Abstract
Objectives
To compare the changes of dimensions of the intervertebral disc and neural foramen between the anterior lumbar interbody fusion and the posterolateral fusion in the lumbar spine.
Summary of Literature Review
There are few reports comparing an anterior lumbar interbody fusion with pedicle screw fixation and a posterolateral fusion with pedicle screw fixation.
Materials and Methods
We studied 62 patients with degenerative lumbar diseases who underwent minimal anterior lumbar interbody fusion with pedicle screw fixation (group I, 40 patients) or who underwent posterolateral fusion with pedicle screw fixation (group II, 22 patients). We measured the height of disc and the height, width, and area of the neural foramen measured in 1-mm reconstructive sagittal images of computed tomography before and 6 months after the operation. The factors were independently measured by three different observers.
Results
Disc height was increased by a mean of 39.1±3.28% in group I and 3.1±2.99% in group II. The height of the neural foramen was increased by a mean of 18.7±4.21% in I and 1.0±2.34% in II. The area of neural foramen was increased by a mean of 21.5±3.50% in I and -2.1±4.39% in II, with significant differences between groups in all parameters.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Dennis S, Watkins R, Landaker S, Dillin W, Springer D. Comparison of disc space heights after anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine. 1989; 14:876–878.

2). Kirkaldy-Willis WH. The relationship of structural pathology to the nerve root. Spine. 1984; 9:49–52.

3). Crock HV. Normal and pathological anatomy of the lumbar spinal nerve root canals. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1981; 63:487–490.

4). An HS, Glover JM. Lumbar spinal stenosis: Historical perspective, classification, and pathoanatomy. Semin Spine Surg. 1994. 67–77.
5). Giles LG, Kaveri MJ. Some osseous and soft tissue caus-es of human intervertebral canal (foramen) stenosis. J Rheumatol. 1990; 17:1474–1481.
6). Panjabi M, Takata K, Goel V. Kinematics of lumbar intervertebral foramen. Spine. 1983; 8:348–357.

8). Lane JD, Moore ES. Transperitoneal approach to the intervertebral disc in the lumbar area. Annals Surg. 1948; 127:537–551.
9). Kim NH, Lee JW. Anterior interbody fusion versus posterolateral fusion with transpedicular fixation for isthmic spondylolisthesis in adults. Spine. 1999; 24:812–816.

10). Suk KS, Jeon CH, Lee HM, Kim NH, Kim HC. Comparison between posterolateral fusion with pedicle screw fixation and anterior interbody fusion in spondylolytic spodylolisthesis of the lumbar spine. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 1999; 6:397–406.
11). Hasegawa T, An HS, Haughton VM, Nowicki BH. Lumbar foraminal stenosis: Critical heights of the intervertebral discs and foramina: A cryomicrotome study in cadavera. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995; 77:32–38.
12). Stephens MM, Evans JH, O'Brien JP. Lumbar intervertebral foramens: An in vitro study of their shape in relation to intervertebral disc pathology. Spine. 1991; 16:525–529.
13). Inufusa A, An HS, Glover JM, McGrady L, Lim TH, Riley LH 3rd. The Ideal Amount of Lumbar Foraminal Distraction for Pedicle Screw Instrumentation. Spine. 1996; 21:2218–2223.

14). Chen D, Fay LA, Lok J, Yuan P, Edwards WT, Yuan HA. Increasing neuroforaminal volume by anterior interbody distraction in degenerative lumbar spine. Spine. 1995; 20:74–79.

15). Mayoux-Benhamou MA, Revel M, Aaron C, Chomette G, Amor B. A morphometric study of the lumbar foramen. Influence of flexion-extension movements and of iso-lated disc collapse. Surg. and Radiol. Anat. 1989; 11:97–102.
16). Shirado O, Zdeblick TA, McAfee PC, Warden KE. Biomechnical evaluation of methods of posterior stabilization of the spine and posterior lumbar interbody arthrodesis for lumbosacral isthmic spondylolisthesis: A calf-spine model. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991; 73:518–526.
17). Inoue S, Watanabe T, Goto S, Tanahashi K, Takata K, Sho E. Degenerative spondylolisthesis: Pathophysiology and results of anterior interbody. Clin Orthop. 1988; 227:90–102.
Go to : 
Figures and Tables%
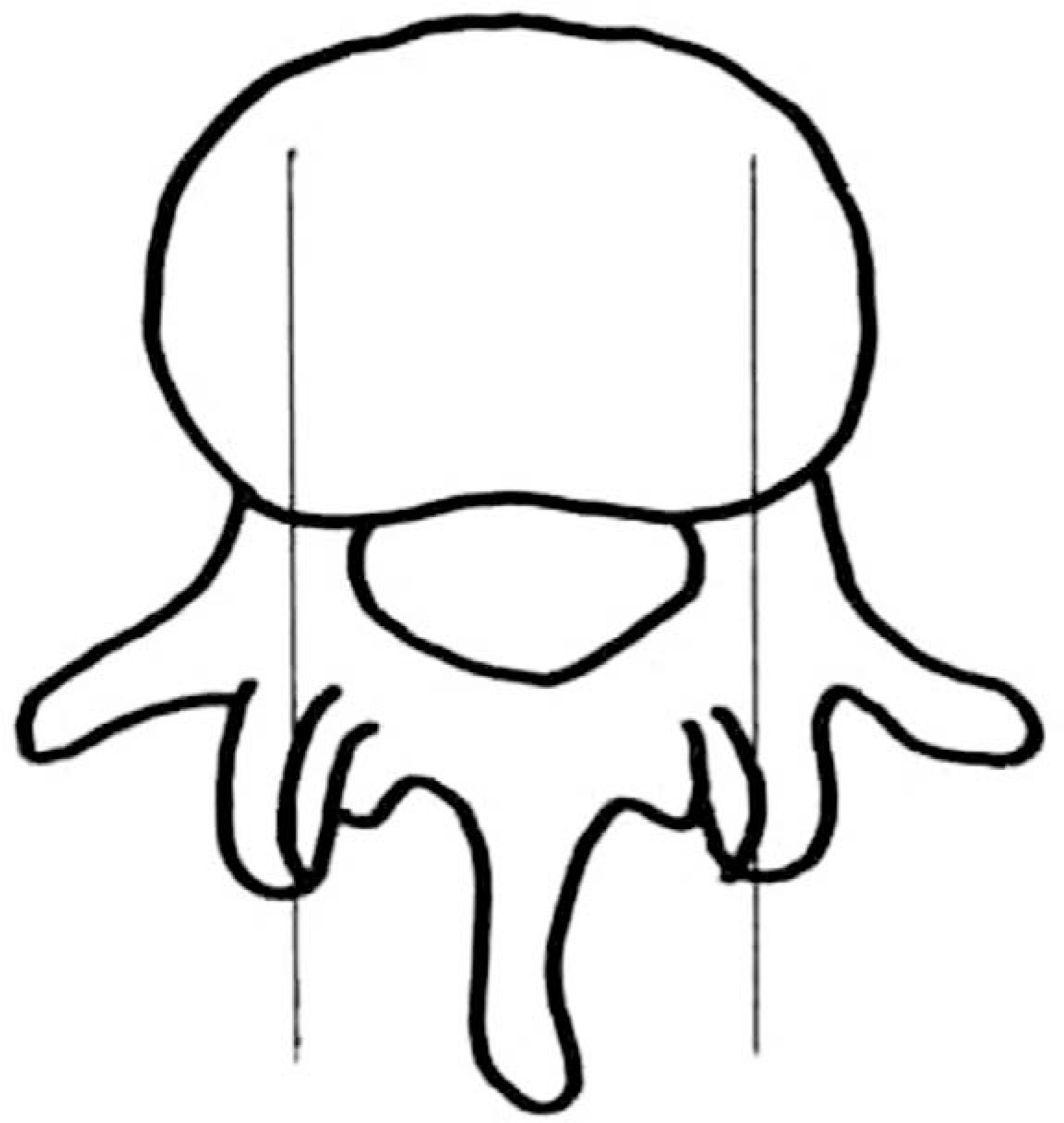 | Fig. 1.Schematic picture for CT measurement were done via sagittal reconstruction at the level of the mid pedicle on axial CT cut |
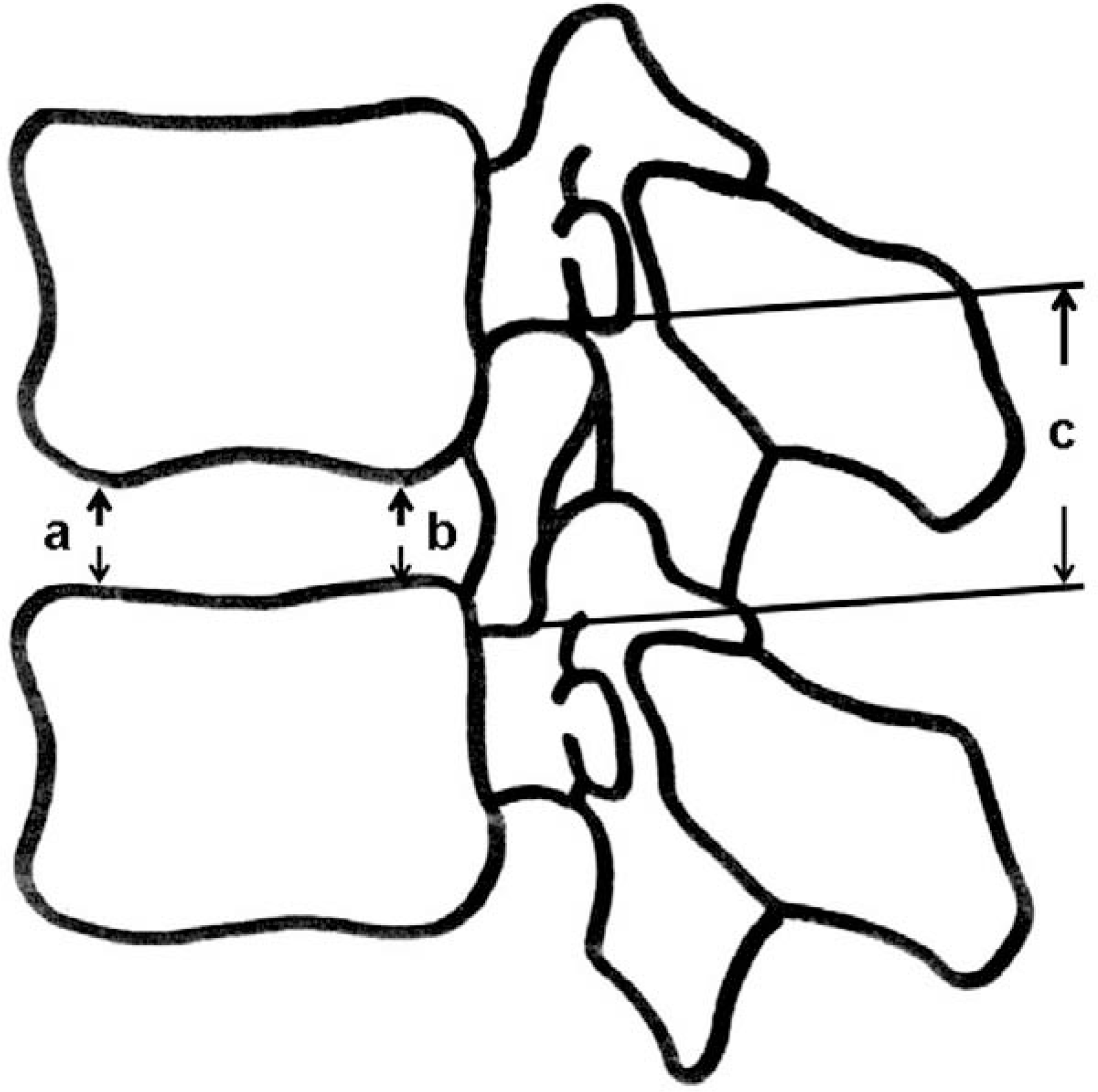 | Fig. 2.Diagram showing the measurements made on the discs and neuroforamina. a : anterior disc height, b : posterior disc height, c : neuroforminal height |
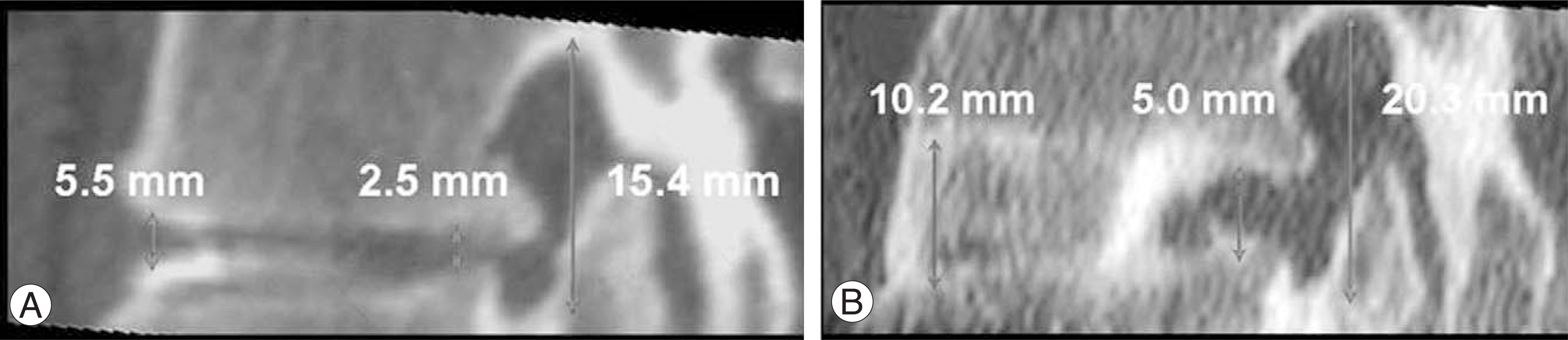 | Fig. 3.A 62-year-old woman with spinal stenosis on L4-5 that treated anterior interbody fusion with pedicle screw fixation. (A) Left side sagittal reconstruction image of preoperative CT scan (B) Left side sagittal reconstruction image of seven-month postoperative CT scan shows marked increase of the disc height, width and area of neural foramen. |
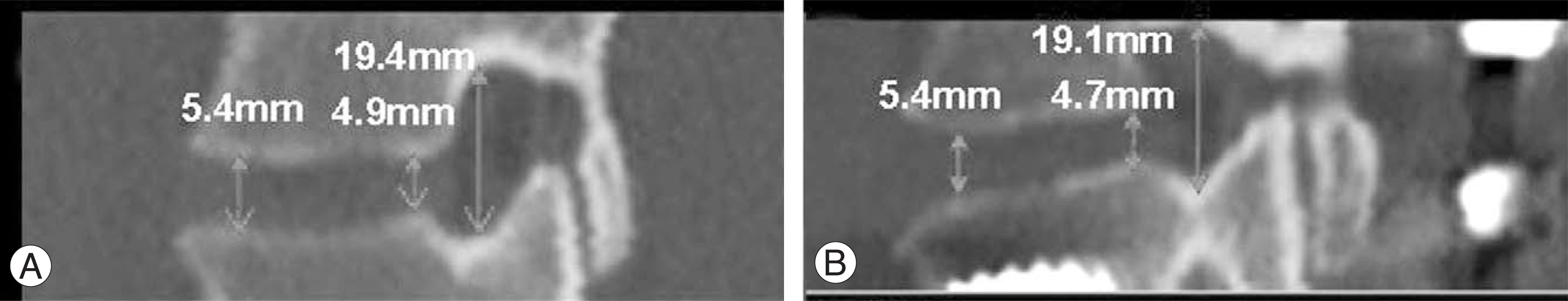 | Fig. 4.A 65-year-old woman with spinal stenosis on L4-5 that treated posterolateral fusion with pedicle screw fixation. (A) Left side sagittal reconstruction image of preoperative CT scan (B) Left side sagittal reconstruction image of six-month postoperative CT scan shows slight decrease of the posterior disc height, width and area of neural foramen. |
Table 1.
Changes of anatomical parameters and statistical results by paired t-test after anterior interbody fusion with pedicle screw fixation or posterolateral fusion with pedicle screw fixation.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download