Abstract
Purpose
To review the results of the treatment of dural tears, sustained during operations on the lumbar spinal disorders.
Materials and Methods
From Jan. 1991 to Dec. 2000, 694 consecutive patients had a decompression of the lumbar spine, 35(5%) patients sustained a dural tear during the operations. Of 32 patients who were followed up for more than one year, 29 patients were detected dural tear intraoperatively. 24 patients were treated with primary repair, 4 patients with fibrin glue and one patient with dural reconstruction and fibrin glue. Postoperative management consisted of closed wound drainage for an average of 3.3 days and bed rest for an average of 9.3 days.
Results
The total subfascial drains averaged an output of 626(18- 1698) milliliters of 32 patients. Clinical symptoms were complained of headache in 12 patients, nausea in 7 patients, dizziness and vomiting in 2 patients postoperatively, but all had resolution of these symptoms after conservative treatment. A superficial wound infection occurred in one of these patients, managed with antibiotic therapy. Whereas the deep wound infection occurred in one, managed with wound debridement and antibiotic therapy successfully. A mean follow up of 34 months was available and showed satisfactory clinical results for 29 of the patients(91%).
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Bosacco SJ, Gardner MJ, Guille JT. E valu ati on and treatment of dural tears in lumbar spine surgery. Clin Orthop. 389:238–247. 2001.
2). Cain JE, Dryer RF, Barton BR. Evaluation of dural closure techniques: Suture methods, fibrin adhesive sealant, and cyanoacrylate polymer. Spine. 13:720–728. 1988.
3). Cammisa FP, Eismont FJ, Green BA. Dural laceration occurring with burst fracture and associated laminar fractures. J Bone Joint Surg. 71A:1044–1052. 1989.
4). Cammisa FP, Girardi FP, Sangani PK, Parvataneni HK, Cadag S, Sandhu HS. Incidental durotomy in spine surgery. Spine. 25:2663–2667. 2000.

5). Eismont FJ, Wiesel FW, Rothman RH. Treatment of dural tears associated with spinal surgery. J Bone Joint Surg. 63A:1132–1136. 1981.

6). Finnegan WJ Fenlin JM, Marvel JP, Nardini RJ, Rothman RH. Results of surgical intervention in the sympathetic multiply-operated back patient. Analysis of sixty- seven cases followed for three to seven years. J Bone Joint Surg. 61A:1077–11082. 1979.
7). Foty D, Johnson JP, Kirsch AJ, Bruce JN, Waren JJ. Dural closure with laser tissue welding. Otolaryngol.-head and Neck Surg. 115:513–518. 1996.
8). Hodges SD, Humphreys SC, Eck JC, Covington LA. Management of incidental durotomy without mandatory bed rest. Spine. 24:2062–2064. 1999.

9). Jones AAM, Stambongh JL, Balderston RA. Long term results of lumbar spinal surgery complicated by unintended incidental durotomy. Spine. 14:443–446. 1989.
10). Kitchel SH, Eismont FJ, Green BA. Closed sub -arachnoid drainage for management of cerebrospinal fluid leakage after an operation on the spine. J Bone Joint Surg. 71A:984–987. 1989.
12). Lauerman WC, Wiesel SW. Management of the patient with failed low back surgery. (in. Chapman MW, editor. Chapman's orthopaedic surgery. 3rd ed. phildelphia: Lppincott Williams & Wilkins;p. 3861. 2001. .).
13). Lenke LG, Pridwell KH, Bull D, Betz RR, Baldus C, Schoenecker PL. Result of in situ fusion isthmic spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disorders. 5:433–442. 1992.
14). Mayfield FH, Kurokawa K. Watertight closure of spinal duramater; Technical note. J Neurosurg. 43:639–640. 1975.
15). Miller PR, Elder FW. Meningeal pseudocyst (me-ningocele spurius) following laminectomy. Report of ten cases. J Bone Joint Surg. 50A:268–276. 1968.
16). Nash CL, Kaufman B, Frankel VH. Postsurgical meningeal pseudocyst of the lumbar spine. Clin Orthop. 75:167–178. 1971.
17). Patel MR, Louie W, Rachlin J. Postoperative cerebrospinal fluid leaks of the lumbosacral spine: management with percutaneous fibrin glue. Am J Neuroradiol. 17:495–500. 1996.
18). Wang JC, Borlman HH, Riew KD. Dural tears secondary to operations on the lumbar spine. J Bone Joint Surg. 80A:1728–1732. 1998.
Go to : 
Figures and Tables%
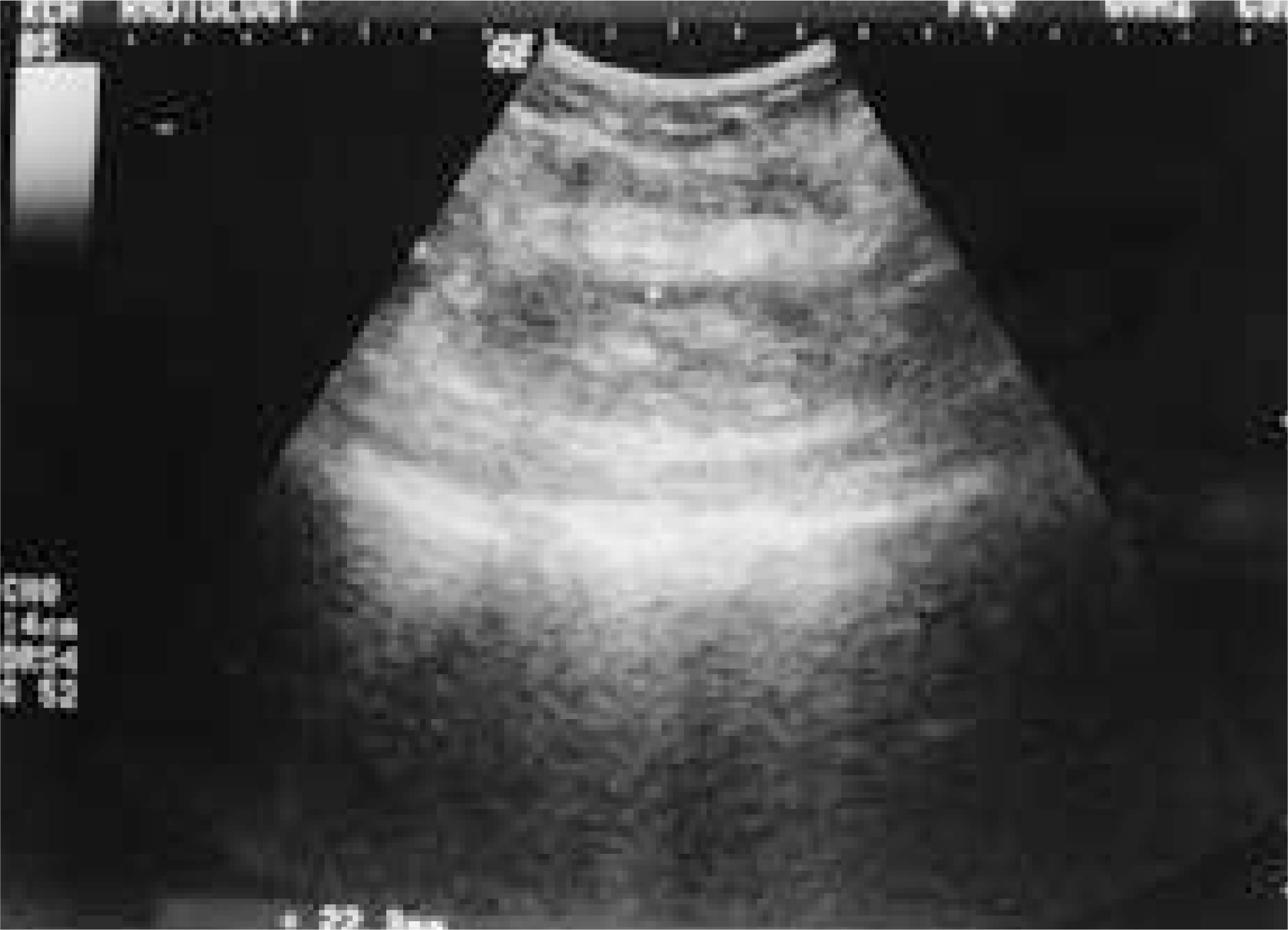 | Fig. 1.Longitudinal sonogram of 52 years old woman(No. 20). An abnormal fluid-filled cyst is seen as a hypoechoic lesion under the paraspinal muscle. |
Table 1.
Morbidity of dural tears according to diagnosis
| HNP† | Stenosis | Revision | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No∗. of patients | 209 | 416 | 69 | 694 |
| No. of tears | 3(1%) | 24(6%) | 8(12%) 3 | 35(5%) |
Table 2.
Summary of patients
| No. | Age | Sex | Dx.∗ | Detect | Op† | Dura Tx‡ | drain day | T. amount(ml)§ | Sxs|| | CI. result¶ | Rad.∗∗ | Cxs†† | F/U(M)†† |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 67 | M | Stenosis | intraop | decom & fu§§ | repair & Fi|| || | 2 | 239 | G | В | 12 | ||
| 2 | 57 | M | Stenosis | intraop | de com & fu | repair & Fi | 2 | 417 | G | В | 23 | ||
| 3 | 60 | F | spondylolisthesis | intraop | decom & fu | repair & Fi | 3 | 140 | nausea | G | С | 16 | |
| 4 | 66 | M | spondylolisthesis | intraop | decom & fu | repair & Fi | 5 | 1609 | G | В | 12 | ||
| 5 | 50 | F | Stenosis | postop | decom & fu | 6 | 817 | headache | G | А | 25 | ||
| 6 | 49 | F | spondylolisthesis | intraop | decom & fu | repair | 3 | 706 | headache | E | А | 96 | |
| 7 | 50 | F | Stenosis | intraop | decom & fu | repair | 2 | 301 | headache & dizziness | G | В | 58 | |
| 8 | 56 | F | Stenosis | intraop | decom & fu | repair & Fi | 2 | 681 | G | В | 98 | ||
| 9 | 68 | M | revision | intraop | decom & fu | repair & Fi | 6 | 955 | headache | G | D | infection | 19 |
| 10 | 50 | M | spondylolisthesis | intraop | decom & fu | Fi | 1 | 283 | nausea | G | В | 38 | |
| 11 | 64 | F | spondylolisthesis | intraop | decom & fu | repair & Fi | 2 | 498 | headache | G | В | 12 | |
| 12 | 18 | F | HNP” | intraop | decom | repair & Fi | 6 | 480 | headache | G | 12 | ||
| 13 | 62 | F | spondylolisthesis | intraop | decom & fu | repair & Fi | 3 | 509 | nausea | F | А | 20 | |
| 14 | 57 | F | revision | intraop | decom & fu | repair & Fi | 2 | 610 | nausea & vomiting | E | А | 70 | |
| 15 | 71 | M | revision | intraop | decom & fu | repair & Fi | 3 | 1276 | headache | F | А | 39 | |
| 16 | 62 | F | spondylolisthesis | intraop | decom & fu | repair & Fi | 2 | 399 | G | В | numbness | 31 | |
| 17 | 62 | F | Stenosis | intraop | decom | repair | 3 | 574 | E | 83 | |||
| 18 | 62 | F | Stenosis | intraop | decom | repair | 2 | 165 | dizziness & vomiting | G | 80 | ||
| 19 | 57 | F | Stenosis | intraop | decom & fu | repair | 2 | 291 | G | В | numbness | 39 | |
| 20 | 52 | F | Stenosis | intraop | decom & fu | Fi | 6 | 1047 | G | А | 22 | ||
| 21 | 54 | F | spondylolisthesis | intraop | decom & fu | repair & Fi | 4 | 1063 | G | В | 34 | ||
| 22 | 66 | F | spondylolisthesis | intraop | decom & fu | repair & Fi | 5 | 1698 | headache & nausea | G | А | 33 | |
| 23 | 36 | F | Stenosis | intraop | decom & fu | repair & Fi | 3 | 269 | G | А | 12 | ||
| 24 | 78 | M | Stenosis | intraop | decom & fu | repair & Fi | 3 | 161 | nausea | E | С | 21 | |
| 25 | 55 | M | spondylolisthesis | intraop | decom & fu | Fi | 3 | 392 | E | А | 47 | ||
| 26 | 43 | M | revision | intraop | decom | Fi | 2 | 18 | headache & nausea | E | 13 | ||
| 27 | 48 | F | revision | intraop | decom & fu | repair & Fi | 4 | 1066 | headache | G | D | 12 | |
| 28 | 66 | F | spondylolisthesis | intraop | decom & fu | repair & Fi | 2 | 384 | F | С | infection | 12 | |
| 29 | 27 | M | revision | intraop | decom | repair & Fi | 1 | 199 | G | 19 | |||
| 30 | 21 | M | revision | postop | decom & fu | 5 | 539 | G | В | 12 | |||
| 31 | 56 | F | spondylolisthesis | intraop | decom & fu | repair & Fi | 3 | 605 | headache | G | А | numbness | 37 |
| 32 | 53 | F | revision | postop | decom & fu | 6 | 1647 | headache | E | В | 22 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download