1. Kim Z, Min SY, Yoon CS, Lee HJ, Lee JS, Youn HJ, et al. The basic facts of Korean breast cancer in 2011: results of a nationwide survey and breast cancer registry database. J Breast Cancer. 2014; 17:99–106.

2. Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell. 2009; 139:871–890.

3. Roussos ET, Keckesova Z, Haley JD, Epstein DM, Weinberg RA, Condeelis JS. AACR special conference on epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer progression and treatment. Cancer Res. 2010; 70:7360–7364.

4. Foroni C, Broggini M, Generali D, Damia G. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and breast cancer: role, molecular mechanisms and clinical impact. Cancer Treat Rev. 2012; 38:689–697.

5. Zeisberg M, Neilson EG. Biomarkers for epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. J Clin Invest. 2009; 119:1429–1437.

6. Ioachim E, Charchanti A, Briasoulis E, Karavasilis V, Tsanou H, Arvanitis DL, et al. Immunohistochemical expression of extracellular matrix components tenascin, fibronectin, collagen type IV and laminin in breast cancer: their prognostic value and role in tumour invasion and progression. Eur J Cancer. 2002; 38:2362–2370.

7. Christensen L. The distribution of fibronectin, laminin and tetranectin in human breast cancer with special attention to the extracellular matrix. APMIS Suppl. 1992; 26:1–39.
8. Sung CO, Park CK, Kim SH. Classification of epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotypes in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma is strongly associated with patient prognosis. Mod Pathol. 2011; 24:1060–1068.

9. Kim A, Bae YK, Gu MJ, Kim JY, Jang KY, Bae HI, et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype is associated with patient survival in small intestinal adenocarcinoma. Pathology. 2013; 45:567–573.

10. Ryu HS, Park do J, Kim HH, Kim WH, Lee HS. Combination of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell-like phenotypes has independent prognostic value in gastric cancer. Hum Pathol. 2012; 43:520–528.

11. Kim A, Shin HC, Bae YK, Kim MK, Kang SH, Lee SJ, et al. Multiplication of chromosome 17 centromere is associated with prognosis in patients with invasive breast cancers exhibiting normal HER2 and TOP2A status. J Breast Cancer. 2012; 15:24–33.

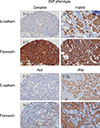
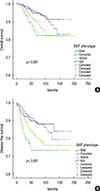
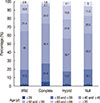
12. Bae YK, Kim A, Kim MK, Choi JE, Kang SH, Lee SJ. Fibronectin expression in carcinoma cells correlates with tumor aggressiveness and poor clinical outcome in patients with invasive breast cancer. Hum Pathol. 2013; 44:2028–2037.

13. Elston CW, Ellis IO. Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer I The value of histological grade in breast cancer: experience from a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology. 1991; 19:403–410.

14. Hammond ME, Hayes DF, Dowsett M, Allred DC, Hagerty KL, Badve S, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer (unabridged version). Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2010; 134:e48–e72.
15. Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Hicks DG, Dowsett M, McShane LM, Allison KH, et al. Recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 2013; 31:3997–4013.

16. Choi JE, Kang SH, Lee SJ, Bae YK. Androgen receptor expression predicts decreased survival in early stage triple-negative breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015; 22:82–89.

17. Huber MA, Kraut N, Beug H. Molecular requirements for epithelialmesenchymal transition during tumor progression. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005; 17:548–558.

18. Morel AP, Lièvre M, Thomas C, Hinkal G, Ansieau S, Puisieux A. Generation of breast cancer stem cells through epithelial-mesenchymal transition. PLoS One. 2008; 3:e2888.

19. Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan A, Zhou AY, et al. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell. 2008; 133:704–715.

20. Sarrió D, Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, Hardisson D, Cano A, Moreno-Bueno G, Palacios J. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer relates to the basal-like phenotype. Cancer Res. 2008; 68:989–997.

21. Prat A, Parker JS, Karginova O, Fan C, Livasy C, Herschkowitz JI, et al. Phenotypic and molecular characterization of the claudin-low intrinsic subtype of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2010; 12:R68.

22. Chuthapisith S, Eremin J, El-Sheemey M, Eremin O. Breast cancer chemoresistance: emerging importance of cancer stem cells. Surg Oncol. 2010; 19:27–32.

23. Işeri OD, Kars MD, Arpaci F, Atalay C, Pak I, Gündüz U. Drug resistant MCF-7 cells exhibit epithelial-mesenchymal transition gene expression pattern. Biomed Pharmacother. 2011; 65:40–45.

24. Creighton CJ, Chang JC, Rosen JM. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in tumor-initiating cells and its clinical implications in breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2010; 15:253–260.

25. Creighton CJ, Li X, Landis M, Dixon JM, Neumeister VM, Sjolund A, et al. Residual breast cancers after conventional therapy display mesenchymal as well as tumor-initiating features. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009; 106:13820–13825.
26. Logullo AF, Nonogaki S, Pasini FS, Osório CA, Soares FA, Brentani MM. Concomitant expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition biomarkers in breast ductal carcinoma: association with progression. Oncol Rep. 2010; 23:313–320.
27. Choi Y, Lee HJ, Jang MH, Gwak JM, Lee KS, Kim EJ, et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition increases during the progression of in situ to invasive basal-like breast cancer. Hum Pathol. 2013; 44:2581–2589.
28. Iwatsuki M, Mimori K, Yokobori T, Ishi H, Beppu T, Nakamori S, et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer development and its clinical significance. Cancer Sci. 2010; 101:293–299.






 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download