Abstract
Study Design
A retrospective study to analyze the results of posterior lumbar interbody fusion, using laminar bone and titanium block, with pedicle screw instrumentation.
Objectives
To evaluate the clinical and radiological results of posterior lumbar interbody fusion, using laminar bone and titanium block, with pedicle screw instrumentation.
Summary of literature review: Several studies have demonstrated the results of posterior lumbar interbody fusion, there has been no report on our method.
Materials and Methods
From March 2001 to May 2002, seventeen patients were treated by posterior lumbar interbody fusion, using laminar bone block, from spinous process and titanium block. All patients were clinically followed up over 12 months. The mean age of the patients and followup were 58 years and 15 months, respectively. The clinical results were evaluated by Kim’s criteria and radiological union, and the subsidence of disc space and change of the lordotic curve were assessed by a simple X-ray.
Results
The satisfactory clinical result and radiological union rates were 83.3 and 90.4%, respectively. The mean subsidence of the disc space and change of the lordotic curve were 0.8 mm and 1.6 degrees, respectively. There was one complication of a wrong insertion of the pedicle screw to the disc space.
Conclusion
Posterior lumbar interbody fusion using laminar bone and titanium block showed an acceptable radiological union rate and clinical results. This could be a good alternative method for obtaining initial stability and bony union without taking a bone graft from the posterior ilium in various spinal lesions.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
2). Lin PM. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion: Complication and fitfalls. Clin Orthop. 1985; 193:90–102.
3). Brantigan JW, Steffee AD, Geiger JM. A carbon fiber implant to aid interbody fusion. Mechanical testing. Spine. 16(6 Suppl):S277–285. 1991.
4). Ma GW. Posterior lumbar interbody fusionwith special -ized instruments. Clin Orthop. 1985; 193:57–63.
7). Verlooy J, De Smedt K, Selosse P. Failure of a modified posterior lumbar interbody fusion technique to produce adequate pain relief in isthmic spondylolytic grade I spondylolisthesis patients. Spine. 1993; 18:1491–1495.
8). Shin BJ, Kim KJ, Kwon H, Seo YS, Kim YI, Na SK. Results of PLIF using laminar chips in spinal lesions. J Korean Spine Surg. 1998; 2:284–292.
9). Takeda M. Experience in posterior lumbar interbody fusion: Unicortical versus bicortical autologous grafts. Clin Orthop. 1985; 193:120–126.
10). Schlegel KF, Pon A. The biomechanics of posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) in spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop. 1985; 193:115–119.

11). Shin BJ, Kim KJ, Ha SS, Jung SH, Kwon H, Kim YI. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion using laminar bone block, J Korean Spine Surg. 1999; 6:110–116.
12). Kim SS, Denis F, Lonstein JE, Winter RB. Factors affecting fusion rate in adult spondylolisthesis. Spine. 1990; 15:979–984.

13). Hutter CG. Posterior intervertebral fusion. A 25-year study. Clin Orthop. 1983; 179:86–96.
14). Lin PM, Cautilli RA, Joyce MF. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Clin Orthop. 1985; 193:57–63.

15). Simmons JW. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion with posterior elements as chip graft. Clin Orthop. 1985; 193:85–89.
18). Loguidice VA, Johnson RG, Guyer RD, Stith WJ, Ohnmeiss DD. Anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine. 1988; 13:336–369.

19). Denis S, Watkins R, Landaker S, Dillin W, Springer D. Comparison of disc space heights after anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine. 1988; 14:876–878.

20). Nasca RJ, Montgomery RD, Moeini SM, Lemons JE. Intervertebral spacer as an adjunct to anterior lumbar fusion. J Spinal Disord. 1988; 11:136–141.
Go to : 
Figures and Tables%
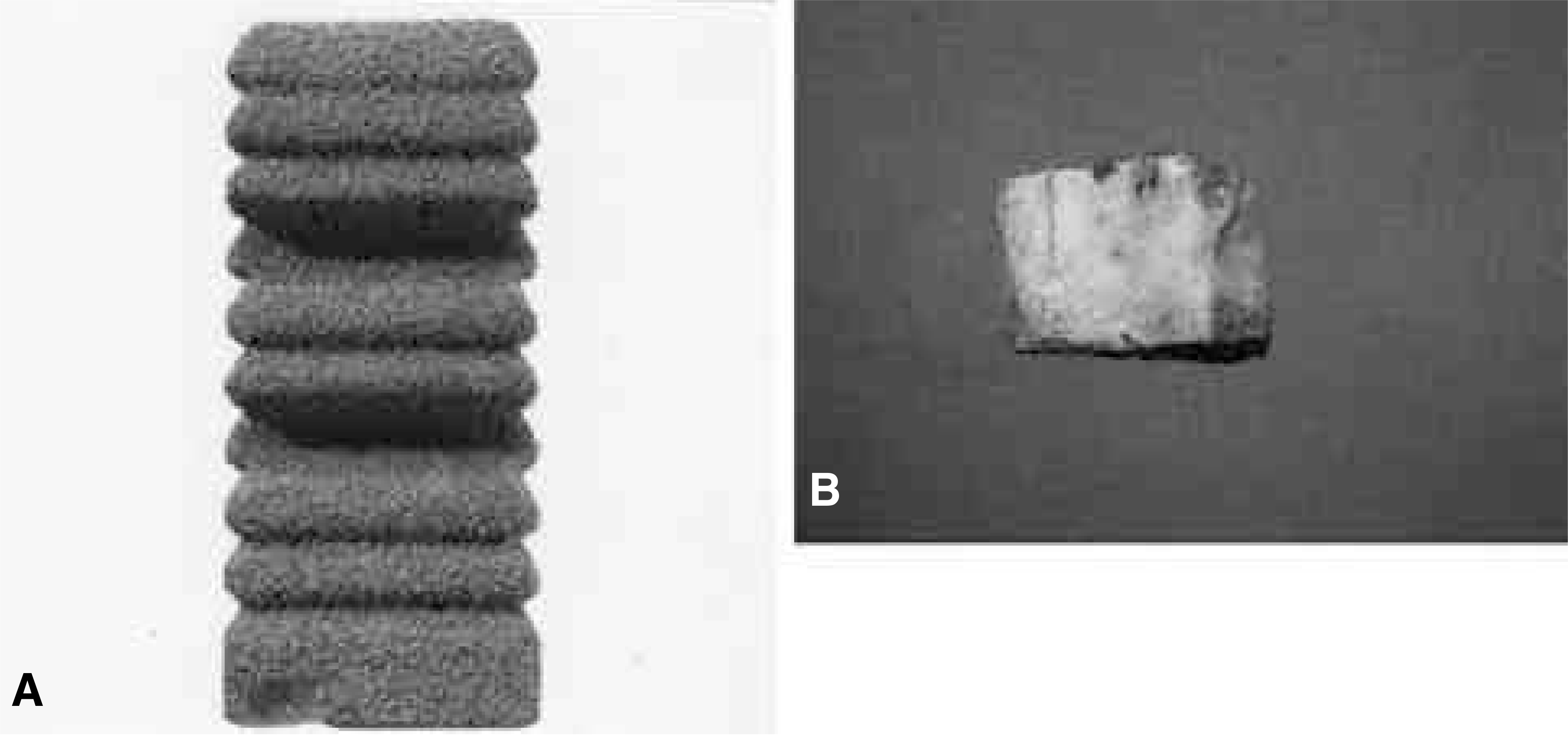 | Fig. 1.(A) Photograph showing titanium block (Prospace). (B) Photograph showing en bloc osteotomized lamina and spinous process with removal of soft tissue. |
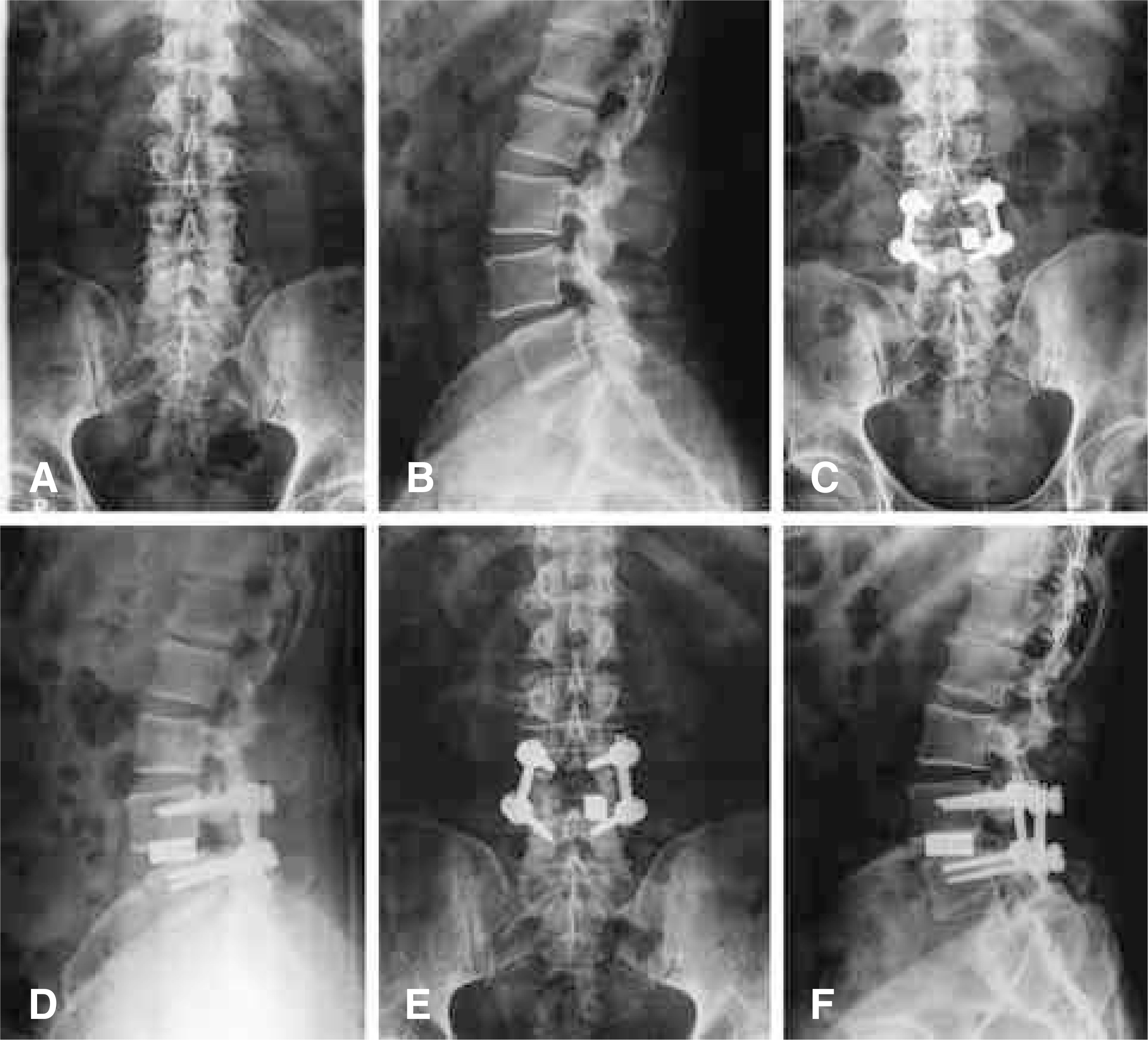 | Fig. 2.A 55-year-old male patient with spondylolisthesis L4 on L5 (case 10). (A, B) Preoperative anteroposterior and lateral roentgenograms showing anterior slippage of L4. (C, D) Postoperative anteroposterior and lateral roentgenograms shows well fixed graft and titanium block with maintaining of intervertebral disc space and reduction of spondylolisthesis. (E, F) Roentgenograms at the final followup showing complete union without settlement. Clinically the patient achieved an excellent result. |
Table 1.
The results of PLIF using Laminar Bone Block and Titanium Block.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download