Abstract
Objective
To analyze incidence, causes and prognosis of the spinal nerve root injury during the degenerative low back surgery.
Summary of Literature Review
There were very few studies about intraoperative spinal nerve root injuries during low back surgery.
Materials and Methods
Six hundred and twenty seven patients underwent degenerative low back surgery from Jan 1990 to Jan 2001 were included in this study. All patients were operated on by the first author and operation records made by the author himself were reviewed. Eight cases of intraoperative spinal nerve root injury were identified and causes and level of injuries, preoperative diagnosis, types of surgery and followup clinical results were analyzed.
Results
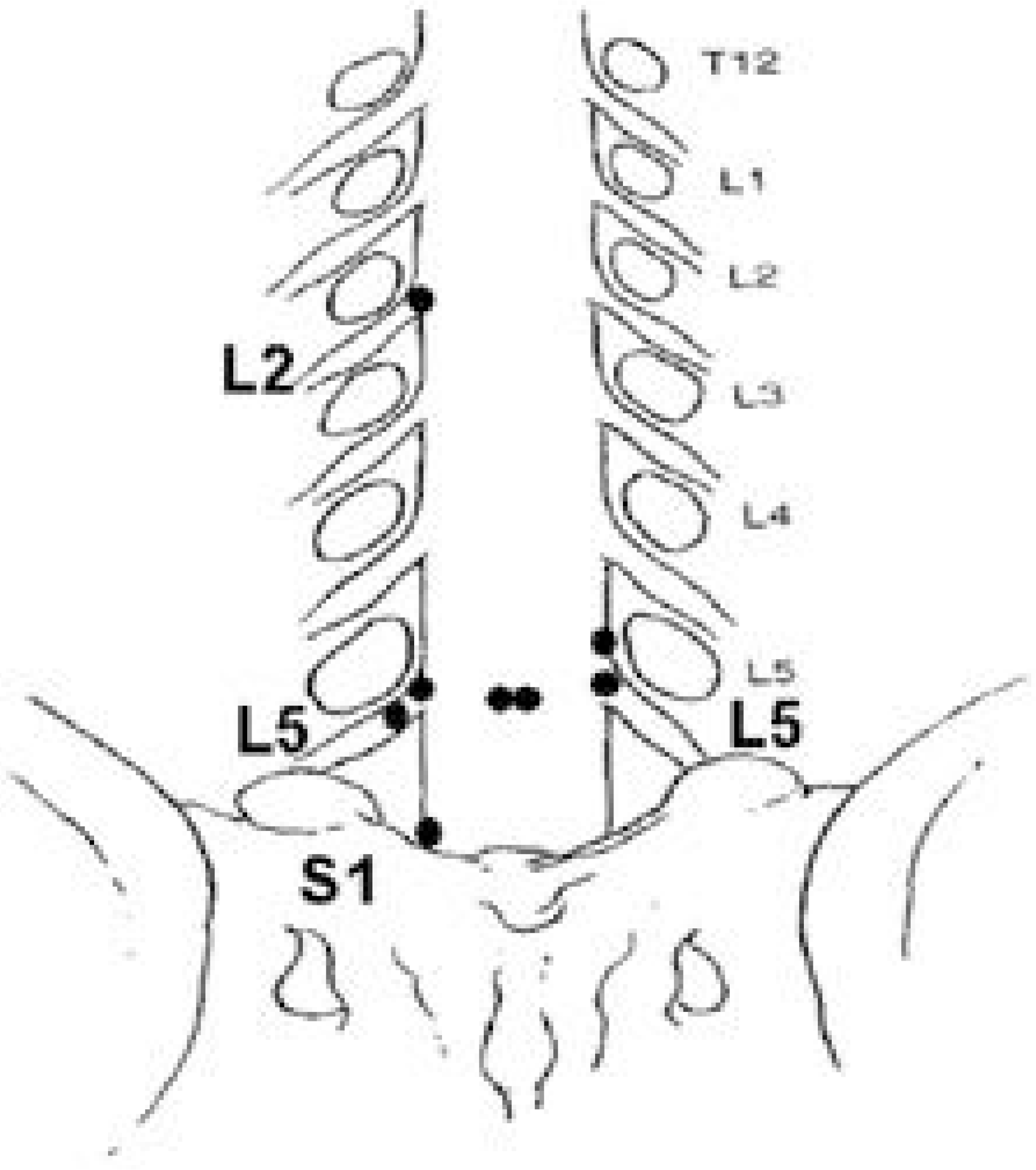
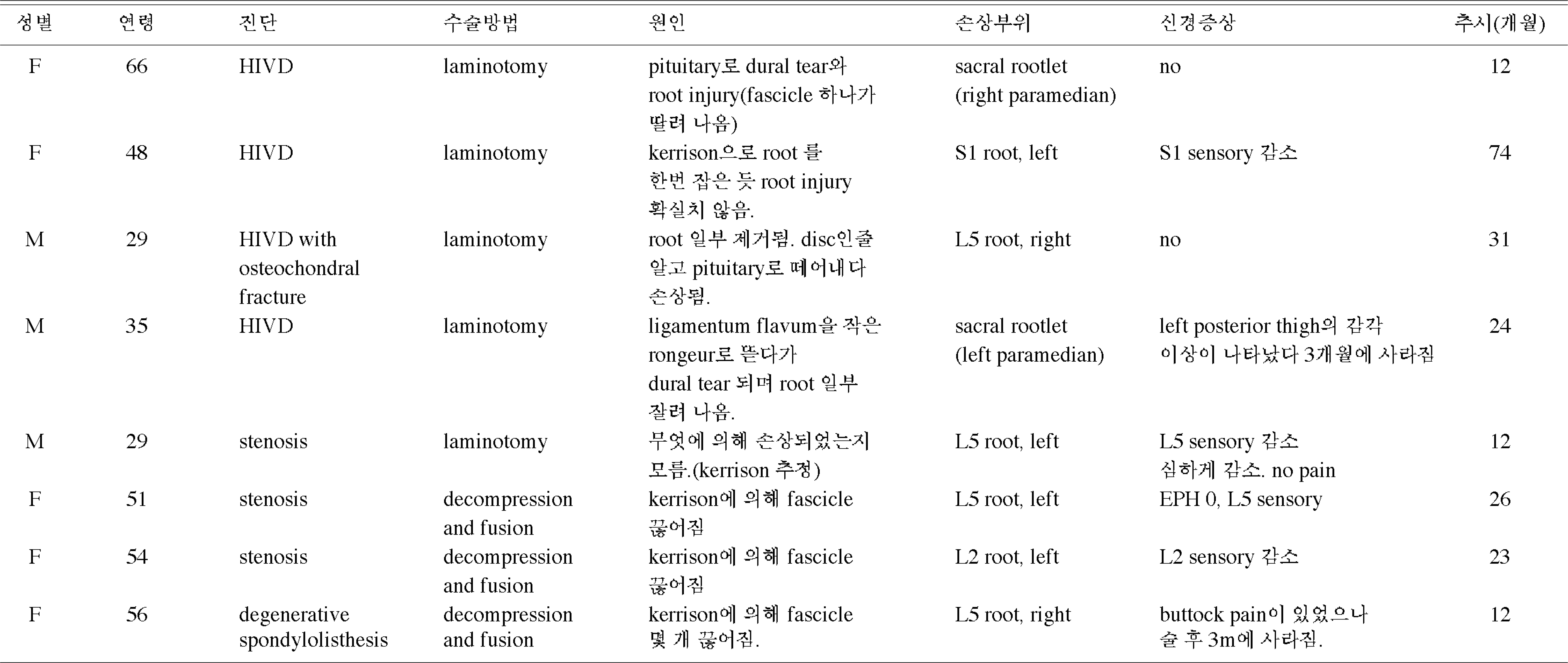
Eight cases of nerve root injury were developed during 5 posterior laminotomies for discectomy and 3 instrumentation and fusion. Spinal nerve root injuries were caused by Kerrison punch in 4 cases, pituitary forcep in 2, rongeur in 1, and not cer-tain but probably by Kerrison punch in 1case. The levels of injuries were 5th lumbar nerve root in 4 cases, and 1st sacral nerve root and 2nd lumbar nerve root in 1 case respectively. Two cases had sacral nerve rootlet injury with paramedian dural tear but the level of root injury was uncertain. Six of 8 patients had symptoms. There were sensory loss in 4 patients, pain in 2, and one patient had both sensory loss and loss of big toe extension power. Neurological symptoms were not improved throughout the followup period, but 2 patients who had pain were resolved their symptoms by 3 months.
Conclusions
Incidental spinal nerve root injury occurred in 1.3 percentage of the patients who underwent low back surgery. Half of them had neurologic symptoms and they showed poor prognosis. However motor deficit was relatively uncommon and it might be related to the anatomical characteristics of spinal nerve root.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
2). Cohen MS, Wall EJ, Olmerker K, Rydevik BL, Garfin SR. Anatomy of the spinal nerve roots in the lumbar and lower thoracic spine.(in Rothman RH and Simeone FA eds. The spine. 4th ed.Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co;p. 83. 1999. .).
3). Cohen MS, Wall EJ, Brown RA, et al. Cauda equina anatomy: extrathecal nerve roots and dorsal root ganglia. Spine. 15:1248–1251. 1990.
4). Gordon RB. Complications of lumbar spine surgery.(in Wiessel SW eds. The lumbar spine. 2nd ed.Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co;p. 1724. 1996. .).
5). Jonsson B, Stromqvist B. Lumbar spine surgery in the elderly: Complications and surgical results. Spine. 19:1431–1435. 1994.
6). Matsui H, Kitagawa H, Kawaguchi T, Tsuji H. Phy-siologic changes of nerve root during poeterior lumbar discectomy. Spine. 20:654–659. 1995.
8). Shin BJ, Shin YS, Kim YI, Rah SK, Choi CU. Co n -joined nerve roots associated with congenital absence of lumbosacral articular facet: A case report. J Korean Spine Surg. 2:290–295. 1995.
9). Stambough JL, Simeone FA. Neurogenic complications in spinal surgery.(in Rothman RH and Simeone FA eds. The spine. 4th ed.Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co;p. 1724. 1999. .).
10). Stambough JL, Booth RE. Complication in spine surgery as a consequence of anatomic variations.(in Garfin SR eds. Complications of spine Surgery. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins;1989. .).
11). Sunderland S. Advances in diagnosis and treatment of root and peripheral nerve injury. Adv Neurol. 22:271–305. 1979.
13). Tew JM Mayfield FH. Surgery of the anterior cervical spine: Prevention of complications.(in Dunsker SB eds. Seminars in neurological surgery: Cervical spondylosis. New York: Raven Press;1980. .).
Go to : 




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download