Abstract
Objectives
To identify the natural course of the prevertebral soft tissue swelling after a one- or two- level anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (A CDF) and to help prevent potentially lethal airway complications after an A CDF.
Summary of Literature Review: A irway complication after anterior cervical surgery is rare but potentially lethal.
Materials and Methods
Eighty- seven patients who underwent a one- or two- level A CDF with a plate and screws were examined. Cervical spine lateral radiography was taken preoperatively, on the immediate postoperative day, 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th and 5th day after surgery. Prevertebral soft tissue was measured from C2 to C6 on the cervical spine lateral radiography.
Results
Prevertebral soft tissue swelling occurred postoperatively and increased markedly on the second day after surgery. The peak prevertebral soft tissue swelling was observed on the second and third day after surgery. The prevertebral soft tissue swelling was decreased gradually from the 4th day after surgery. Prominent swelling of the prevertebral soft tissue was found at the 2nd, 3rd and 4th cervical spine. There were no significant differences in the prevertebral soft tissue swelling between the one- level and two- level A CDF group. Only one patient required reintubation (1.1%)
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Emery SE, Smith MD, Bohlman HH. Upp er-ai rw ay obstruction after multilevel cervical corpectomy for myelopathy. J Bone Joint Surg. 1991; 73-A:544–551.
2). Fujiwara H, Nakayama H, Takahashi H, Shimizu M, Hanaoka K. Postoperative respiratory disturbance after anterior cervical fusion. Masui. 1998; 47(4):475–478.
3). Epstein NE, Hollingsworth R, Nardi D, Singer J. Can airway complications following multilevel anterior cervical surgery be avoided? J Neurosurg. 2001; 94(2s):185–188.

4). Sagi HC, Beutler W, Carroll E, Connolly PJ. Airway complications associated with surgery on the anterior cervical spine. Spine. 2002; 27(9):949–953.

5). DeBehnke DJ, Havel CJ. Utility of prevertebral soft tissue measurements in identifying patients with cervical fracture. Ann Emerg Med. 1994; 24(6):1119–1124.
6). Uppal GS, Akmakjian J. Outpatient cervical spine fusions. Abstract book of 14th annaual meeting of North American Spine Society. 1999; 158.
Go to : 
Figures and Tables%
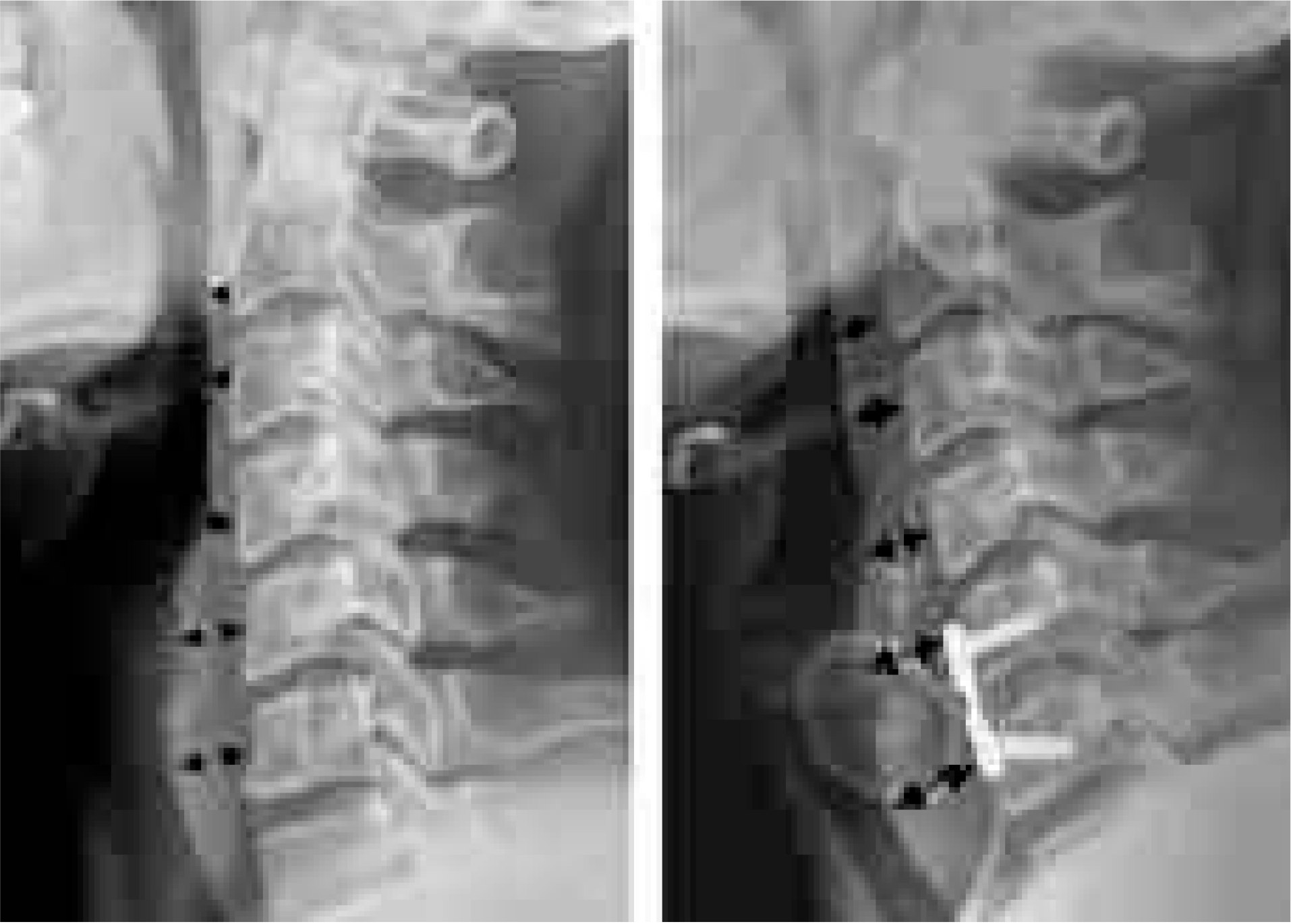 | Fig. 1.The prevertebral soft tissue was measured the distance between the anterior surface of each vertebral body and the air shadow of the airway. |
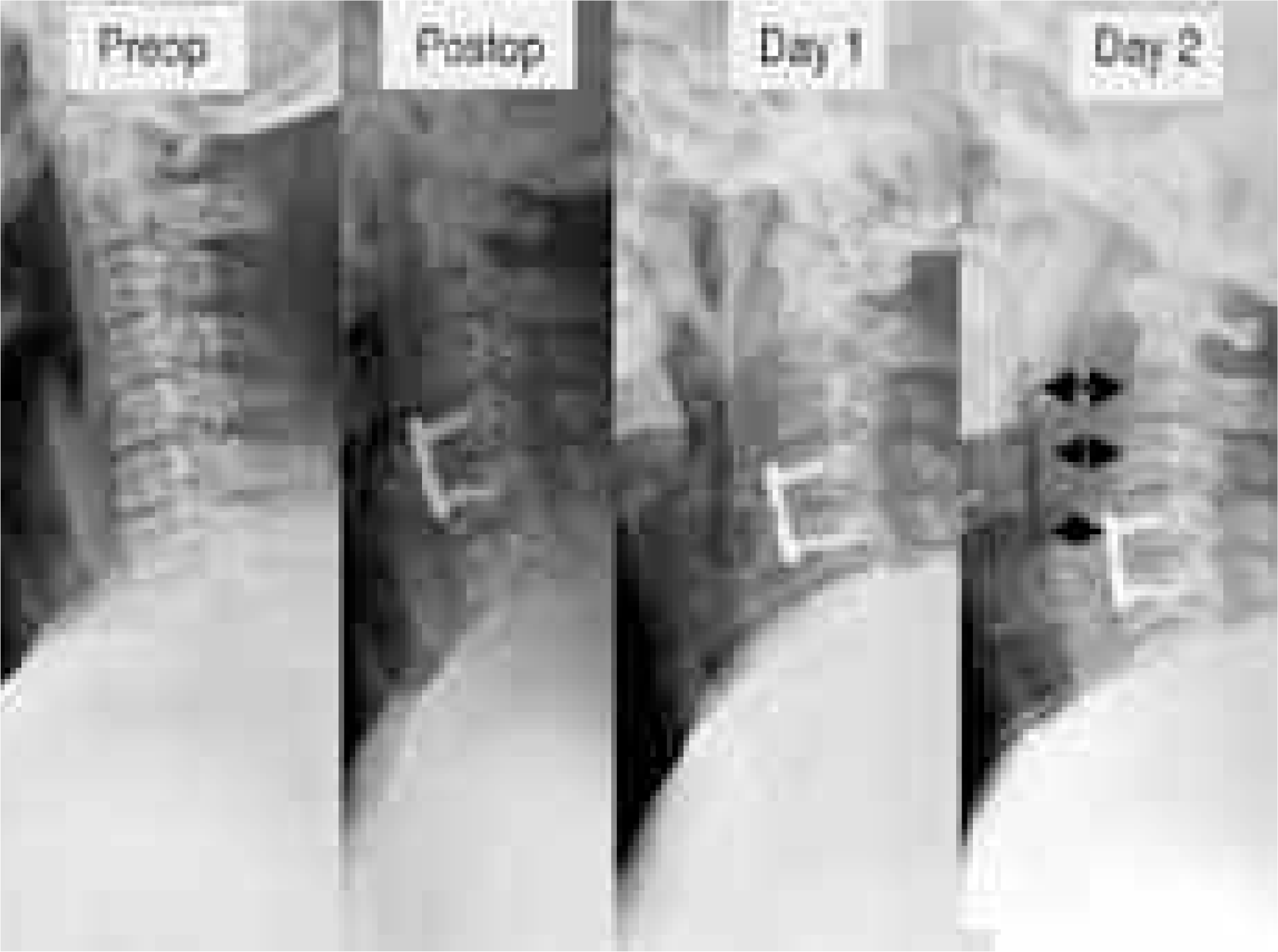 | Fig. 2.ACDF C4-5 was performed due to disc herniation at C4-5 in a 42-year-old male patient. The 2nd day after the surgery, he complained severe dyspnea. Cervical spine lateral radiography showed severe prevertebral soft tissue swelling. |
Table 1.
Serial measurements of prevertebral soft tissue
Table 2.
Comparison of prevertebral soft tissue between proximal to C5 surgery group and distal to C5 surgery group
| Time | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level | Preop (mm) | Postop | Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | Day 4 | Day 5 | |||||||
| Prox* | Dist† | Prox | Dist | Prox | Dist | Prox | Dist | Prox | Dist | Prox | Dist | Prox | Dist | |
| C2 | 3.6 | 3.5 | 6.4 | 4.5 | 8.4 | 5.0 | 13.1 | 8.5 | 11.2 | 8.7 | 9.2 | 6.1 | 8.1 | 4.9 |
| C3 | 3.9 | 3.6 | 7.3 | 5.6 | 11.7 | 6.8 | 15.5 | 11.0 | 14.1 | 12.0 | 10.8 | 10.1 | 11.1 | 7.9 |
| C4 | 5.9 | 6.2 | 9.8 | 9.7 | 13.0 | 11.1 | 16.6 | 13.2 | 15.1 | 14.5 | 13.5 | 12.6 | 13.9 | 11.1 |
| C5 | 13.7 | 14.8 | 15.6 | 16.4 | 17.6 | 16.9 | 17.9 | 17.4 | 17.7 | 18.2 | 16.4 | 16.8 | 17.8 | 16.3 |
| C6 | 15.6 | 15.3 | 17.2 | 17.1 | 18.5 | 17.6 | 17.7 | 17.0 | 18.0 | 18.1 | 17.8 | 18.1 | 18.9 | 17.6 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download