Abstract
Purpose
Accurate preoperative assessment of breast cancer is important to determine the extent of disease and the plan for surgery. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of preoperative breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in breast cancer patients.
Methods
Between January 2001 and October 2007, 457 consecutive patients who had undergone surgical treatment for breast cancer were retrospectively studied. We compared 303 patients from the non-preoperative MRI group (group A) to 154 patients from the preoperative MRI group (group B). The impact of preoperative MRI was evaluated for each patient with regard to changes in therapeutic intervention.
Figures and Tables
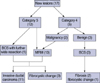 | Fig 1Seventeen new lesions diagnosed by MRI have been managed as follows.
MRM=modified radical mastectomy; BCS=breast conserving surgery.
*The figures in parentheses mean the number of cases.
|
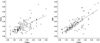 | Fig 2Regression graph shows the predicted tumor size by sonography and MRI versus histological size. Tumor size was more accurately defined in MRI (R2=0.589) than sonography (R2=0.411). |
References
1. Fischer U, Kopka L, Grabbe E. Breast carcinoma: effect of preoperative contrast-enhanced MR Imaging on the therapeutic approach. Radiology. 1999. 213:881–888.

2. Martincich L, Montemurro F, Cirillo S, Mara V, Derosa G, Ponzone R, et al. Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the prediction of tumor response in patients with locally advanced breast cancer receiving neoadjuvant chemo-therapy. Radilo Med (Torino). 2003. 106:51–58.
3. Bedrosian I, Mick R, Orel SG, Schnall M, Reynolds C, Spitz F, et al. Changes in the surgical management of patients with breast carcinoma based on preoperative magnetic resonance imaging. Cancer. 2003. 98:468–473.

4. Faverly DR, Hendiriks JH, Holland R. Breast carcinomas of limited extent: frequency, radiologic-pathologic characteristics, and surgical margin requirements. Cancer. 2001. 91:647–659.
5. Esserman L, Nola H, Yassa L, Barclay J, Frankel S, Sickles E. Utility of magnetic resonance imaging in the management of breast cancer: evidence for improved preoperative staging. J Clin Oncol. 1999. 17:110–119.

6. Gatzemeier W, Liersch T, Stylianou A, Buttler A, Becker H, Fischer U. Preoperative MR mammography in breast carcinoma. Effect on operative treatment from the surgical viewpoint. Chirurg. 1999. 70:1460–1468.

7. Kim DY, Moon WK, Cho N, Ko ES, Yang SK, Park JS, et al. MRI of the breast for the detection and assessment of the size of ductal carcinoma in situ. Korean J Radiol. 2007. 8:32–39.

8. Chung A, Saouaf R, Scharre K, Phillips E. The impact of MRI on the treatment of DCIS. Am Surg. 2005. 71:705–710.

9. Cha ES. Magnetic resonance findings of breast diseases. J Korean Breast Cancer Soc. 2003. 6:247–254.

10. Schelfout K, Vangoethem M, Kersschot E, Colpaert C, Schelfout AM, Leyman P, et al. Contrast-enhanced MR imaging of breast lesions and effect on treatment. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2004. 30:501–507.

11. Hollingsworth AB, Stough RG. Preoperative breast MRI for locoregional staging. J Okia State Med Assoc. 2006. 99:505–515.
12. Pavic D, Koomen MA, Kuzmiak CM, Lee YH, Pisano ED. The role of magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosis and management of breast cancer. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2004. 3:527–541.

13. Bilimoria KY, Cambic A, Hansen NM, Bethke KP. Evaluating the impact of preoperative breast magnetic resonance imaging on the surgical management of newly diagnosed breast cancers. Arch Surg. 2007. 142:441–447.

14. Dao TN, Lamont JP, Knox SM. Clinical utility of breast magnetic resonance imaging in patients presenting with primary breast cancer. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2007. 20:227–230.

15. Braun M, Pölcher M, Schrading S, Zivanovic O, Kowalski T, Flucke U, et al. Influence of preoperative MRI on the surgical managementof patients with operable breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008. 111:179–187.

16. Buxant F, Scuotto F, Hottat N, Noel JC, Simon P. Does preoperative magnetic resonance imaging modify breast cancer surgery? Acta Chir Belg. 2007. 107:288–291.

17. Kang HJ, Lee JS, Kim HL, Song BJ, Kim JS, Oh SJ, et al. The clinical significance of preoperative MRI for determination of surgery in breast cancer. J Breast Cancer. 2006. 9:343–348.

18. Anastassiades O, Iakovou E, Stavridou N, Gogas J, Karameris A. Multicentricity in breast cancer. A study of 366 cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1993. 99:238–243.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download