Abstract
An intradural extramedullary metastasis to the spinal nerve root across dura mater is extremely rare. The authors encountered a case 39-year-old man who suffered radiculopathy arising from a soft mass around nerve root mimicking a nerve sheath tumor compressing the 4th lumbar nerve root in the right intervertebral foramen between the 4th and 5th lumbar spine. After an excisional biopsy, the metastatic infiltration of adenocarcinoma was confirmed pathologically. The primary lesion was found to be an intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with multiple metastases. This report suggests that an intradural metastatic tumor can show similar clinical and radiographic findings to other disease,s such as a nerve sheath tumor. The results also suggest that proper diagnosis and further treatment are possible only by pathological confirmation after and excisional biopsy.
REFERENCES
1). Edelson RN, Deck MD, Posner JB. Intramedullary spinal cord metastasis. Clinical and radiologic findings in 9 cases. Neurology. 1972; 22:1222–1231.
2). Barron KD, Hirano A, Araki S, Terry RD. Experience with metastatic neoplasms involving the spinal cord. Neurology. 1959; 9:91–106.
3). Strang RR. Metastatic tumors of the cervical spinal cord. Med J Aust. 1962; 49:205–206.
4). Okamoto H, Shinkai T, Matsuno Y, Saijo N. Intradural parenchymal involvement in the spinal subarachnoid space associated with primary lung cancer. Cancer. 1993; 72:2583–2588.

5). Barolat-Romana G, Benzel EC. Spinal intradural extraarachnoid metastasis. Surg Neurol. 1983; 19:137–143.

6). Kim P, Ebersold MJ, Onofrio BM, Quast LM. Surgery of spinal nerve schwannoma. Risk of neurological defecit after resection of involved root. J Neurosurg. 1989; 71:810–814.
Fig. 1.
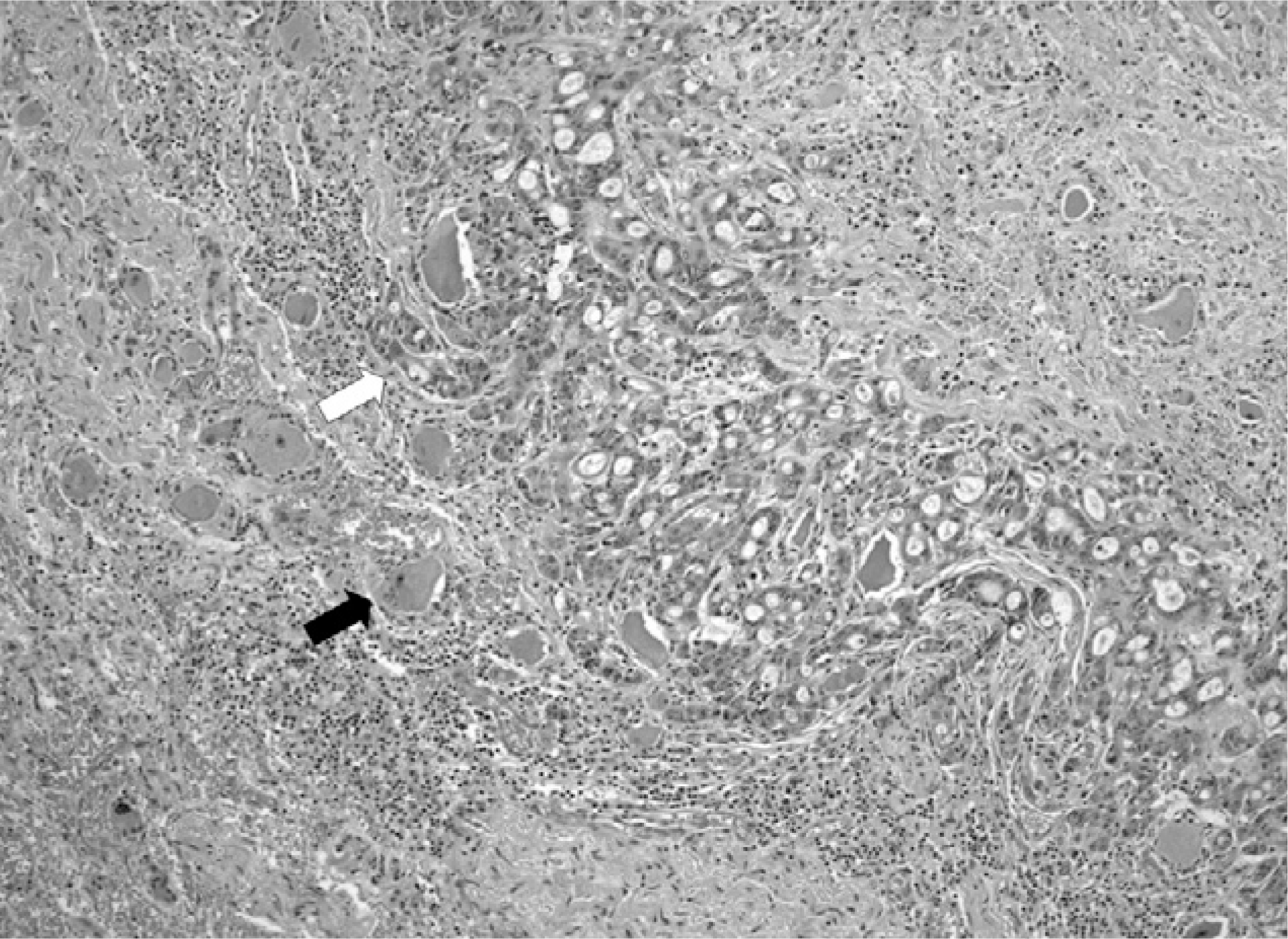
Findings of Magnetic Resonance Imaging. A. Axial T2-weighted image (TR 3500/TE107) is showing a right-sided fusiform shaped spinal nerve root mass (arrow) with intermediate signal intensity compressing spinal nerve. B. Sagittal T1-weighted image (TR 300/TE 10) is showing isointense mass (arrow) enlarging intervertebral neural foramen. C-D. Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted fat suppression axial (TR 467/TE 10) and sagittal (TR 350/TE 9) images are showing highly enhancing mass (arrow) with internal cystic or necrotic portion.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download