Abstract
Objectives
To investigate and report the iatrogenic form of spinal infections that occur after injection therapy in the spine.
Summary of Literature Review
An iatrogenic infection after injection therapy in the spine is rarely reported to be a serious complication. However, an increase in the number of immunocompromised patients, the aging of the population, and particularly an increase in spinal procedureshave precipitated a rise in the incidence of spinal infections.
Materials and Method
Iatrogenic spinal infections occurred in 8 patients after various injection therapy in the spine, which included an epidural steroid injection or trigger point injection for various spinal conditions. The medical records and images of these patients regarding the clinical findings, risk factors, and treatments were analyzed.
Results
The pathologic conditions of the spinal infection were discitis in four patients with a concomitant infection in the epidural space and paraspinal muscles, an epidural abscess, and solitary muscular abscess or myositis in the other 3 patients. The systemic risk factors contributing to the infections were diabetes mellitus, metastatic cancer, and chronic liver disease in four patients. For treatment, intensive antibiotic therapy was applied to all patients. Six of the 8 patients underwent surgical drainage for abscesses and/or fusion to stabilize the infected segments. The infections were eventually controlled in all patients.
Conclusion
Iatrogenic pyogenic infections of the spine after injection therapy in the spine is a serious complication with regard morbidity and treatment. To avoid these serious complications, a specialist experienced in aseptic techniques should perform these spinal procedures, particularly in those patients with the risk factors.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Brodsky AE, Binder WF. Lumbar discography-its value in diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc lesions. Spine. 1979; 4:110–120.
2). Massie WK, Stevans DB. A critical evaluation of discography. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1967; 49:1243–1244.
3). Fraser RD, Vernon-Roberts B, Osti OL. Iatrogenic discitis. (in Wiesel SW, Weinstein JN, Herkowitz H, Dvorak J, Bell G eds, The lumbar spine. 2nd ed.Philadelphia: Saunders;p. 899–916. 1996.
4). McCulloch JA. Chemoneucleolysis: Experiences with 2000 cases. Clin Orthop. 1980; 146:128–135.
5). Chan ST, Leung S. Spinal epidural abscess following steroid injection for sciatica: case report. Spine. 1989; 14:106–108.
6). Fernand R, Lee CK. Post laminectomy disc space infection: A review of the literature and a report of three cases. Clin Orthop. 1986; 209:215–218.
7). Currier LC, Eismont FJ. Infections of the spine. (in Herkowitz HN, Garfin SR, Balderston RA, Eismont FJ, Bell GR, Wiesel SW eds, Rothman-Simeone The spine. 4th ed.Philadelphia: Saunders;p. 1207–1258. 1999.
8). Mulholland R, McCall I. Magnetic resonance imaging of the lumbar spine. (in. Wiesel SW, Weinstein JN, Herkowitz H, Dvorak J, Bell G, editors. The lumbar spine. 2nd ed.Philadelphia: Saunders;p. 353–376. 1996.
9). Smith AS, Taylor TK. Infectious and inflammatory processes of the spine. Radiol Clin N Am. 1991; 29:809–827.
10). Lee JC, Doh HW, Cho YI, Kim KJ, Kim YI, Shin BJ. Pyogenic arthritis and paraspinal abscess following facet joint steroid injection. - A case report - J Kor Soc Spine Surg. 2003; 10:196–201.
11). Boden SD, David DO, Dina TS, Sunner JL, Wiesel SW. Postoperative diskitis: Distinguishing early MR imaging findings from normal postoperative disk space changes. Radiol. 1992; 184:765–771.

12). Bergman I, Wald ER, Meyer JD, Painter MJ. Epidural abscess and vertebral osteomyelitis following serial lumbar punctures. Pediatrics. 1983; 72:476–480.

13). Coapes CM, Roysam GS. Vertebral osteomyelitis secondary to epidural catheter use. Spine. 2001; 26:1492–1494.

14). Wheatherley CR, Jafferay D, Mehta M, O'Brien JP. Vertebral collapse following spinal anesthesia. Spine. 1991; 16:591–594.

15). Yue WM, Tan SB. Distant skip level discitis and vertebral osteomyelitis after caudal epidural injection: A case report of a rare complication of epidural injections. Spine. 2003; 28:E209–E211.

Go to : 
Figures and Tables%
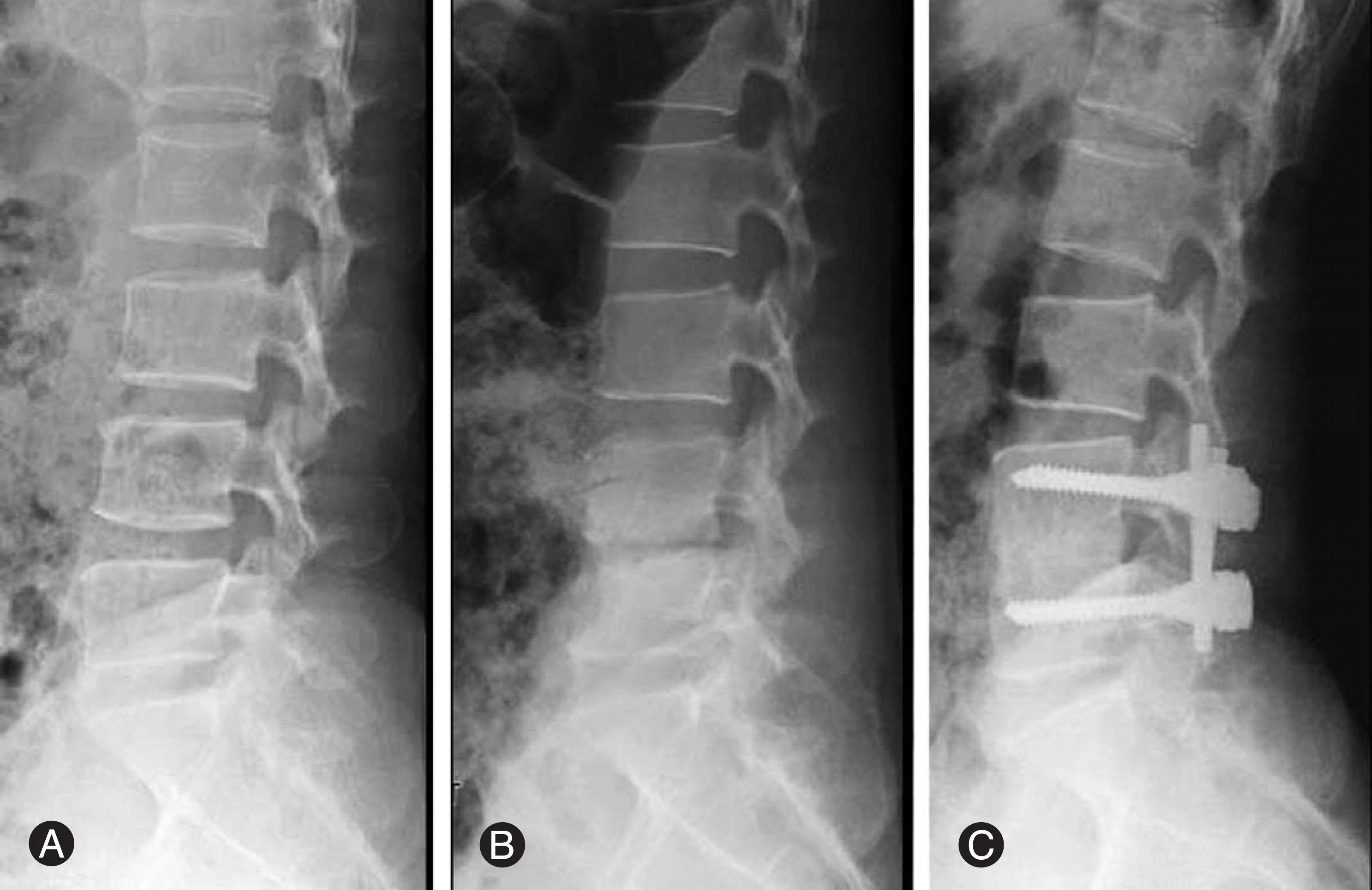 | Fig. 1.Case 7. A 35 years old female with disc herniation at L4-5, the initial radiograph (A) shows no narrowing of disc space. (B) Radiograph at 6 weeks after epidural steroid injections shows marked narrowing of disc space and blurring of end plates. (C) Good interbody fusion 17 months after anterior debridment and bone graft with internal fixation. |
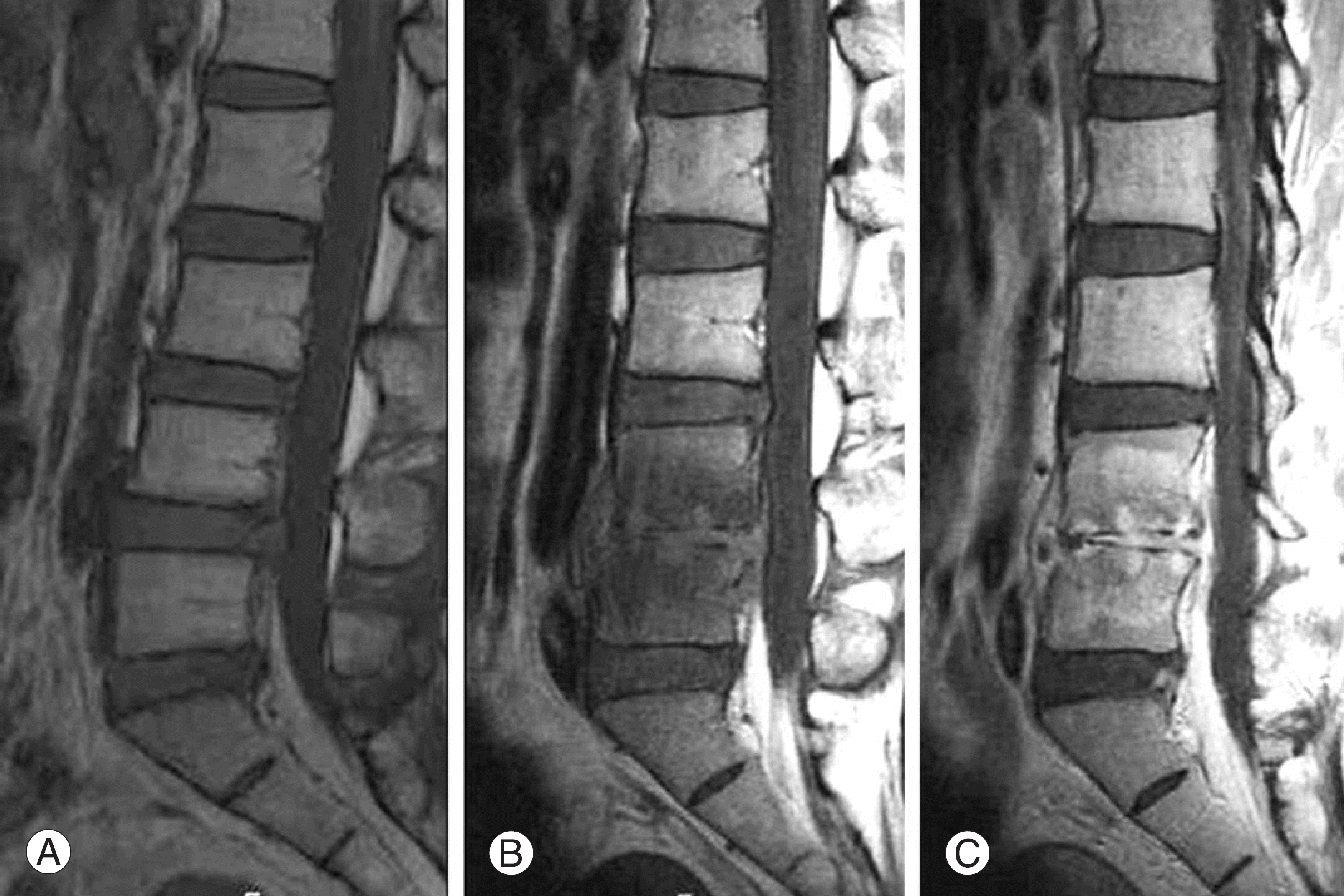 | Fig. 2.Case 7. Initial MRI (A) shows disc herniation at L4-5. 6 weeks after epidural steroid injections MRI shows low signal in the adjacent vertebral bodies at T1 weighted image (B) and high signal in adjacent vertebral bodies at enhanced image (C), sug-gesting discitis. |
Table 1.
Summary of Cases.
| No. | Age/Sex | Primary Diagnosis | Combined Disease | Injection Therapy | Blood Culture | Local Culture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 64/F | Degenerative | Hypertension | Epidural | Staph. | - - |
| spondylolisthesis | injection | aureus | ||||
| 2. | 73/F | Lumbar | Alcoholism & | Trigger point | E. Coli | E. Coli |
| sprain | Chronic hepatitis | injection | ||||
| 3. | 52/F | Metastatic | DM* & | Epidural | - - | Staph. |
| carcinoma | Renal cell Ca. | catheterization | aureus | |||
| 4. | 63/F | Degenerative | Hypothyroidism | Epidural | - - | Coagul.(-) |
| spondylolisthesis | injection | staph. | ||||
| 5. | 80/F | Degenerative | Hypertension | Epidural | Staph. | - - |
| spondylolisthesis | injection | aureus | ||||
| 6. | 63/F | Degenerative | DM* | Trigger point | Negative | Staph. |
| spondylolisthesis | injection | aureus | ||||
| 7. | 35/F | Disc | - - | Epidural | Negative | Negative |
| herniation | injection | |||||
| 8. | 58/M | Lumbar | DM* | Trigger point | Staph | Staph. |
| sprain | injection | aureus | aureus |
Table 2.
Summary of Cases.
| No. | Infection Site | Infection Pathology | Surgery | F/U |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Lower lumbar | Myositis | - - | 15 m |
| paraspinal | ||||
| 2. | Lower lumbar | Myositis & | Incision & | 18 m |
| paraspinal | Abscess | drainage | ||
| 3. | Upper lumbar | Epidural abscess | Laminectomy & | 5 m |
| drainage | ||||
| 4. | L4-5 | Discitis & | PL† fusion & | 24 m |
| Lower lumbar | Epidural infection | Int. fixation | ||
| 5. | L4-5 | Discitis & | - - | 25 m |
| Lower lumbar | Epidural infection | |||
| 6. | Lower lumbar | Myositis & | Incison & | 19 m |
| paraspinal | Abscess | drainage | ||
| 7. | L4-5 | Discitis | Ant. fusion & | 17 m |
| Int. fixation | ||||
| 8. | L5-S1 | Discitis & | Incison & | 12 m |
| Psoas muscle | Abscess | drainage |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download