Abstract
Objectives
The correct discrimination of a compressed root is very important for proper decompression. With a foraminal disc herniation, the cephalad root is compressed. The diagnostic importance of the clinical and radiological findings was investigated.
Summary of literature Review
A compressed root, due to a herniated disc, is known as a caudal root (i. e. L5 root compressed by L4- 5 disc herniation). In some cases, a prolapsed disc may compress the cephalad root, resulting in a difficult diagnosis.
Material and Method
The medical records, plain X - ray and MRI of 17 patients were reviewed, and the physical examination and MRI findings were carefully evaluated to retrospectively document the efficacy of the diagnoses. Every MRI image of each patient was graded according to the 4 point ranking system of diagnostic efficacy devised by the authors. The clinical outcomes and postoperative complications were also investigated.
Results
Ten, 5 and 2 of the 17 patients had L4- 5, L5- S1 and L3- 4 foraminal disc herniations, respectively. Eight of 10 L4- 5 cases showed a positive femoral nerve stretching test. The knee jerk reflex was diminished in 7 patients, with bilateral hypore-flexia in the other 3. The bodycut axial MRI image was the most effective, and the coronal images were also very helpful, whereas the routine axial images were of least value. Most cases achieved a satisfactory clinical result.
Conclusions
Foraminal disc herniations seem to be reasonably common. For the accurate discrimination of a compressed root, a thorough physical examination seems to be very important. When MRI is performed for these cases, in addition to routine studies, the bodycut axial and coronal MRI images are effective and useful, and their use is strongly recommended.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Bronx NY. Foraminal and far lateral lumbar disc herniations: surgical alternatives outcome measures. Spinal Cord. 2002; 40(10):491–500.
2). Darden BV, Wade JF, Alexander R, Wood KE. Far lateral disc herniations treated by microscopic fragment excision. Techniques and results. Spine. 1995; 20(13):1500–5.
3). Greiner-Perth R, Bohm H, Allam Y. A new technique for the treatment of lumbar far lateral disc herniation: technical note and preliminary results. Eur Spine J. 2003; 12(3):320–4.

5). Lauder TD. Physical examination signs, clinical symptoms, and their relationship to electrodiagnostic findings and the presence of radiculopathy. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2002; 13(3):451–67.

6). Maroon JC, Kopitnik TA, Schulhof LA, Abla A. D iag -nosis and microsurgical approach to far-lateral disc herniation in the lumbar spine. J Neurosurg. 1990; 72(3):378–82.
7). Ozveren MF, Bilge T, Barut S, Eras M. C ombined approach for far-lateral lumbar disc herniation. Neurol Med Chir. 2004; 44(3):118–22.
8). Porchet F, Chollet-Bornand A, Tribolet N. L ong-term follow up of patients surgically treated by the far-lateral approach for foraminal and extraforaminal lumbar disc herniations. Neurosurg Spine. 1999; 90(1):59–66.
9). Rust MS, Olivero WC. Far-lateral disc herniations: the results of conservative management. J Spinal Disord. 1999; 12(2):138–40.
Go to : 
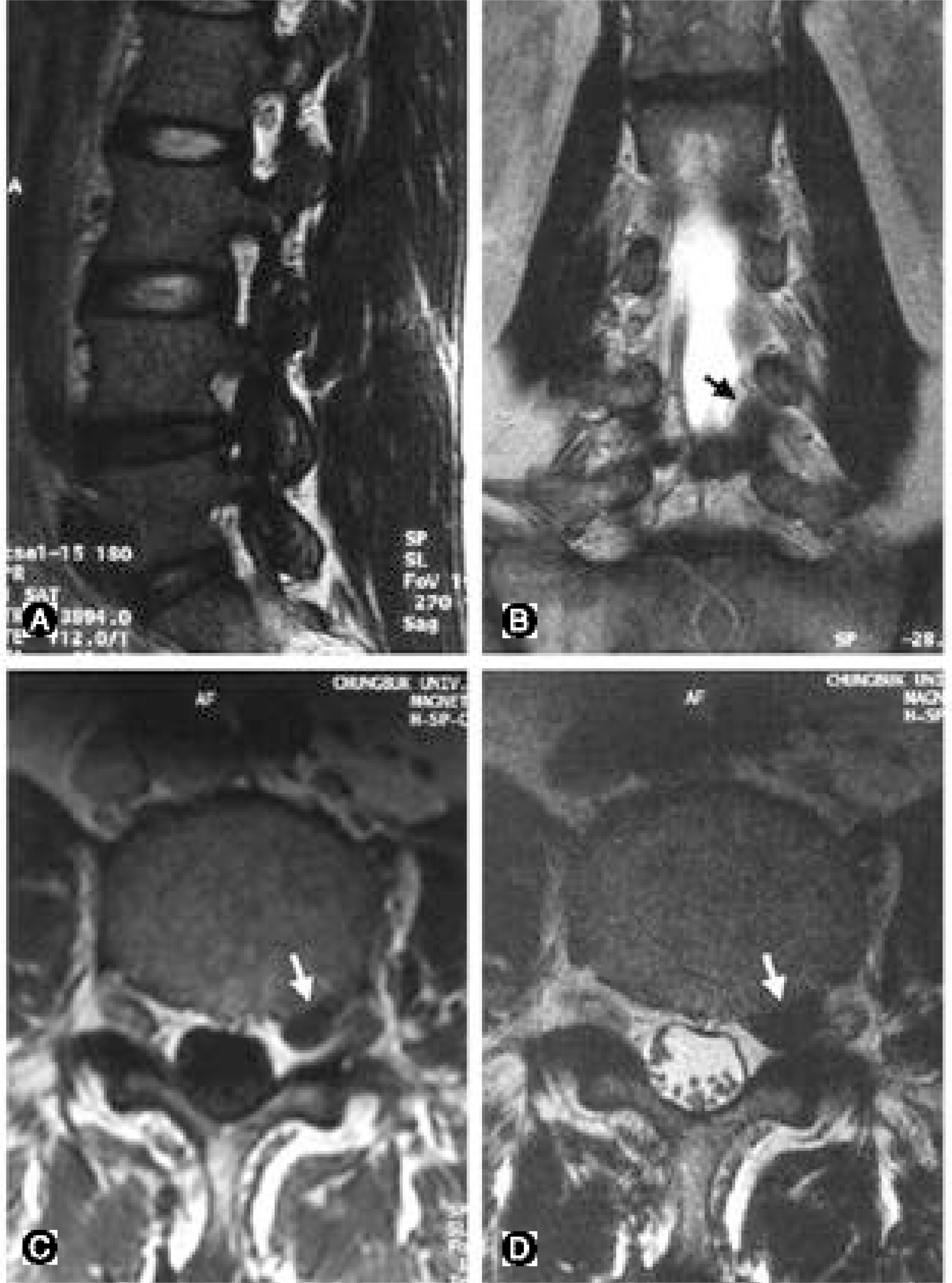 | Fig. 2.A 59 year-old man with severe radiating pain on left lower extremity. (A) T2 sagittal image shows protrusion of L4-5 disc, which usually suggests compression of L5 root. (B) T2-coronal view shows upward migration of disc material from L4-5, compressing left L4 root (dark arrow). (C, D) T1 (C) and T2 (D) bodycut axial views showing compression of left L4 root by disc material (white arrows). |
Table 1.
Authors’ Grading of Diagnostic Efficacy of Each MR Image
| Grade | 0 | no abnormality |
| 1 | abnormal, but problem unknown | |
| 2 | disc problem, compressed root unknown | |
| 3 | compressed root confirmed by this image |
Table 2.
Physical examination and MRI gradings in L4-5 foraminal disc herniation
Table 3.
Physical examination and MRI gradings in L5-S1 foraminal disc herniation




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download