Abstract
Objectives
The purpose of this study was to assess the clinical features and functional outcomes of patients having undergone percutaneous vertebroplasty, with bone cement, for an osteoporotic compression fracture.
Summary of Literature Review
The clinical result of percutaneous vertebroplasty is good and satisfactory. Percutaneous vertebroplasty is a useful treatment for an osteoporotic compression fracture of the vertebral body.
Materials and Methods
A mong 83 patients who underwent percutaneous vertebroplasty, with bone cement, between January 2000 and June 2001, 47 patients(79 vertebral bodies), followed- up for more than 3 years were selected; the mean followup period was 42.6 months. We compared the postoperative clinical and radiological findings immediately and at the 1, 2 and 3-year followups. The clinical outcomes were graded as excellent, good, fair, low and poor. The height of vertebral body, the leakage of bone cement and adjacent vertebral body fracture were also assessed. Statistical analyses were performed using Chi-squared and Student t- tests.
Results
The immediate postoperative clinical results were either excellent or good in 45 patients(95.7%). The last followup showed excellent or good results in 42 patients(89.4%). There was no statistically significance in connection with the followup duration (P>0.05). The heights of the vertebral bodies on plain radiographs were 78.0% immediately postoperation, and 76.5% at the last followups, with no statistically significant difference in the heights of the vertebral bodies on followup. Cement leakage was noted in 29(35.4%) out of the 79 vertebral bodies. In 4 patients(7 vertebrae), an additional compression fracture of adjacent vertebral bodies was found
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Gilbert P, Deramond H, Rosat P, Le Gars D. Note pril -iminaire sur le traitement des angiomes vertebraux per vertebroplastie acrylique percutanee. Neurochirurgie. 1987; 33:166–168.
2). Alvarez L, Perez-Higueras A, Quinones D, Calvo E, Rossi RE. Vertebroplasty in the treatment of vertebral tumors: postprocedural outcome and quality of life. Eur Spine J. 2003; 12:356–360.

3). Cho YS, Cho SD, Kim BS, Park TW, Cho SH. Percutaneous vertebroplasty on osteoporotic compressive vertebral fracture. J Kor Ortho Assoc. 2002; 37:13–18.
4). Gangi A, Guth S, Imbert JP, Marin H, Dietmann JL. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: indications, technique and results. Radiographics. 2003; 23:10.

5). Kim CH, Choi YJ, Baek SK, et al. Vertebroplasty on osteoporotic compression fracture. J Korean Fracture Soc. 2002; 15:124–128.

6). Barath K, Martin JB, Fasel HJ, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: method indications, results. Orv Hetil. 2003; 143:2469–2477.
7). Evans AJ, Jensen ME, Kip KE, et al. Vertebral compression fracture: pain reduction and improvement in functional mobility after percutaneous polymethylmethacrylate vertebroplasty retrospective report of 2455 cases. Radiology. 2003; 226:366–372.
8). Fiflueiredo N. Amaral Filho JC, Serra Ada R, Nogueira AM, Garcia VC, Weissheimer FL. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: option of treatment for osteoporotic vertebral fracture. Arq Neurosiquiatr. 2003; 61:625–630.
9). Goh LH, Tan SB, Liaw JS. Advances in surgical treatment of osteoporotic fracture of the spine. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2002; 31:623–630.
10). Hendritse CA, Kalmijn S, Voormolen MH, Verhaar HJ, Mali WP. Percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: review of the literature. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2003; 9:1553–1559.
11). Hoffmann RT, Jakobs TF, Wallnofer A, Reiser MF, Helmberger TK. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: indication, contraindications, and technique. Radiolote. 2003; 43:709–717.
12). Martinez-Quinone FR, Hernadez-Sanchez G. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: technique and early results in 25 procedures. Neurocirugia(Astur). 2003; 14:332–332.
13). Mehbod A, Aunoble S, Le Huec JC. Vertebroplasty for osteoporotic spine fracture: prevention and treatment. Eur Spine J. 2003; 12(Suppl 2):155–162.

14). Nakano M, Hirano N, Matsuura K, et al. Percutaneous transpedicular vertebroplasty with calcium phosphate cement in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression and burst fracture. J Neurosurg. 2002; 97:287–293.
15). Zoarski GR, Snow P, Olan WJ, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic compression fractures: quantitative prospective evaluation of long term outcome. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2002; 13:139–148.
16). Jensen ME. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: a new therapy for the treatment of painful vertebral body compression fractures. Am J Neuroradiol. 1999; 20:375–7.
17). Uppin AA, Hirsch JA, Centenera LV, Pfilfer BA, PAzianos AG, Choi IS. Occurrence of new vertebral body fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty in patients with osteoporosis. Radiology. 2003; 226:119–124.

18). Diamond TH, Champion B, Clark WA. Management of acute osteoporotic vertebral fracture (a nonrandomized trial comparing percutaneous vertebroplasty with conservative therapy). Am J Med. 2003. 57–265.
19). Perez-Higueras A, Alvarez L, Rossi RE, Quinones D, Al-Assir I. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: longterm clinical and radiological outcome. Neroradiology. 2002; 44:950–954.
20). Tsai TT, Chen WJ, Lai PL, et al. Polymethylmethacrylate cement dislodgement following percutaneous vertebroplasty: a case report. Spine. 2003; 28:457–460.
21). Yeom JS, Kim WJ, Choy WS, Lee CK, Chang BS, Kang JW. Leakage of cement in percutaneous transpedicular vertebroplasty for painful osteoporotic compression fractures. J Bone Joint Surg. 2003; 85(B):83–89.

22). Mousavi P, Roth S, Finkelstein J, Cheung G, Whyne C. Volumetric quantification of cement leakage following percutaneous vertebroplasty in metastatic and osteoporotic vertebrae. J Neurosurg. 2003; 99:56–59.

23). Shin KS, Kim JS, Lee DW. Surgical treatment of root injury after percutaneous vertebroplasty: case report. J Kor Spine Surg. 2002; 9:54–58.

24). Berlemann U, Ferguson SJ, Nolte LP, Heini PF. Adjacent vertebral failure after vertebroplasty. A biomechanical investigation. J Bone Joint Surg. 2002; 84(B):748–752.
Go to : 
Figures and Tables%
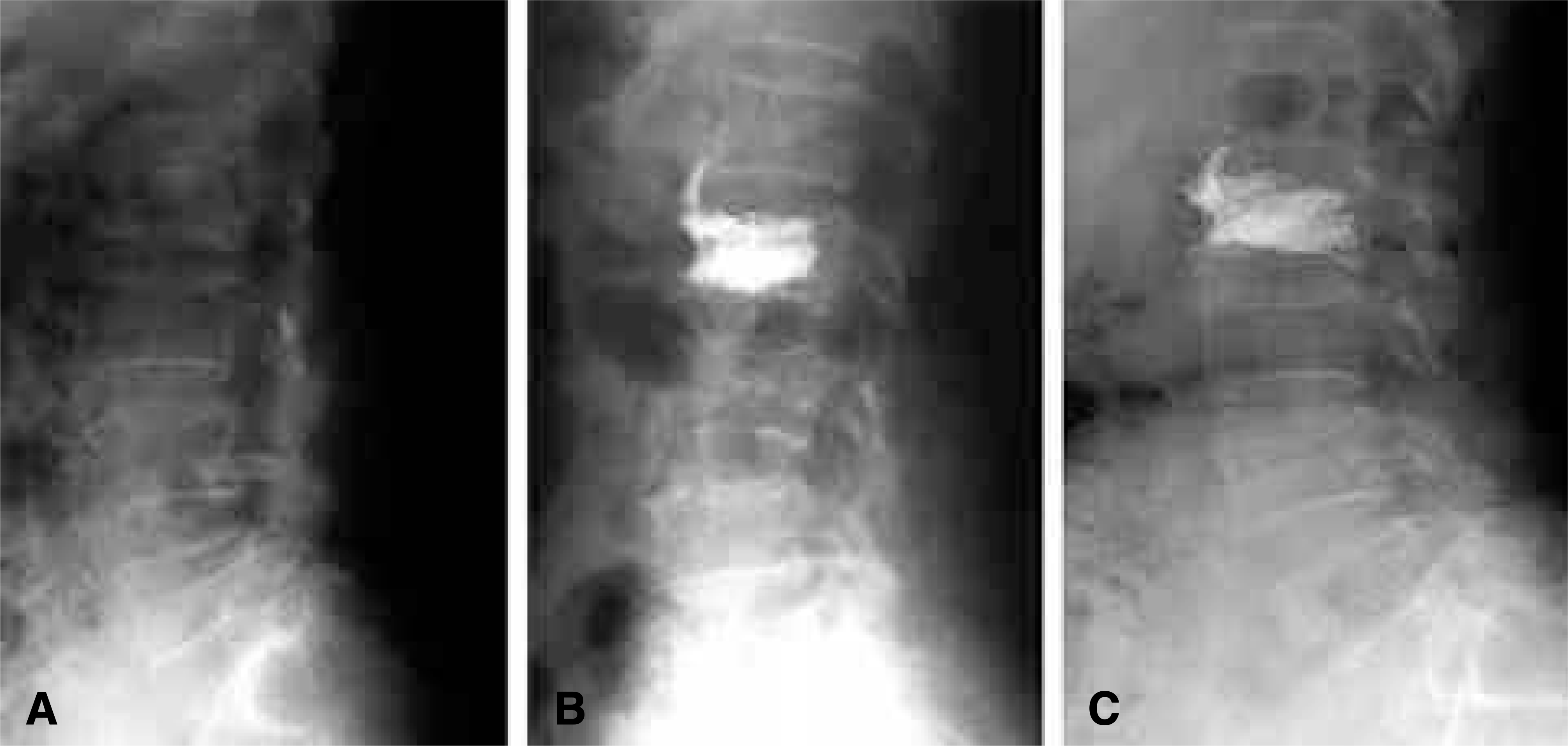 | Fig. 1.Simple lateral radiographs of 64 year-old female with L2 compression fracture. (A) Preoperative radiograph showed L2 compression fracture (75% of body height). (B) Postoperative radiograph showed percutaneous vertebroplasty on L2(95% of body height restoration). (C) Postoperative 3 year follow up radiograph showed no body collapse of cement injected vertebra. |
Table 1.
Clinical outcome
| F/u | Grading (n*) | Score | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Excellent | Good | Fair | Low | Poor | ||
| postop | 42 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 4.82 |
| 1 yr | 40 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 4.74 |
| 2 yr | 39 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 4.72 |
| 3 yr | 36 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 4.61 |
| (P>0.05) | ||||||




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download