Abstract
Purpose
Malignant phyllodes tumors are rare breast tumors. Information on the prognosis and optimal treatment of these lesions is not yet sufficient. The aim of this study was to determine parameters that predict the recurrence of malignant phyllodes tumors of the breast.
Methods
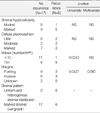
Retrospectively, we reviewed the medical records and pathological slides of 23 patients with malignant phyllodes tumors that had undergone surgical treatment from 1988 to 2006. The age of the patients, tumor size, type of surgery, resection margin, adjuvant therapy and pathological characteristics of the tumors such as stromal hypercellularity, cellular phleomorphism, mitosis, margins, and stromal pattern were examined.
Results
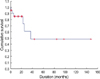
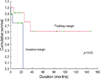
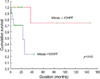
The mean age of the patients was 41 yr. The tumor size ranged from 1 cm to 25 cm, with a median of 7.42 cm. The median follow-up time was 29.0 months. Recurrence was observed in 6 patients (26.1%) and the 5-yr disease free survival was 48.9%. Risk factors for recurrence of a malignant phyllodes tumor were a mitotic index greater than 10 per high-powered field (p=0.0242) and an invasive margin (p=0.0437).
Figures and Tables
References
1. Auger M, Hana W, Kahn HJ. Cystsarcoma phyllodes of the breasst and its mimics: An immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1989. 113:1231–1235.
2. Kleer CG, Giordano TJ, Braun T, Oberman H. Pathologic, immunological, and molecular features of benign and malignant phyllodes tumors of the breast. Mod Pathol. 2001. 13:185–190.
3. Kim HJ, Kim TS, Kang HJ, Cho JC, Park IA, Noh DY, et al. Clinical analysis of phyllodes tumor of the breast. J Korean Surg Soc. 2000. 58:352–360.
4. Lee BJ, Pack GT. Giant intracanalicular fibroadenomyxoma of the breast. The so-called cystosarcoma phyllodes mammae of Johannes Muller. Ann Surg. 1931. 15:250–268.
5. Noguchi S, Aihara T, Motomura K, Inaji H, Imaoka S, Koyama H, et al. Phyllodes Tumor of the Breast: Pathology, Histogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Breast Cancer. 1996. 3:79–92.

6. Hines JR, Murad TM, Beal JM. Prognostic indicators in cystosarcoma phyllodes. Am J Surg. 1987. 153:276–280.
7. Page JE, Williams JE. The radiological features of phyllodes tumor of the breast with clinico-pathological correlation. Clin Radiol. 1991. 44:8–12.

8. Tavassoli FA, Devilee P. WHO Classification of Tumors, Pathology and genetics of the breast and female genital organs. 2003. 1st ed. Lyon: IARC Press.
9. Azzopardi JG, Ahmed A, Millis RR. Problems in breast pathology. Major Probl Pathol. 1979. 11:1–466.
10. Cole-Beugler C, Soriano R, Kurtz AB. Ultrasound X-ray mammography and histopathology of cystosarcoma phyllodes. Radiology. 1983. 146:481.

11. Kwak JH, Son BH, Lee PC, Ahn SH. Clinical chareteristic and recurrence patterns of malignant phyllodes tumor. J Korean Surg Soc. 2000. 58:465–470.
12. Abdalla HM, Sakr MA. Predictive factors of local recurrence and survival following primary surgical treatment of phyllodes tumors of the breast. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2006. 18:125–133.
13. Ku KB, Bang MJ, Choi JW, Lee YS, Park JH, Kim HO, et al. Clinical, Pathologic and Immunohistochemical Features of Phyllodes Tumor of the Breast. J Korean Breast Cancer Soc. 2004. 7:185–192.

14. Salvadori B, Cusumano F, Del Bo R, Delledonne V, Grassi M, Rovini D, et al. Surgical treatment of phyllodes tumors of the breast. Cancer. 1989. 63:2532–2536.

15. Kesterson GH, Georgiade N, Seigler HF, Barton TK, McCarty KS Sr, McCarty KS Jr. Cystosarcoma phylloides. A steroid receptor and ultrastructure analysis. Ann Surg. 1979. 190:640–647.

16. Cohn-Cedermark G, Rutqvist LE, Rosendahl I, Silfverswarf C. Prognostic factors in cystosarcoma phyllodes: a clinicopathologic study of 77 patients. Cancer. 1991. 68:2017–2022.

17. Macdonald OK, Lee CM, Tward JD, Chappel CD, Gaffney DK. Malignant phyllodes tumor of the female breast: association of primary therapy with cause-specific survival from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) program. Cancer. 2006. 107:2127–2133.
18. The Korean Breast Cancer Society. Survival analysis of Korean breast cancer patients diagnosed between 1993 and 2002 in Korea-A nationwide study of the cancer registry. J Korean Breast Cancer Soc. 2006. 9:214–229.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download