Abstract
Purpose
X-ray microscopy with synchrotron radiation might be a useful tool for novel x-ray imaging in the clinical and laboratory settings. This technique provides detailed images of internal structures non-invasively. It also has the potential to resolve some of the limitations of conventional breast imaging. We evaluated high resolution synchrotron imaging of breast tissues from normal breasts and breasts with fibroadenomas and cancer.
Methods
A new x-ray microscope was installed on the 1B2 beamline of a Pohang Light Source, at a third generation synchrotron radiation facility in Pohang, Korea. The phase contrast x-ray energy was set at 6.95 keV and the x-ray beam was monochromatized by a W/B4C monochromator. Formalin-fixed or unfixed female breast tissue from normal breast as well as breasts with fibroadenomas and carcinoma were attached onto the Kapton film. The sample was positioned 25 m away from the beam source. The x-ray image of the sample was converted into a visual image on the CsI (TI) scintillation crystal, and magnified 20 times by the microscopic objective lens. After an additional 10 fold digital magnification, this visual image was captured by a full frame CCD camera.
Results
The monochromated x-ray microscopic images of female breast tissue from normal breast, fibroadenoma and carcinoma cases were evaluated. The total magnifying power of the microscope was ×200. This synchrotron radiation imaging enabled us to observe detailed structures of breast tissue without sample preparation such as staining or fixation.
Conclusion
Using monochromated synchrotron radiation, the x-ray microscopic images of the normal breast and breasts with fibroadenomas and cancer were obtained. From the images obtained, the x-ray microscopic imaging of breast tissue with synchrotron radiation appears to have great potential for clinical and research purposes such as oncology studies, early detection of cancer and as an aid to the pathological diagnosis in the future.
Figures and Tables
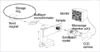 | Fig 1The layout of the 1B2 beamline optics. A x-ray microscope was insalled on the 1B2 beamline of a Pohang Light Source, at a third generation synchrotron radiation facility in Pohang, Korea. |
 | Fig 2Normal breast tissue. This is the monochromated synchrotron image of normal breast of premenopausal woman. It shows normal ductal structures (arrows), fat tissue (arrowheads) and supporting fibrous stroma. The specimen is 2.7×1.6 mm in size, 30 µm thick, unfixed. |
 | Fig 3Fibroadenoma. This is the monochromated synchrotron image of fibroadenoma of premenopausal woman. It shows homogeneous densities with characteristic fibrous connective tissues (arrows) and stromal proliferation. The specimen is 1.2×0.4 mm in size, 30 µm thick, unfixed. |
 | Fig 4Breast cancer. This is the monochromated synchrotron image of breast cancer of postmenopausal woman. It shows typical histopathologic findings of breast cancer such as stromal proliferation (arrowhead), loss of ductal structure, infiltrating tumor cells into adjacent fat tissues (arrows). The specimen is 2.3×1.4 mm in size, 10 µm thick, formalin-fixed. |
References
1. Ministry of health and welfare, Republic of Korea. Annual report of the central cancer registry in Korea (2002.1.-2002.12.). 2003.
2. Longo R, Pani S, Arfelli F, Dreossi D, Olivo A, Poropat P, et al. Morphological breast imaging: tomography and digital mammography with synchrotron radiation. Nuclear Insturments and Methods in Physics Research A. 2003. 497:9–13.

3. Arfelli F, Bonvicini V, Bravin A, Cantatore G, Castelli E, Palma LD, et al. Mammography with synchrotron radiation: Phase-detection techniques. Radiology. 2000. 215:286–293.

4. Burattini E, Cossu E, Maggio CD, Gambaccini M, Indovina PL, Marziani M, et al. Mammography with synchrotron radiation. Radiology. 1995. 195:239–244.

5. Lee CH, Weinreb JC. The use of magnetic resonance imaging in breast cancer screening. J Am Coll Radiol. 2004. 1:176–182.

6. Orel SG, Schnall MD. MR imaging of the breast for the detection, diagnosis, and staging of breast cancer. Radiology. 2001. 220:13–30.

7. Youn HS, Jung SW. Observations of a human hair shaft with an x-ray microscope. Phys Med Biol. 2005. 50:5417–5420.

8. Choi CH, Kim HT, Choe JY, Kim JK, Youn HS. Application of synchrotron radiation imaging for non-destructive monitoring of mouse rheumatoid arthritis model. AIP Conference Proceedings. 2007. 879:1952–1955.

9. Jheon SH, Youn HS, Kim HT, Choi GH, Kim JK. High-resolution x-ray refraction imaging of rat lung and histological correlations. Microsc Res Tech. 2006. 69:656–659.

10. Arfelli F. Synchrotron light and imaging systems for medical radiology. Nucl Instrum Meth Phys Res A. 2000. 454:11–25.

11. Ando M, Bando H, Chen Z, Chikaura Y, Choi CH, Endo T, et al. 2D and 3D refraction based x-ray imaging suitable for clinical and pathological diagnosis. AIP Conference Proceedings. 2007. 879:1899–1902.

12. Hwu Y, Hsieh H, Lu MJ, Tsai WL, Lin HM, Goh WC, et al. Coherence-enhanced synchrotron radiology: Refraction versus diffraction mechanisms. J Appl Phys. 1999. 86:4613–4618.

13. Arfelli F, Assante M, Bonvicini V, Bravin A, Cantatore G, Castelli E, et al. Low dose phase contrast x-ray medical imaging. Phys Med Biol. 1998. 43:2845–2852.
14. Michiel MD, Olivo A, Tromba G, Arfelli F, Bovicini V, Bravin A, et al. Phase contrast imaging in the field of mammography. Medical applications of synchrotron radiation. 1998. Springer-Verlag;78–82.

15. Dill T, Dix WR, Hamm W, Jung M, Lohmann M, Reime B, et al. Intravenous coronary angiography with synchrotron radiation. Eur J Phys. 1998. 19:499–511.
16. Longo R, Pani S, Arfelli F, Dreossi D, Olivo A, Poropat P, et al. Morphological breast imaging: tomography and digital mammography with synchrotron radiation. Nucl Instrum Meth in Phys Res. 2003. 497:9–13.

17. Betz O, Wegst U, Weide D, Heethoff M, Helfen L, Lee WK, et al. Imaging applications of synchrotron X-ray phase-contrast microtomography in biological morphology and biomaterials science. I. General aspects of the technique and its advantages in the analysis of millimetre-sized arthropod structure. J Microsc. 2007. 227:51–71.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download