INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Chemicals and reagents
Cell lines, cell culture, and treatments
Immunolocalization of PKCα in MDAMB-231 cells
Immunoblotting to detect PKCα translocation
Cell cycle analysis
MTT viability assay and morphological analysis of breast cancer cells
Discrimination of live, dead, and necrotic cells by flow cytometry
DNA fragmentation assay
Detection of mitochondrial membrane potential
Determination of mitochondrial cyt c release
Caspase-3 and caspase-9 assay
Measurement of reactive oxygen species (ROS) level in MBAMB-231 cells
LDH activity assay
RESULTS
Alkyl cinnamates mediate PKC translocation to the plasma membrane
Figure 2
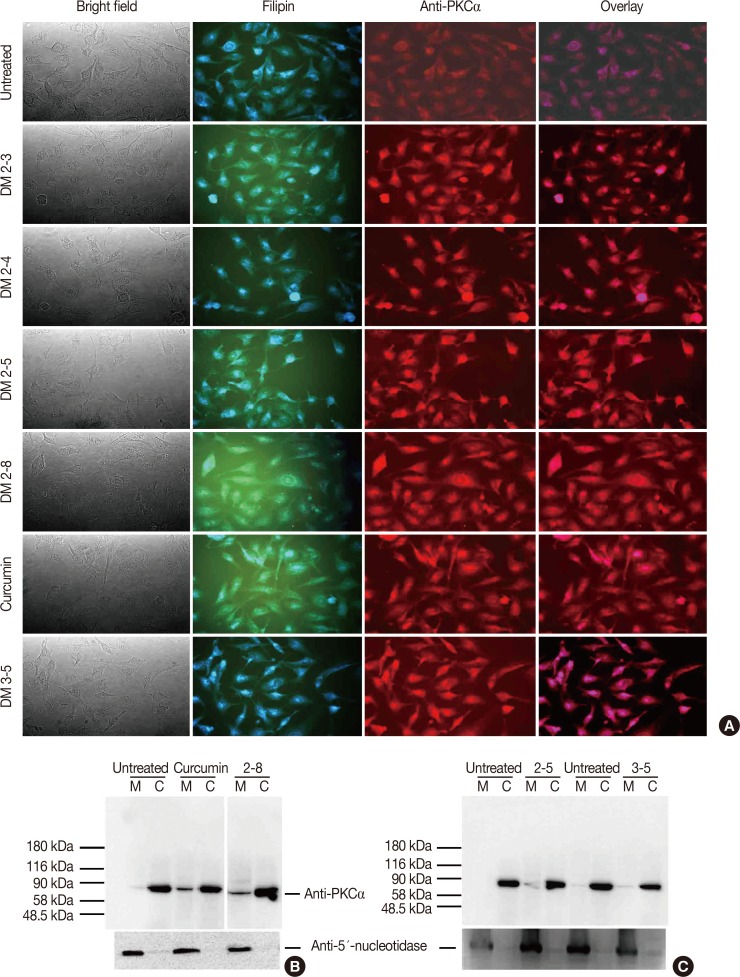
Alkyl cinnamates have potential to exhibits protein kinase C (PKC)-α translocation from cytosol to the plasma membrane in MDAMB-231 cells. (A) Immunolocalization of PKCα in MDAMB-231 treated with different alkyl cinnamates to monitor PKC translocation from cytosol to plasma membrane. MDAMB-231 cells were treated and PKCα immunolocalization was done as given in Methods. In each panel, bright field, PKCα (red), filipin to stain cell membrane (blue) and overlay. Untreated cells show a low level of PKCα at plasma membrane compared to significant high signal in alkyl cinnamate treated cells. (B, C) Immunoblotting of PKCα in MDAMB-231 treated with different alkyl cinnamates to monitor PKC translocation from cytosol to plasma membrane. MDAMB-231 cells were treated and PKCα immunolocalization was done as given in Methods. The purity of cytosolic or membrane fraction was asses by testing the presence of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and 5′-nucleotidase in these fractions. LDH activity assay was performed as described previously whereas presence of 5′-nucleotidase was done by immune-blotting with anti-5′-nucleotidase antibodies. Untreated cells show a basal level of PKCα at plasma membrane whereas a high level of PKCα was found in alkyl cinnamate treated cells.
Alkyl cinnamates disturb the cell cycle and arrest cancer cells in G2/M phase
Figure 3
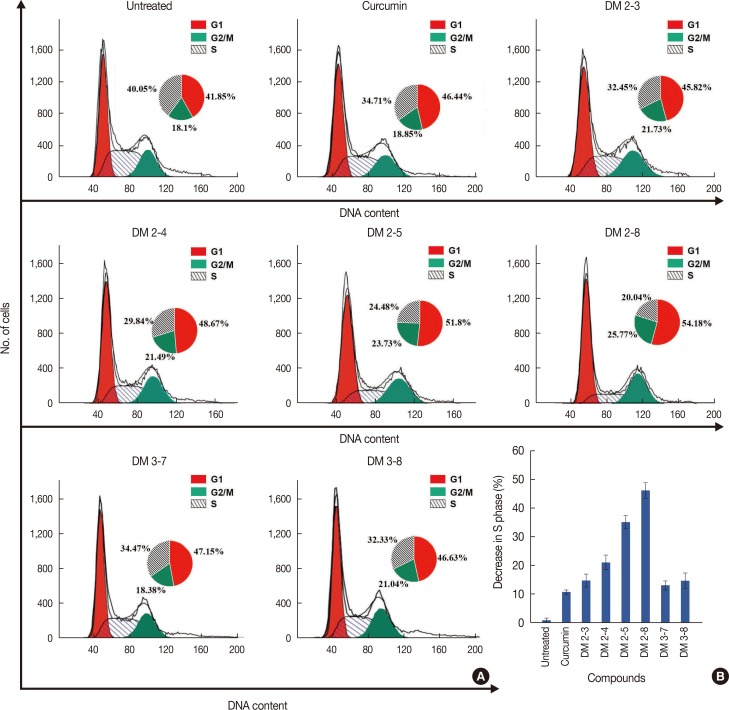
Alkyl cinnamates disturb cell-cycle in MDAMB-231w cells. (A) Cells were treated with different alkyl cinnamates (half maximal inhibitory concentrations [IC50]) for 24 hours in incomplete media, stained with propidium iodide as given in Methods, and immediately analyzed by flow cytometry. The cells treated with different compounds show G2/M arrest and reduction of S phase. (B) Plot of change in S phase of MDA-MB-231 cells treated with different alkyl cinnamates.
Alkyl cinnamates induce cellular damage and death in breast cancer cells
Table 1
Activity of novel DM compounds against breast cancer cells
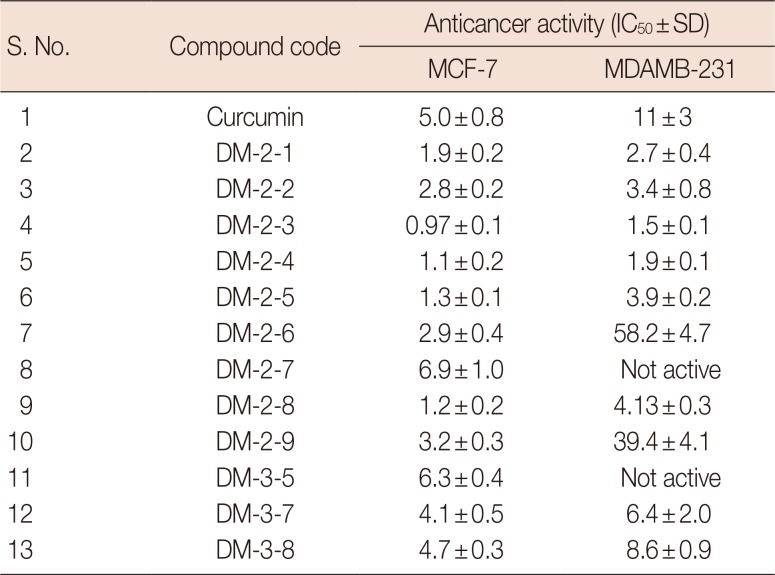
Breast cancer cells (MDA-MB231 or MCF-7) are treated with different heterocyclic compounds in serum-free media for 48 hours and cell viability was measured by MTT assay. The viability of untreated cells are considered as 100% and used to calculate the percentage change in viability of compound treated cells. IC50 of individual compounds were calculated and expressed in µg/mL.
S.No.=serial number; MTT=3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide; IC50=half maximal inhibitory concentrations.
Alkyl cinnamates target cancer cells through induction of apoptosis
Figure 4
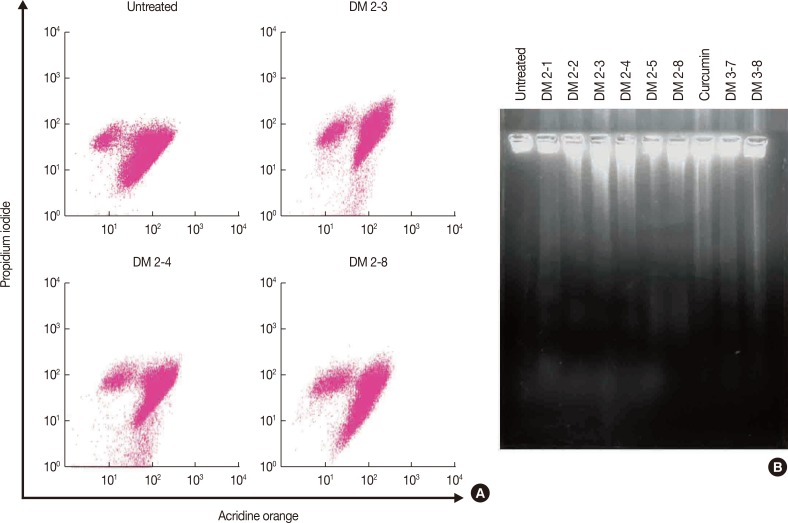
Alkyl cinnamates are causing death of MDAMB-231 following apoptosis. (A) MDAMB-231 treated with different alkyl cinnamates and distribution of healthy, dead, apoptotic and necrotic cells. Cells were treated alkyl cinnamates (IC50 for 24 hours), stained with acridine orange and propidium iodide and analyzed by flow cytometry. (B) MDAMB-231 treated with different alkyl cinnamates exhibits DNA fragmentation. Cells were treated with different alkyl cinnamates (the IC50 values of the compounds for 12 hours) in serum-free media and samples were processed for DNA laddering analysis. A laddering pattern of DNA is observed in alkyl cinnamate treated cells compared to the intact genomic DNA in untreated cells.
Apoptosis in breast cancer cells is induced via the mitochondrial pathway
Figure 5
Loss of mitochondrial membrane potential in alkyl cinnamates treated MDAMB-231 breast cancer cells. MDAMB-231 breast cancer cells were treated with alkyl cinnamates (IC50) in serum-free media for 24 hours. After treatment, cells were stained with JC-1 dye for 20 minutes and were observed in Cytell Imaging System (GE Healthcare). Alkyl cinnamates treated cells show a decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential as indicated by loss of orange and appearance of green fluorescence (scale bar, 130 µm).
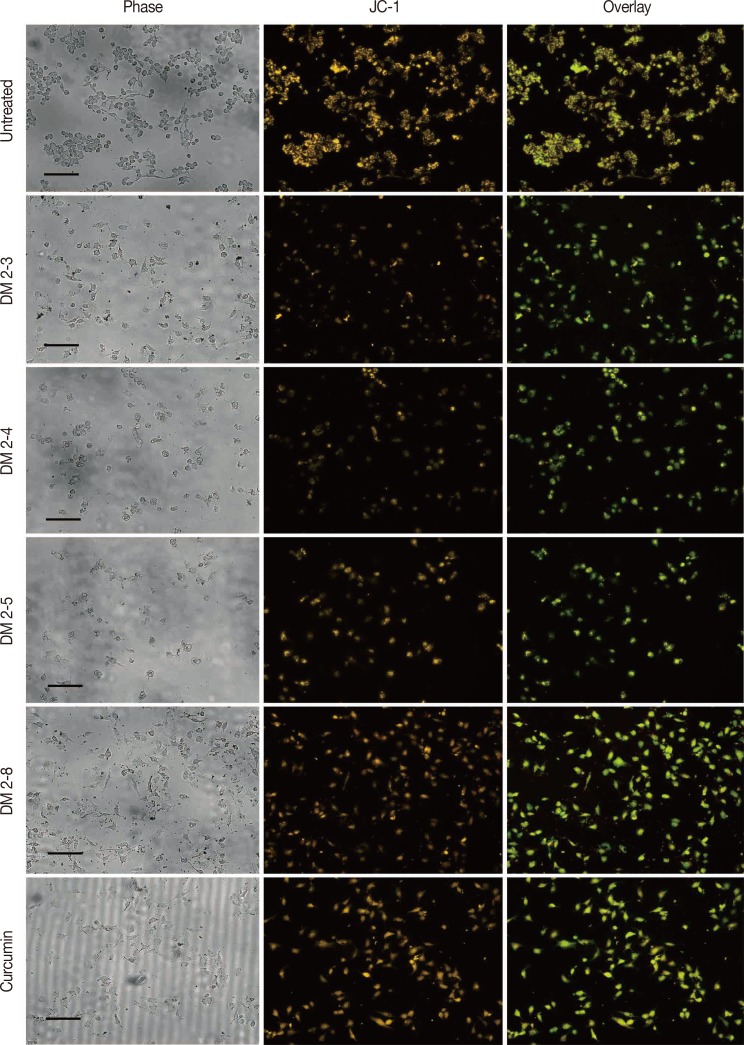
Figure 6
Release of cytochrome-c (cyt c) from alkyl cinnamate treated MDAMB-231 breast cancer cells. MDAMB-231 breast cancer cells were treated with alkyl cinnamates (IC50) in serum-free media for 24 hours. After treatment, cells were immune-stained with anti-cyt c antibodies and location of mitochondria in MDAMB-231 cells is determined by loading the cells with MitoTracker (BD-Biosciences; 200 nM for 45 minutes) as given in material and methods. Labelled cells were observed in a fluorescent microscope 80i (Nikon). In each panel, bright field, cyt c (green), MitoTracker Red (red) is given. High resolution fluorescence microscopy detected release of cyt c from DM2-3, DM2-4, DM2-5 and curcumin treated cells. Untreated cells seem healthy with the cyt c signal overlapping with MitoTracker signal.
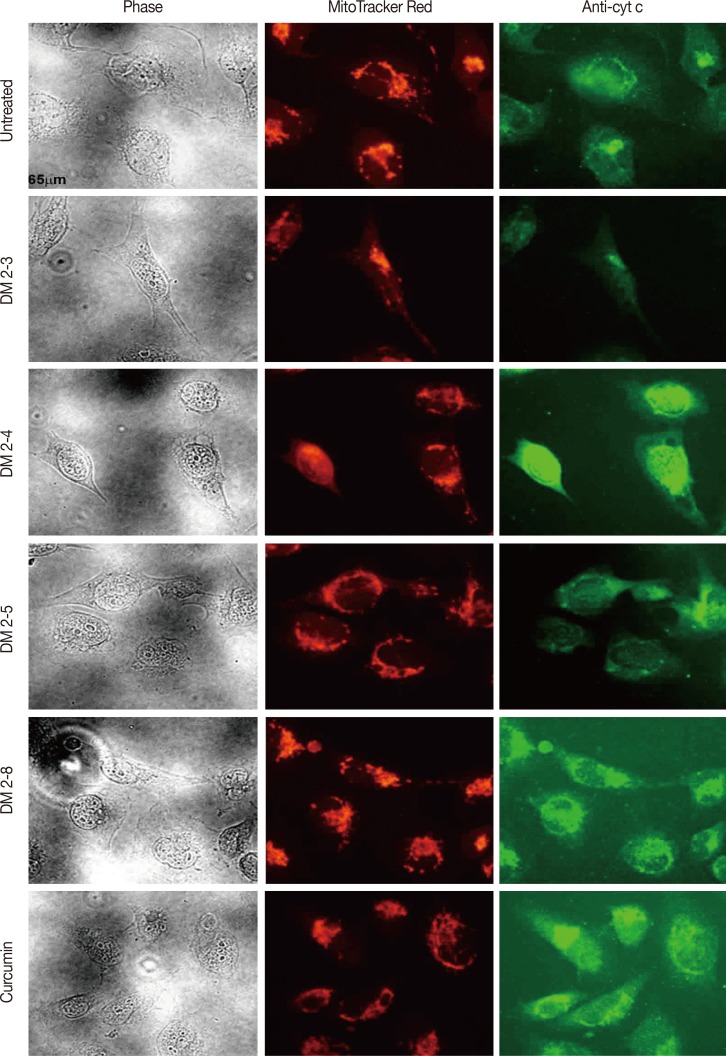
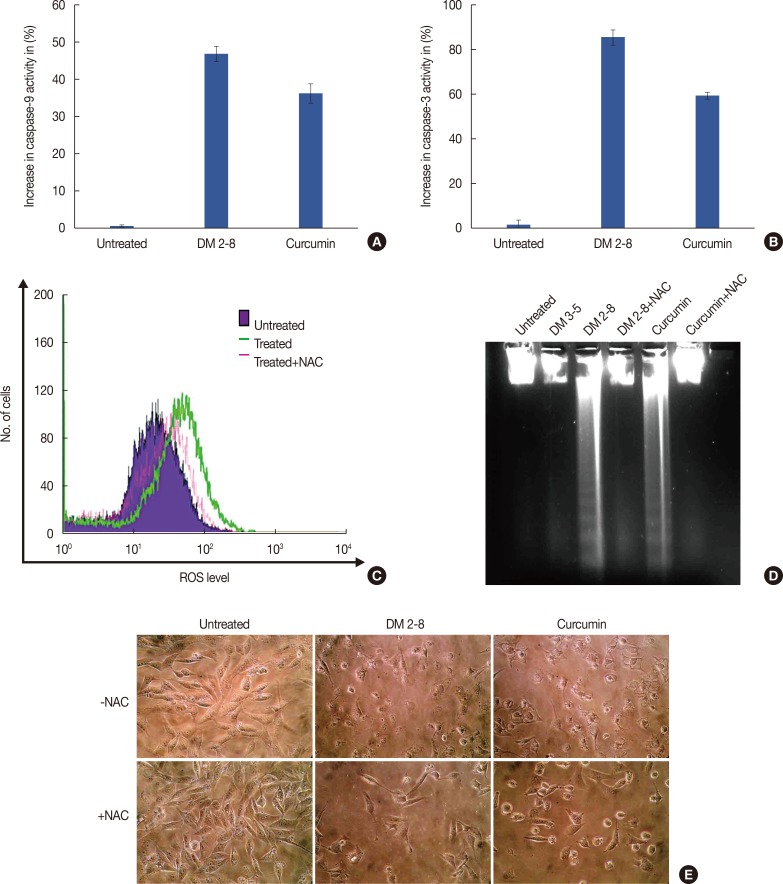
Figure 7
Cytochrome C release activates down-stream cytosolic caspases. Caspase 9 (A) and caspase 3 (B) activity in MDAMB-231 cells treated with alkyl cinnamates. Caspase-3 activity levels increased by 90% and 65% in DM2-8 and curcumin. (C) Flow cytometric measurement of reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels in alkyl cinnamate treated breast cancer cells. Cells were treated with alkyl cinnamates (IC50) for 3 hours and DCF-DHA was used as a ROS probe. DM-2-8 treated cells show an increased level of ROS compared to untreated cells. The preincubation of cells in N-acetylcysteine (NAC) reduces ROS level in treated cell. The preincubation of cells in N-acetylcysteine (NAC) reduces ROS level and apperance of DNA fragments (D) in treated cell. Cells were treated with DM 2-8 or curcumin in the absence or presence of NAC (5 mM) and presence of NAC give intact genomic DNA with no visible appearance of DNA fragments. (E) Microscopic observation of MDAMB-231 cells treated with DM-2-8 or curcumin for 48 hours in absence or presence of NAC. Images were taken with high resolution Nikon L22 camera. Cells preincubated with NAC gives an improved cellular morphology compared to DM-2-8 or curcumin treated cells.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download