Abstract
Objectives
The aim of this study was to analyze the long term followup results of the isthmic spondylolisthesis patients who had been treated with pedicle screw fixation and fusion, and were followed up for more than 5 years. An attempt was made to determine the differences between posterior lumbar interbod fusion(PLIF) and posterolateral fusion (PLF).
Summary of Literature Review
The surgical treatment of isthmic spondylolisthesis has developed markedly after the introduction of spine fusion and pedicle screw fixation. However, the longterm prognosis after such treatments has not been investi-gated sufficiently.
Materials and Methods
Among 53 patients, 38(72%) patients were examined more than 5 years after surgery. The clinical results were evaluated according to Kim's criteria. Radiologically, the degree of slippage and disc height was measured. The changes in the adjacent segments were also observed.
Results
PLIF was performed in 26 patients and PLF was performed in 12 patients. In the PLIF group, the clinical results were ‘excellent’ in 15 patients, ‘good’ in 8, ‘fair’ in 2, and ‘poor’ in 1. In the PLF group, the results were ‘excellent’ in 8 patients, ‘good’ in 2, ‘fair’ in 1, and ‘poor’ in 1. According to the fusion method, a satisfactory outcome was obtained in 89% of patients in the PLIF group, and 83% in the PLF group, without any statistically significant differences. Radiological analysis was available in 28(52.8%) patients. There were no statistically significant differences between the PLIF and PLF groups in terms of the reduction and maintenance of slippage and the disc height.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Jacobs WC, Vreeling A, De Kleuver M. Fusion for low-grade adult isthmic spondylolisthesis: a systematic review of the literature. Eur Spine J. 2006; 15:391–402.

2). Carragee EJ. Single-level posterolateral arthrodesis, with or without posterior decompression, for the treatment of isthmic spondylolisthesis in adults. A prospective, randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997; 79:1175–1180.

3). Deguchi M, Rapoff AJ, Zdeblick TA. Posterolateral fusion for isthmic spondylolisthesis in adult: analysis of fusion rate and clinical result. J Spinal Disord. 1998; 11:459–464.
4). De Loubresse CG, Bon T, Deburge A, Lassale B, Benoit M. Posterolateral fusion for radicular pain in isthmic spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996; 323:194–201.

5). Kim NH, Kim DJ. Anterior interbody fusion for spondylolisthesis. Orthopedics. 1991; 14:1069–1076.

6). Taillard W. Spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents. Acta Orthop Scand. 1954; 24:115–144.
7). Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Bullis D, Betz RR, Baldus C, Schoenecker PL. Results of in situ fusion for isthmic spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disorder. 1992; 5:433–442.

8). Hashimoto T, Shigenobu K, Kanayama M, Harada M, Oha F, Ohkoshi Y, Tada H, Yamamoto K, Yamane S. Clinical Results of single-level posterior lumbar interbody fusion using the Brantigan I/F carbon cage filled with a mixture of local morselized bone and bioactive ceramic granules. Spine. 2002; 27:258–262.

9). Esses SI, Natout N, Kip P. Posterior interbody arthrodesis with a fibular strut graft in spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995; 77:172–176.

11). Suk SI, Lee CK, Kim WJ, Lee JH, Cho KJ, Kim HG. Adding posterior lumbar interbody fusion to pedicle screw fixation and posterolateral fusion after decompression in spondylolytic spondylolisthesis. Spine. 1997; 22:210–220.

12). Stauffer RN, Coventry MB. Posterolateral lumbar spine fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1972; 54:1195–1204.
13). Herkowitz HN, Kurz LT. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis. A prospective study com-paring decompression with decompression and intertransverse process arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991; 73:802–808.

14). Rothman RH, Simeone FA. The surgical treatment of spondylolisthesis in adult in the spine. 3rd ed.Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co:;1992. p. 913–969.
16). Kuslich SD. Lumbar interbody cage fusion for back pain. Spine. 1999; 13:295–311.
17). Madan S, Boeree NR. Outcome of posterior lumbar interbody fusion versus posterolateral fusion for spondylolytic spondylolisthesis. Spine. 2002; 27:1536–1542.

18). Inamdar DN, Alagappan M, Shyam L, Devadoss S, Devadoss A. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion versus intertransverse fusion in the treatment of lumbar spondylolisthesis. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2006; 14:21–26.

19). La Rosa G, Conti A, Cacciola F, et al. .:. Pedicle screw fixation for isthmic spondylolisthesis: does posterior lumbar interbody fusion improve outcome over posterolateral fusion? J Neurosurg. 2003; 99:143–150.

20). Kumar MN, Jacquot F, Hall H. Longterm followup of functional outcomes and radiographic changes at adjacent levels following lumbar spine fusion for degenerative disc disease. Eur spine J. 2001; 10:309–313.

21). Rahm MD, Hall BB. Adjacent-segment degeneration after lumbar fusion with instrumentation; a retrospective study. J Spinal Disord. 1996; 9:392–400.
Go to : 
Figures and Tables%
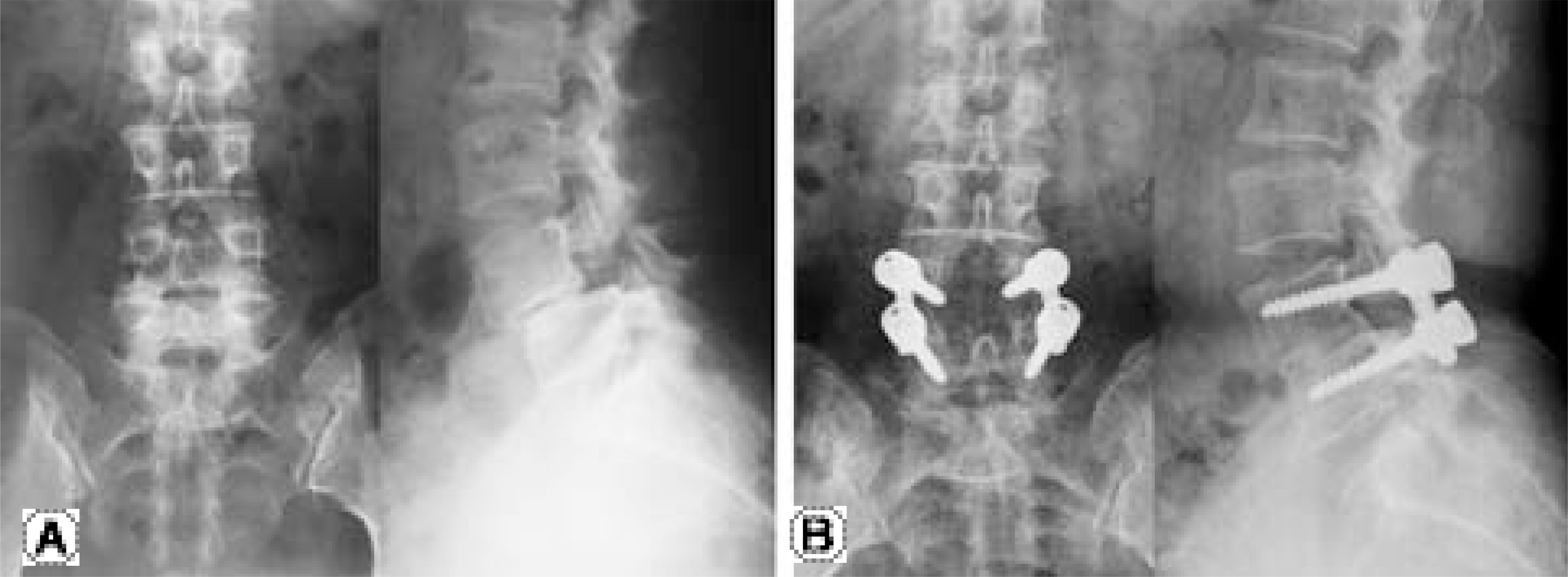 | Fig. 1.Preoperative and final followup anteroposterior and lateral radiograph in a 47-year-old woman. (A) Isthmic spondylolisthesis was found at L4. (B) Nine year after surgery, plain radiographs shows maintenance of correction and solid posterolateral fusion mass. |
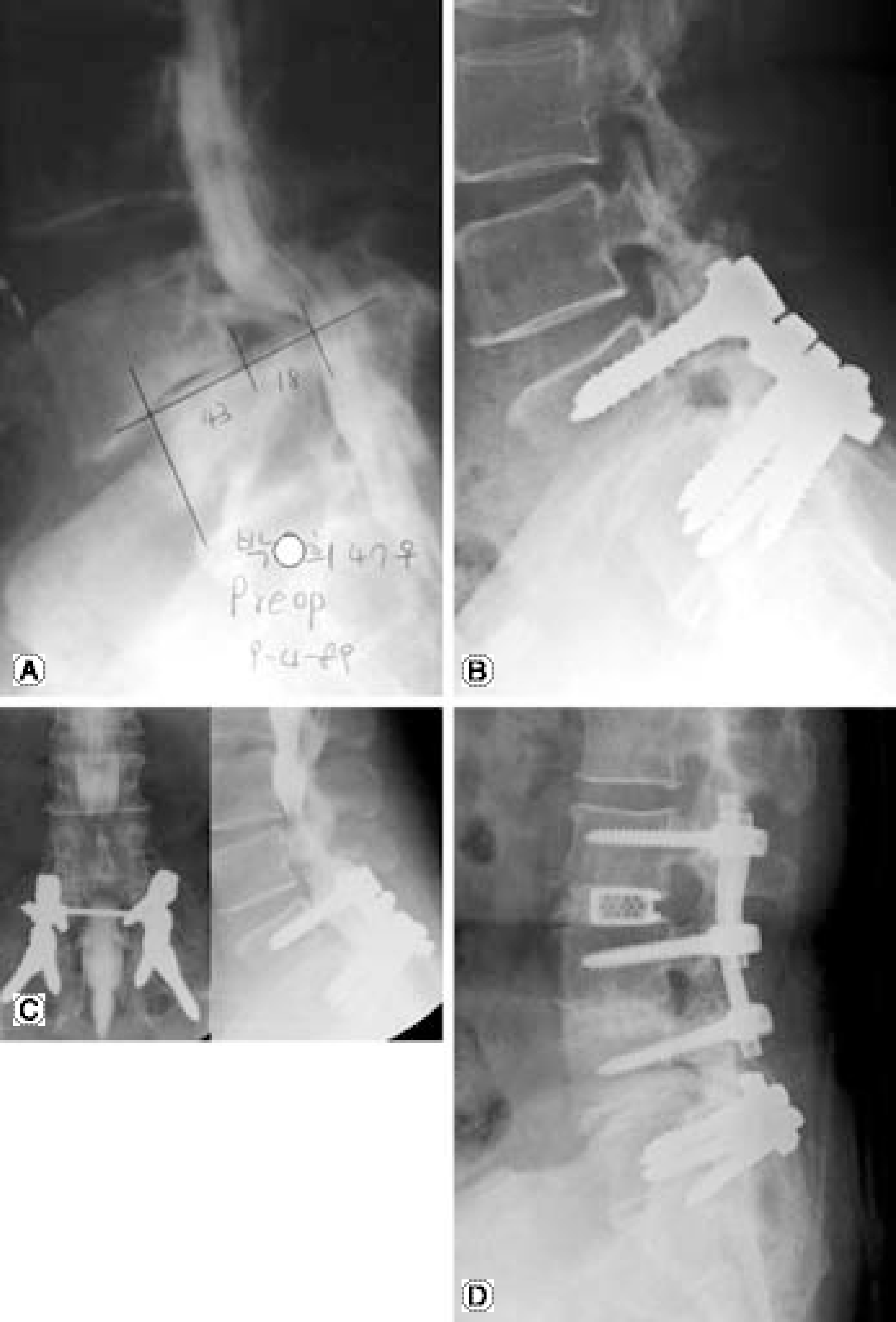 | Fig. 2.(A) Initial myelogram of a 57-year-old woman with spondylolytic spondylolisthesis L5 on S1. (B) Lateral radiograph at 12 year followup shows maintenance of correction. (C) Anteroposterior and lateral myelogram at 14 year followup shows stenosis of L3-4, L4-5. (D) At the revision surgery, decompression and interbody fusion was extended to the L3-4 and L4-5 level without removing S1 and sacral alar screws. |
Table 1.
Criteria for clinical result (by Kim's)
Table 2.
Data of 28 patients who were followed more than 5 years by radiographs
Table 3.
Clinical results
| PLIF (%) (n=26) | PLF (%) (n=12) | |
|---|---|---|
| Excellent | 15(57.7%) | 8(66.7%) |
| Good | 18(30.8%) | 2(16.7%) |
| Fair | 12(37.7%) | 1(38.3%) |
| Poor | 11(33.8%) | 1(38.3%) |
Table 4.
Change of slip percentage
| Preop. | Imm. PO. | Final | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLIF (n=20) | 23.1±17.0% | 10.2±5.3% | 12.2±5.6% |
| PLF (n=8) | 22.7±11.3% | 19.3±5.8% | 12.7±7.4% |
| Total (n=28) | 23.0±18.1% | 19.9±5.3% | 12.4±6.0% |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download