Abstract
Gossypiboma is a mass within body consisting of a cotton matrix surrounded by a foreign-body reaction. Some patients may remain asymptomatic, while others develop early persistent infected conditions. Gossypiboma should be included in a differential diagnosis of a paravertebral mass in postoperative patients, and a thorough and a careful inspection of the surgical field before closure must be performed by surgeons to avoid the complications of gossypiboma even when there are correct counts. We present a patient in whom a gossypiboma at the 4th lumbar spine was encountered 40 years after a partial laminectomy with no subjective symptoms.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
01). Rajput A., Loud PA., Gibbs JF., Kraybill WG. Diagnostic challenges in patients with tumors: case 1. Gossypiboma (foreign body) manifesting 30 years after laparotomy. J Clin Oncol. 2003. 21:3700–3701.
02). Suh DH., Kim EC. Pathologic fracture of femoral neck due to mass suspicious of gossypiboma in proximal thigh. -case report-. J Korean Hip Soc. 2006. 18:493–497.

03). Rappaport W., Haynes K. The retained surgical sponge following intra-abdominal surgery. A continuing problem. Arch Surg. 1990. 125:405–407.
04). Bevernage C., Geusens E., Nijs S. Case report: a gossypiboma in the shoulder. Emerg Radiol. 2006. 12:231–233.

05). IS M., Karatas A., Akgul M., Yildirim U., Gezen F. A retained surgical sponge (gossypiboma) mimicking a paraspinal abscess. Br J Neurosurg. 2007. 21:307–308.

06). Van Goethem JW., Parizel PM., Perdius D., Hermans P., De Moor J. MR and CT imaging of paraspinal textilo-ma(gossypiboma). J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1991. 15:1000–1003.
Go to : 
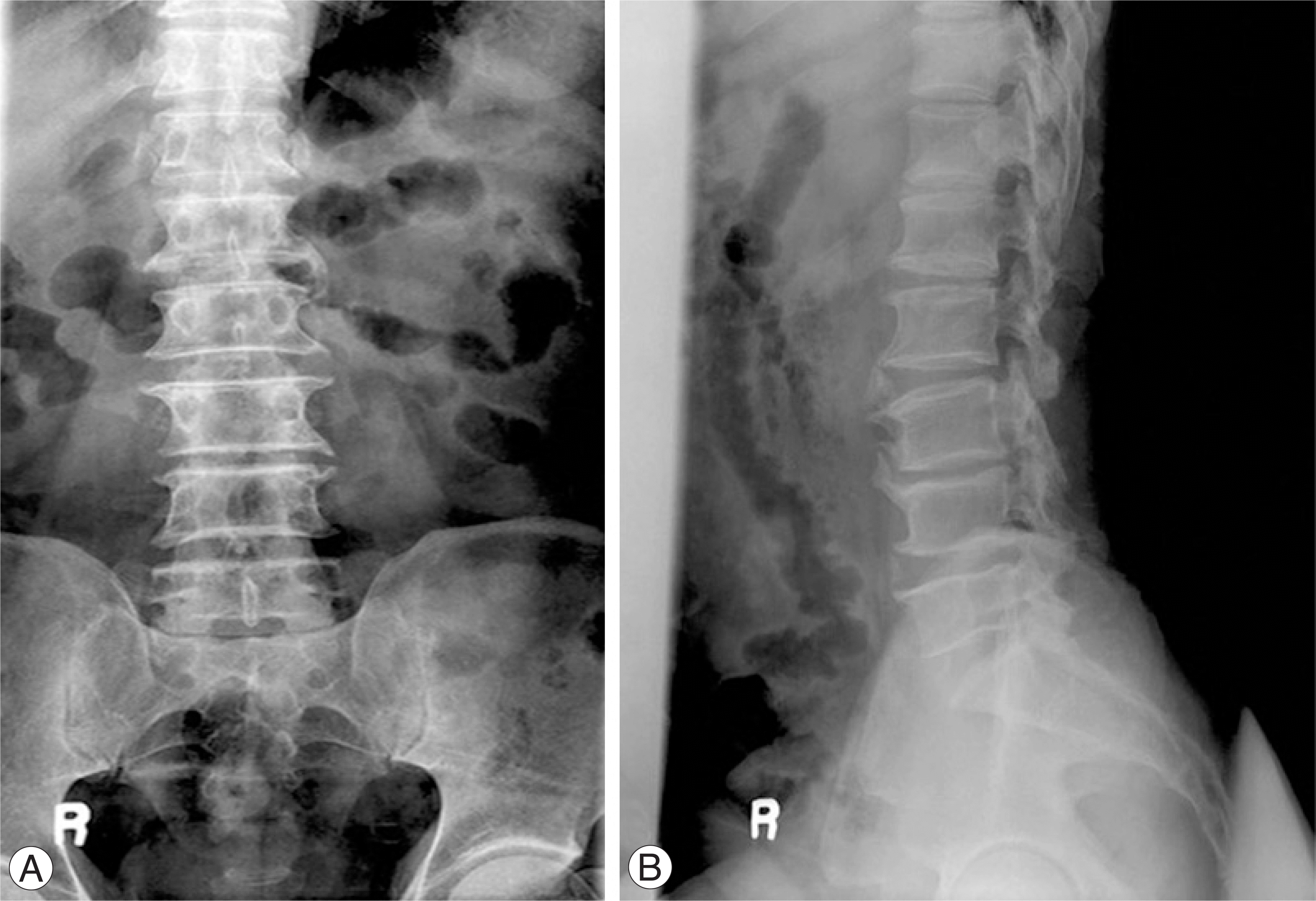 | Fig. 1.A 60-year-old man who underwent left L3 and L4 partial laminectomy 40 years ago. Preoperative (A) anteroposterior and (B) lateral radiographs show left laminectomy state of L3 and L4. |
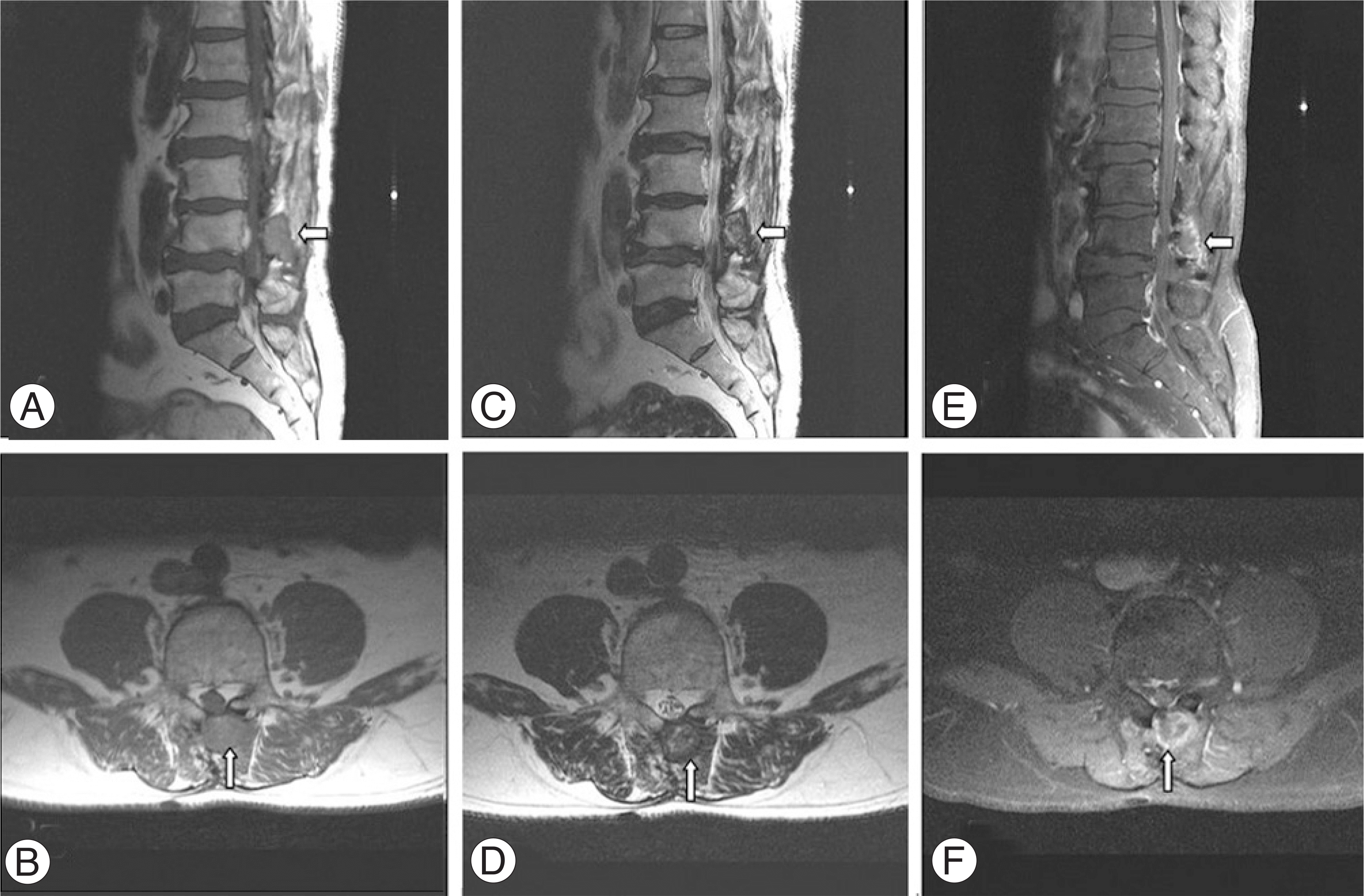 | Fig. 2.
(A) Sagittal and (B) axial T1 weighted images show paravertebral mass with an intermediate signal intensity (arrows). (C) Sagittal and (D) axial T2 weighted images show a high signal intensity within the center of the lesion and a low signal intensity within the peripheral rim (arrows). (E) Sagittal and (F) axial enhanced images reveal strong enhancement of the peripheral rim of the lesion (arrows). |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download