Abstract
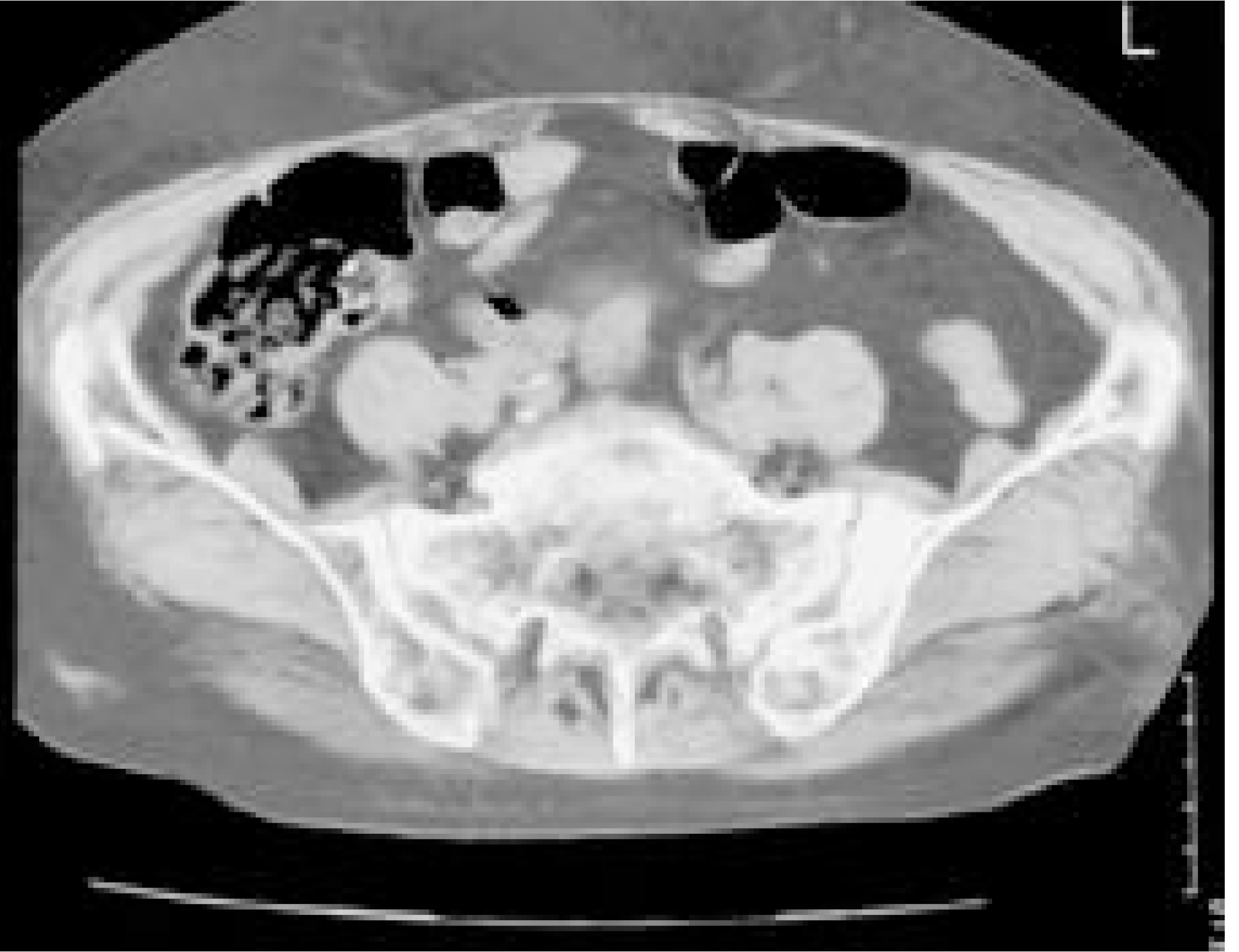
Sacral insufficiency fractures are unexpected causes of inguinal, lower back and buttock pain in elderly women with osteoporosis who have sustained unknown or only minimal trauma. Differential and radiological diagnoses of these fractures are often difficult. Bone scan remains the standard diagnostic tool, but computed tomography or magnetic resonance image may be required to differentiate insufficiency fracture from other diseases such as malignant bone lesion. The fracture usually extends vertically in the sacral ala, parallel to the sacroiliac joints. This distribution suggests that such fractures could be partially caused by weight- bearing transmitted through the spine. We report the treatment of insufficiency sacral fracture in one osteopenic patient who has been confirmed by computed tomography and treated with conservative method that convinced by follow up computed tomography.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Cooper KL, Beabout JW, Swee RG. Insufficiency fractures of the sacrum. Radiology. 156:15–20. 1985.

2). Grangier C, Garcia J, Howarth NR, May M, Rossier P. Role of MRI in the diagnosis of insufficiency fractures of the sacrum and acetabular roof. Skeletal Radiol. 26:517–524. 1997.

3). Hauge MD, Cooper KL, Litin SC. I nsu fficien cy fractures of the pelvis that simulate metastatic disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 63:807–812. 1988.
4). Jean LL, Bruno D, Eric T, Francis B, Francois B. Sacral insufficiency fractures presenting as acute low-back pain. Spine. 18:2502–2506. 1993.

5). Jung JH, Jun JB, Shim SC, et al. Insufficiency fractures of sacrum and pubic rami in rhematoid arthritis. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 5:287–292. 1998.
6). Kim YS, Jo SS. The significance of bone scan in fatigue fractures. J of Korean Orthop Surgery. 19:189–196. 1984.
8). Newhouse KE, Elkhoury GY, Buckwalter JA. Occult sacral fractures on osteopenic patients. J Bone Joint Surg. 74-A:1472–1477. 1992.
Go to : 
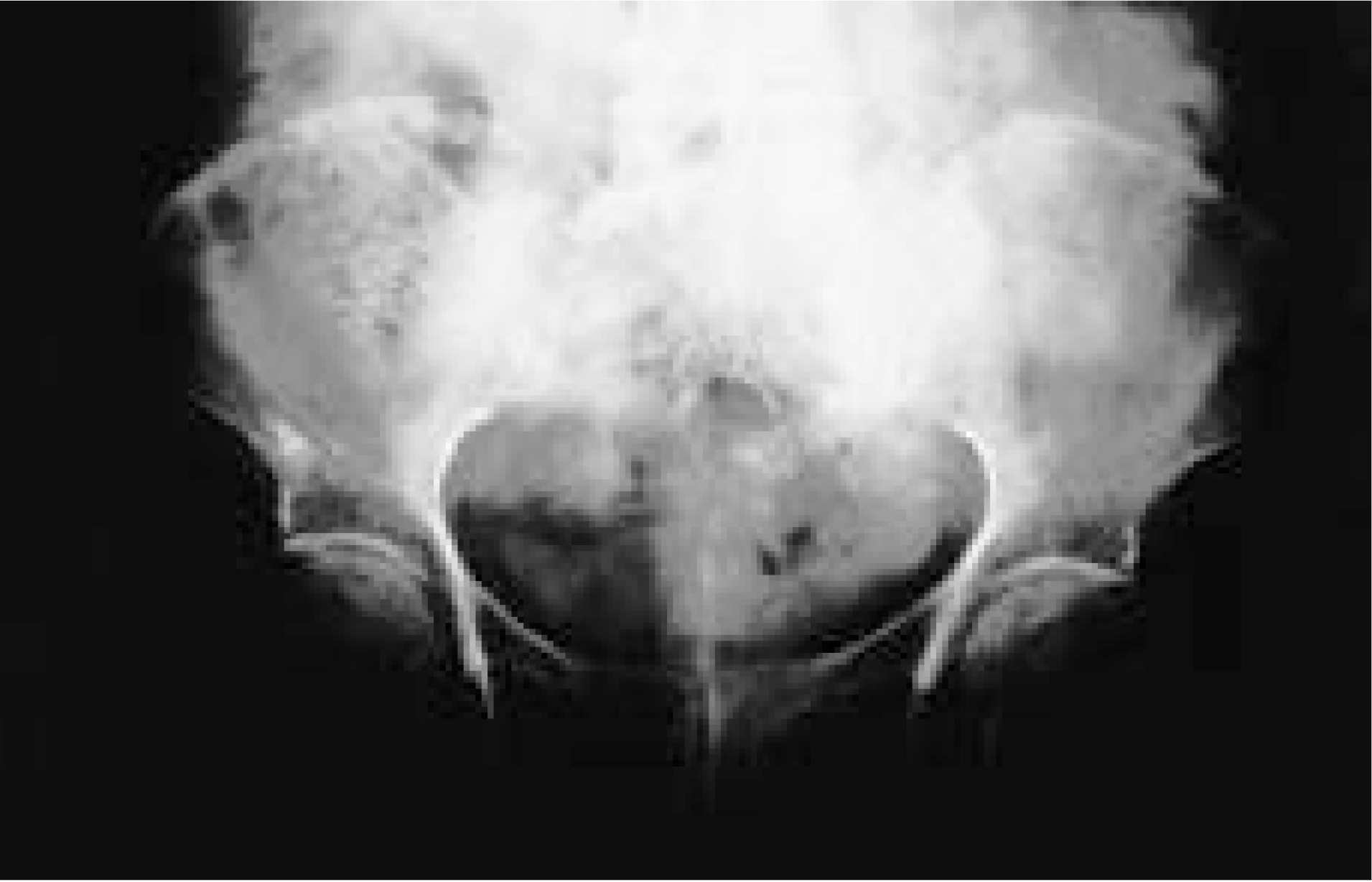 | Fig. 1.Anteroposterior pelvic radiograph showing sclerosis in the left ala is otherwise unremarkable. |
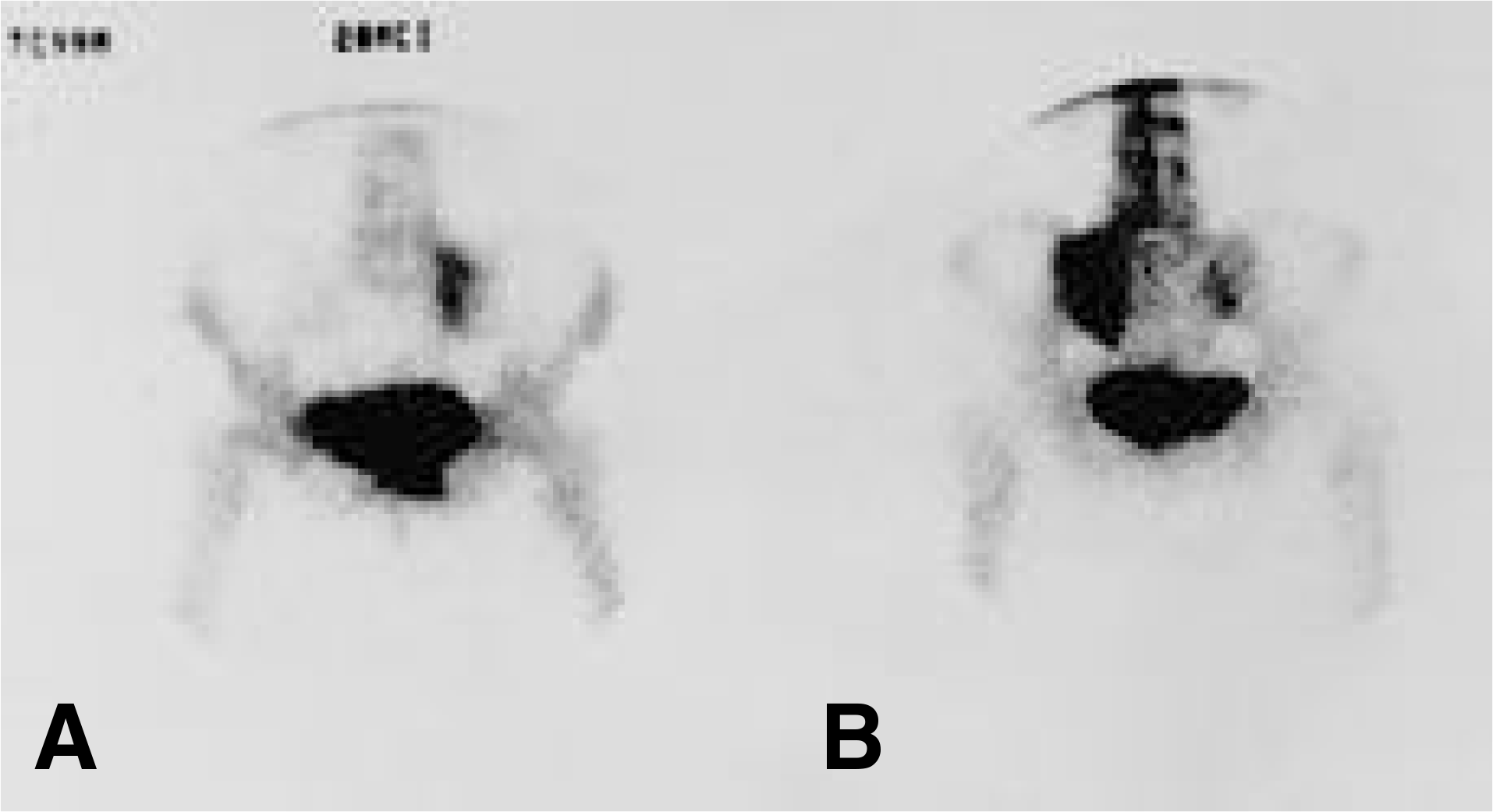 | Fig. 2.Technetium 99m bone scan revealing increased uptake in the left sacral ala. Fig. A. supine position, B. prone position |
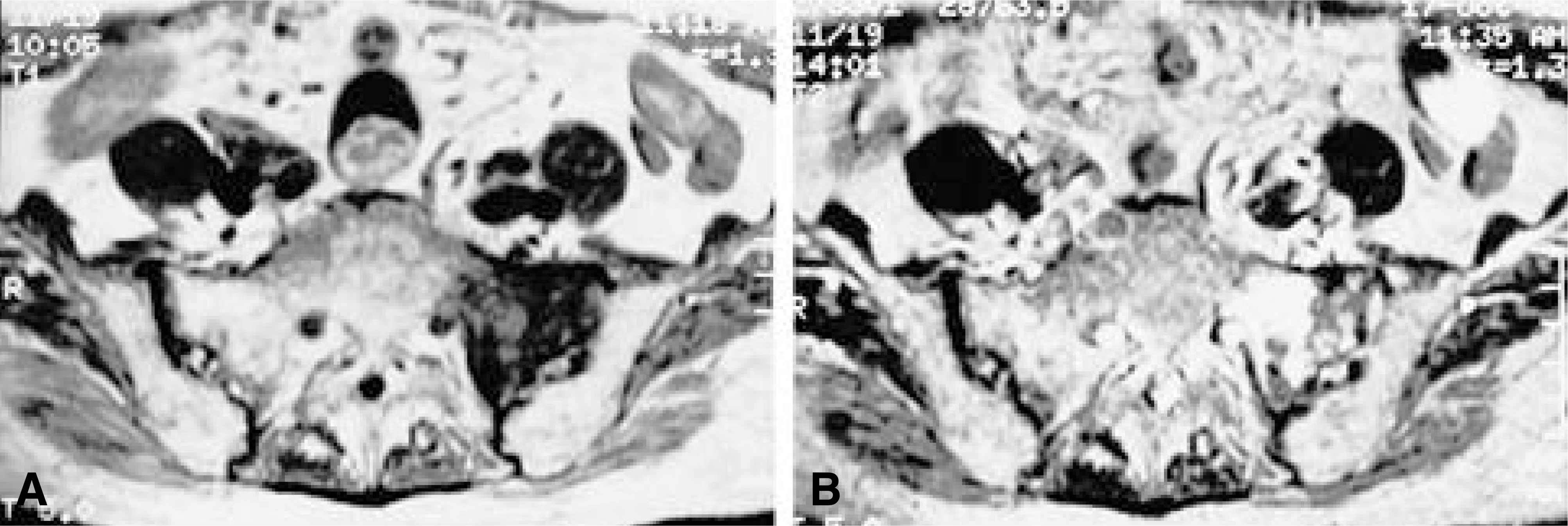 | Fig. 3.T1 and T2-weighted axial images of the sacrum, demonstrating a lesion in the left sacral ala which shows low signal intensity on the T1 image (A) and high signal intensity on the T2 image (B). |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download