrier to the passage of embolic tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1954; 14:403–405. PMID:
13160971.
17. D'Angelo-Donovan DD, Dickson-Witmer D, Petrelli NJ. Sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer: a history and current clinical recommendations. Surg Oncol. 2012; 21:196–200. PMID:
22237143.
18. Kett K, Varga G, Lukács L. Direct lymphography of the breast. Lymphology. 1970; 3:2–12. PMID:
4317224.
19. Krag DN, Weaver DL, Alex JC, Fairbank JT. Surgical resection and radiolocalization of the sentinel lymph node in breast cancer using a gamma probe. Surg Oncol. 1993; 2:335–339. PMID:
8130940.

20. Linehan DC, Hill AD, Akhurst T, Yeung H, Yeh SD, Tran KN, et al. Intradermal radiocolloid and intraparenchymal blue dye injection optimize sentinel node identification in breast cancer patients. Ann Surg Oncol. 1999; 6:450–454. PMID:
10458682.

21. Klimberg VS, Rubio IT, Henry R, Cowan C, Colvert M, Korourian S. Subareolar versus peritumoral injection for location of the sentinel lymph node. Ann Surg. 1999; 229:860–864. PMID:
10363900.

22. Giuliano AE, Kirgan DM, Guenther JM, Morton DL. Lymphatic mapping and sentinel lymphadenectomy for breast cancer. Ann Surg. 1994; 220:391–398. PMID:
8092905.

23. Mamounas ET. Optimal management of the axilla: a look at the evidence. Adv Surg. 2016; 50:29–40. PMID:
27520860.
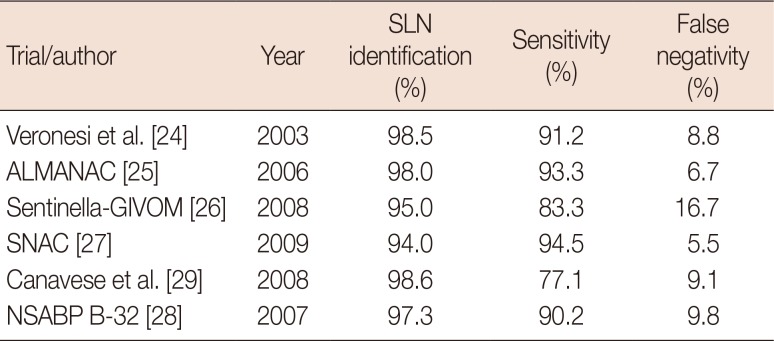
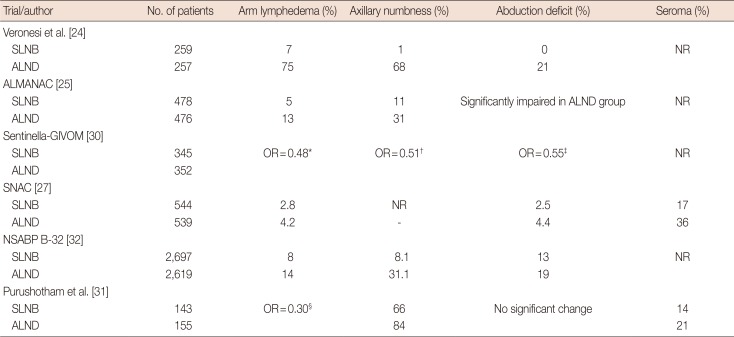
24. Veronesi U, Paganelli G, Viale G, Luini A, Zurrida S, Galimberti V, et al. A randomized comparison of sentinel-node biopsy with routine axillary dissection in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003; 349:546–553. PMID:
12904519.

25. Mansel RE, Fallowfield L, Kissin M, Goyal A, Newcombe RG, Dixon JM, et al. Randomized multicenter trial of sentinel node biopsy versus standard axillary treatment in operable breast cancer: the ALMANAC Trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006; 98:599–609. PMID:
16670385.

26. Zavagno G, De Salvo GL, Scalco G, Bozza F, Barutta L, Del Bianco P, et al. A Randomized clinical trial on sentinel lymph node biopsy versus axillary lymph node dissection in breast cancer: results of the Sentinella/GIVOM trial. Ann Surg. 2008; 247:207–213. PMID:
18216523.
27. Gill G. SNAC Trial Group of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons (RACS) and NHMRC Clinical Trials Centre. Sentinel-lymph-node-based management or routine axillary clearance? One-year outcomes of sentinel node biopsy versus axillary clearance (SNAC): a randomized controlled surgical trial. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009; 16:266–275. PMID:
19050973.

28. Krag DN, Anderson SJ, Julian TB, Brown AM, Harlow SP, Ashikaga T, et al. Technical outcomes of sentinel-lymph-node resection and conventional axillary-lymph-node dissection in patients with clinically node-negative breast cancer: results from the NSABP B-32 randomised phase III trial. Lancet Oncol. 2007; 8:881–888. PMID:
17851130.

29. Canavese G, Catturich A, Vecchio C, Tomei D, Gipponi M, Villa G, et al. Sentinel node biopsy compared with complete axillary dissection for staging early breast cancer with clinically negative lymph nodes: results of randomized trial. Ann Oncol. 2009; 20:1001–1007. PMID:
19174453.

30. Del Bianco P, Zavagno G, Burelli P, Scalco G, Barutta L, Carraro P, et al. Morbidity comparison of sentinel lymph node biopsy versus conventional axillary lymph node dissection for breast cancer patients: results of the sentinella-GIVOM Italian randomised clinical trial. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2008; 34:508–513. PMID:
17614245.

31. Purushotham AD, Upponi S, Klevesath MB, Bobrow L, Millar K, Myles JP, et al. Morbidity after sentinel lymph node biopsy in primary breast cancer: results from a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:4312–4321. PMID:
15994144.

32. Ashikaga T, Krag DN, Land SR, Julian TB, Anderson SJ, Brown AM, et al. Morbidity results from the NSABP B-32 trial comparing sentinel lymph node dissection versus axillary dissection. J Surg Oncol. 2010; 102:111–118. PMID:
20648579.

33. Veronesi U, Viale G, Paganelli G, Zurrida S, Luini A, Galimberti V, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer: ten-year results of a randomized controlled study. Ann Surg. 2010; 251:595–600. PMID:
20195151.
34. Krag DN, Anderson SJ, Julian TB, Brown AM, Harlow SP, Costantino JP, et al. Sentinel-lymph-node resection compared with conventional axillary-lymph-node dissection in clinically node-negative patients with breast cancer: overall survival findings from the NSABP B-32 randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010; 11:927–933. PMID:
20863759.

35. Wang Z, Wu LC, Chen JQ. Sentinel lymph node biopsy compared with axillary lymph node dissection in early breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011; 129:675–689. PMID:
21743996.

36. Petrelli F, Lonati V, Barni S. Axillary dissection compared to sentinel node biopsy for the treatment of pathologically node-negative breast cancer: a meta-analysis of four randomized trials with long-term follow up. Oncol Rev. 2012; 6:e20. PMID:
25992218.

37. Lyman GH, Temin S, Edge SB, Newman LA, Turner RR, Weaver DL, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy for patients with early-stage breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 2014; 32:1365–1383. PMID:
24663048.

38. Chagpar AB. Clinical significance of minimal sentinel node involvement and management options. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2010; 19:493–505. PMID:
20620923.

39. Edge S, Byrd D, Compton C, Fritz AG, Greene F, Trotti A. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th ed. New York: Springer;2009.
40. de Boer M, van Deurzen CH, van Dijck JA, Borm GF, van Diest PJ, Adang EM, et al. Micrometastases or isolated tumor cells and the outcome of breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:653–663. PMID:
19675329.

41. Giuliano AE, Hawes D, Ballman KV, Whitworth PW, Blumencranz PW, Reintgen DS, et al. Association of occult metastases in sentinel lymph nodes and bone marrow with survival among women with early-stage invasive breast cancer. JAMA. 2011; 306:385–393. PMID:
21791687.

42. Cserni G, Gregori D, Merletti F, Sapino A, Mano MP, Ponti A, et al. Meta-analysis of non-sentinel node metastases associated with micrometastatic sentinel nodes in breast cancer. Br J Surg. 2004; 91:1245–1252. PMID:
15376203.

43. van Deurzen CH, de Boer M, Monninkhof EM, Bult P, van der Wall E, Tjan-Heijnen VC, et al. Non-sentinel lymph node metastases associated with isolated breast cancer cells in the sentinel node. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008; 100:1574–1580. PMID:
19001602.

44. Yi M, Giordano SH, Meric-Bernstam F, Mittendorf EA, Kuerer HM, Hwang RF, et al. Trends in and outcomes from sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) alone vs. SLNB with axillary lymph node dissection for node-positive breast cancer patients: experience from the SEER database. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010; 17(Suppl 3):343–351.

45. Bilimoria KY, Bentrem DJ, Hansen NM, Bethke KP, Rademaker AW, Ko CY, et al. Comparison of sentinel lymph node biopsy alone and completion axillary lymph node dissection for node-positive breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:2946–2953. PMID:
19364968.

46. Giuliano AE, Hunt KK, Ballman KV, Beitsch PD, Whitworth PW, Blumencranz PW, et al. Axillary dissection vs no axillary dissection in women with invasive breast cancer and sentinel node metastasis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2011; 305:569–575. PMID:
21304082.
47. Giuliano AE, McCall L, Beitsch P, Whitworth PW, Blumencranz P, Leitch AM, et al. Locoregional recurrence after sentinel lymph node dissection with or without axillary dissection in patients with sentinel lymph node metastases: the American College of Surgeons Oncology Group Z0011 randomized trial. Ann Surg. 2010; 252:426–432. PMID:
20739842.
48. Morrow M, Giuliano AE. To cut is to cure: can we really apply Z11 in practice? Ann Surg Oncol. 2011; 18:2413–2415. PMID:
21717245.

49. Jagsi R, Chadha M, Moni J, Ballman K, Laurie F, Buchholz TA, et al. Radiation field design in the ACOSOG Z0011 (Alliance) Trial. J Clin Oncol. 2014; 32:3600–3606. PMID:
25135994.

50. Shah-Khan M, Boughey JC. Evolution of axillary nodal staging in breast cancer: clinical implications of the ACOSOG Z0011 trial. Cancer Control. 2012; 19:267–276. PMID:
23037494.

51. Galimberti V, Cole BF, Zurrida S, Viale G, Luini A, Veronesi P, et al. Axillary dissection versus no axillary dissection in patients with sentinel-node micrometastases (IBCSG 23-01): a phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013; 14:297–305. PMID:
23491275.

52. Li CZ, Zhang P, Li RW, Wu CT, Zhang XP, Zhu HC. Axillary lymph node dissection versus sentinel lymph node biopsy alone for early breast cancer with sentinel node metastasis: a meta-analysis. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2015; 41:958–966. PMID:
26054706.

53. Massimino KP, Hessman CJ, Ellis MC, Naik AM, Vetto JT. Impact of American College of Surgeons Oncology Group Z0011 and National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project B-32 trial results on surgeon practice in the Pacific Northwest. Am J Surg. 2012; 203:618–622. PMID:
22445745.

54. Caudle AS, Hunt KK, Tucker SL, Hoffman K, Gainer SM, Lucci A, et al. American College of Surgeons Oncology Group (ACOSOG) Z0011: impact on surgeon practice patterns. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012; 19:3144–3151. PMID:
22847123.

55. Beek MA, Verheuvel NC, Luiten EJ, Klompenhouwer EG, Rutten HJ, Roumen RM, et al. Two decades of axillary management in breast cancer. Br J Surg. 2015; 102:1658–1664. PMID:
26694991.

56. Wright GP, Mater ME, Sobel HL, Knoll GM, Oostendorp LD, Melnik MK, et al. Measuring the impact of the American College of Surgeons Oncology Group Z0011 trial on breast cancer surgery in a community health system. Am J Surg. 2015; 209:240–245. PMID:
25236187.

57. Yao K, Liederbach E, Pesce C, Wang CH, Winchester DJ. Impact of the American College of Surgeons Oncology Group Z0011 randomized trial on the number of axillary nodes removed for patients with earlystage breast cancer. J Am Coll Surg. 2015; 221:71–81. PMID:
25899731.

58. Zarebczan Dull B, Neuman HB. Management of the axilla. Surg Clin North Am. 2013; 93:429–444. PMID:
23464694.

59. Rubio IT. Sentinel lymph node biopsy after neoadjuvant treatment in breast cancer: work in progress. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2016; 42:326–332. PMID:
26774943.

60. Baselga J, Bradbury I, Eidtmann H, Di Cosimo S, de Azambuja E, Aura C, et al. Lapatinib with trastuzumab for HER2-positive early breast cancer (NeoALTTO): a randomised, open-label, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2012; 379:633–640. PMID:
22257673.

61. Amersi F, Giuliano AE. Management of the axilla. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2013; 27:687–702. PMID:
23915739.

62. Mamounas EP, Brown A, Anderson S, Smith R, Julian T, Miller B, et al. Sentinel node biopsy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: results from National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project Protocol B-27. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:2694–2702. PMID:
15837984.

63. Classe JM, Bordes V, Campion L, Mignotte H, Dravet F, Leveque J, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for advanced breast cancer: results of Ganglion Sentinelle et Chimiotherapie Neoadjuvante, a French prospective multicentric study. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:726–732. PMID:
19114697.
64. Kelly AM, Dwamena B, Cronin P, Carlos RC. Breast cancer sentinel node identification and classification after neoadjuvant chemotherapy-systematic review and meta analysis. Acad Radiol. 2009; 16:551–563. PMID:
19345896.
65. van Deurzen CH, Vriens BE, Tjan-Heijnen VC, van der Wall E, Albregts M, van Hilligersberg R, et al. Accuracy of sentinel node biopsy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients: a systematic review. Eur J Cancer. 2009; 45:3124–3130. PMID:
19716287.

66. Xing Y, Foy M, Cox DD, Kuerer HM, Hunt KK, Cormier JN. Meta-analysis of sentinel lymph node biopsy after preoperative chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer. Br J Surg. 2006; 93:539–546. PMID:
16329089.

67. Tan VK, Goh BK, Fook-Chong S, Khin LW, Wong WK, Yong WS. The feasibility and accuracy of sentinel lymph node biopsy in clinically node-negative patients after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Surg Oncol. 2011; 104:97–103. PMID:
21456092.
68. van der Heiden-van der Loo M, de Munck L, Sonke GS, van Dalen T, van Diest PJ, van den Bongard HJ, et al. Population based study on sentinel node biopsy before or after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in clinically node negative breast cancer patients: Identification rate and influence on axillary treatment. Eur J Cancer. 2015; 51:915–921. PMID:
25857549.
69. Shen J, Gilcrease MZ, Babiera GV, Ross MI, Meric-Bernstam F, Feig BW, et al. Feasibility and accuracy of sentinel lymph node biopsy after preoperative chemotherapy in breast cancer patients with documented axillary metastases. Cancer. 2007; 109:1255–1263. PMID:
17330229.

70. Alvarado R, Yi M, Le-Petross H, Gilcrease M, Mittendorf EA, Bedrosian I, et al. The role for sentinel lymph node dissection after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients who present with node-positive breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012; 19:3177–3184. PMID:
22772869.

71. Lee S, Kim EY, Kang SH, Kim SW, Kim SK, Kang KW, et al. Sentinel node identification rate, but not accuracy, is significantly decreased after pre-operative chemotherapy in axillary node-positive breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007; 102:283–288. PMID:
17063280.

72. van Nijnatten TJ, Schipper RJ, Lobbes MB, Nelemans PJ, Beets-Tan RG, Smidt ML. The diagnostic performance of sentinel lymph node biopsy in pathologically confirmed node positive breast cancer patients after neoadjuvant systemic therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2015; 41:1278–1287. PMID:
26329781.

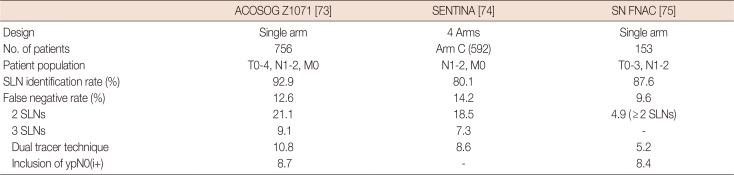
73. Boughey JC, Suman VJ, Mittendorf EA, Ahrendt GM, Wilke LG, Taback B, et al. Sentinel lymph node surgery after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with node-positive breast cancer: the ACOSOG Z1071 (Alliance) clinical trial. JAMA. 2013; 310:1455–1461. PMID:
24101169.
74. Kuehn T, Bauerfeind I, Fehm T, Fleige B, Hausschild M, Helms G, et al. Sentinel-lymph-node biopsy in patients with breast cancer before and after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (SENTINA): a prospective, multicentre cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2013; 14:609–618. PMID:
23683750.

75. Boileau JF, Poirier B, Basik M, Holloway CM, Gaboury L, Sideris L, et al. Sentinel node biopsy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in biopsy-proven node-positive breast cancer: the SN FNAC study. J Clin Oncol. 2015; 33:258–264. PMID:
25452445.

76. Kuerer HM, Albarracin CT, Yang WT, Cardiff RD, Brewster AM, Symmans WF, et al. Ductal carcinoma in situ: state of the science and roadmap to advance the field. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:279–288. PMID:
19064970.

77. Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013; 63:11–30. PMID:
23335087.

78. Ernster VL, Ballard-Barbash R, Barlow WE, Zheng Y, Weaver DL, Cutter G, et al. Detection of ductal carcinoma in situ in women undergoing screening mammography. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2002; 94:1546–1554. PMID:
12381707.

79. Brennan ME, Turner RM, Ciatto S, Marinovich ML, French JR, Macaskill P, et al. Ductal carcinoma in situ at core-needle biopsy: meta-analysis of underestimation and predictors of invasive breast cancer. Radiology. 2011; 260:119–128. PMID:
21493791.

80. Zavotsky J, Hansen N, Brennan MB, Turner RR, Giuliano AE. Lymph node metastasis from ductal carcinoma in situ with microinvasion. Cancer. 1999; 85:2439–2443. PMID:
10357415.

81. Klauber-DeMore N, Tan LK, Liberman L, Kaptain S, Fey J, Borgen P, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy: is it indicated in patients with high-risk ductal carcinoma-in-situ and ductal carcinoma-in-situ with microinvasion? Ann Surg Oncol. 2000; 7:636–642. PMID:
11034239.

82. Ansari B, Ogston SA, Purdie CA, Adamson DJ, Brown DC, Thompson AM. Meta-analysis of sentinel node biopsy in ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Br J Surg. 2008; 95:547–554. PMID:
18386775.

83. Yi M, Krishnamurthy S, Kuerer HM, Meric-Bernstam F, Bedrosian I, Ross MI, et al. Role of primary tumor characteristics in predicting positive sentinel lymph nodes in patients with ductal carcinoma in situ or microinvasive breast cancer. Am J Surg. 2008; 196:81–87. PMID:
18436181.

84. Sun X, Li H, Liu YB, Zhou ZB, Chen P, Zhao T, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy in patients with breast ductal carcinoma in situ: Chinese experiences. Oncol Lett. 2015; 10:1932–1938. PMID:
26622778.

85. Cox CE, Nguyen K, Gray RJ, Salud C, Ku NN, Dupont E, et al. Importance of lymphatic mapping in ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS): why map DCIS? Am Surg. 2001; 67:513–519. PMID:
11409797.
86. Wilkie C, White L, Dupont E, Cantor A, Cox CE. An update of sentinel lymph node mapping in patients with ductal carcinoma in situ. Am J Surg. 2005; 190:563–566. PMID:
16164920.

87. Yen TW, Hunt KK, Ross MI, Mirza NQ, Babiera GV, Meric-Bernstam F, et al. Predictors of invasive breast cancer in patients with an initial diagnosis of ductal carcinoma in situ: a guide to selective use of sentinel lymph node biopsy in management of ductal carcinoma in situ. J Am Coll Surg. 2005; 200:516–526. PMID:
15804465.

88. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Clinical practice guidelines in oncology: breast cancer v.1. 2016. Accessed March 28th, 2016.
http://www.nccn.org.
89. Tousimis E, Van Zee KJ, Fey JV, Hoque LW, Tan LK, Cody HS 3rd, et al. The accuracy of sentinel lymph node biopsy in multicentric and multifocal invasive breast cancers. J Am Coll Surg. 2003; 197:529–535. PMID:
14522317.

90. Gentilini O, Veronesi P, Botteri E, Soggiu F, Trifirò G, Lissidini G, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy in multicentric breast cancer: five-year results in a large series from a single institution. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011; 18:2879–2884. PMID:
21479691.

91. Knauer M, Konstantiniuk P, Haid A, Wenzl E, Riegler-Keil M, Pöstlberger S, et al. Multicentric breast cancer: a new indication for sentinel node biopsy. A multi-institutional validation study. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:3374–3380. PMID:
16849751.
92. Fortunato L, Mascaro A, Amini M, Farina M, Vitelli CE. Sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2008; 17:673–699. PMID:
18486889.

93. Jones NB, Wilson J, Kotur L, Stephens J, Farrar WB, Agnese DM. Contralateral prophylactic mastectomy for unilateral breast cancer: an increasing trend at a single institution. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009; 16:2691–2696. PMID:
19506956.

94. Güth U, Myrick ME, Viehl CT, Weber WP, Lardi AM, Schmid SM. Increasing rates of contralateral prophylactic mastectomy: a trend made in USA? Eur J Surg Oncol. 2012; 38:296–301. PMID:
22305274.
95. Dupont EL, Kuhn MA, McCann C, Salud C, Spanton JL, Cox CE. The role of sentinel lymph node biopsy in women undergoing prophylactic mastectomy. Am J Surg. 2000; 180:274–277. PMID:
11113434.

96. Peralta EA, Ellenhorn JD, Wagman LD, Dagis A, Andersen JS, Chu DZ. Contralateral prophylactic mastectomy improves the outcome of selected patients undergoing mastectomy for breast cancer. Am J Surg. 2000; 180:439–445. PMID:
11182394.

97. Zhou WB, Liu XA, Dai JC, Wang S. Meta-analysis of sentinel lymph node biopsy at the time of prophylactic mastectomy of the breast. Can J Surg. 2011; 54:300–306. PMID:
21651834.

98. Nagaraja V, Edirimanne S, Eslick GD. Is sentinel lymph node biopsy necessary in patients undergoing prophylactic mastectomy? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast J. 2016; 22:158–165. PMID:
26748493.

99. Boughey JC, Cormier JN, Xing Y, Hunt KK, Meric-Bernstam F, Babiera GV, et al. Decision analysis to assess the efficacy of routine sentinel lymphadenectomy in patients undergoing prophylactic mastectomy. Cancer. 2007; 110:2542–2550. PMID:
17932905.

100. Veronesi U, Cascinelli N, Mariani L, Greco M, Saccozzi R, Luini A, et al. Twenty-year follow-up of a randomized study comparing breastconserving surgery with radical mastectomy for early breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002; 347:1227–1232. PMID:
12393819.

101. Voogd AC, Nielsen M, Peterse JL, Blichert-Toft M, Bartelink H, Overgaard M, et al. Differences in risk factors for local and distant recurrence after breast-conserving therapy or mastectomy for stage I and II breast cancer: pooled results of two large European randomized trials. J Clin Oncol. 2001; 19:1688–1697. PMID:
11250998.

102. Lowery AJ, Kell MR, Glynn RW, Kerin MJ, Sweeney KJ. Locoregional recurrence after breast cancer surgery: a systematic review by receptor phenotype. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012; 133:831–841. PMID:
22147079.

103. Derkx F, Maaskant-Braat AJ, van der Sangen MJ, Nieuwenhuijzen GA, van de Poll-Franse LV, Roumen RM, et al. Staging and management of axillary lymph nodes in patients with local recurrence in the breast or chest wall after a previous negative sentinel node procedure. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2010; 36:646–651. PMID:
20537838.

104. Maaskant-Braat AJ, Voogd AC, Roumen RM, Nieuwenhuijzen GA. Repeat sentinel node biopsy in patients with locally recurrent breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013; 138:13–20. PMID:
23340861.

105. Ahmed M, Baker R, Rubio IT. Meta-analysis of aberrant lymphatic drainage in recurrent breast cancer. Br J Surg. 2016; 103:1579–1588. PMID:
27598038.






 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download