Abstract
Objectives
To analyze the height changes of the intervertebral disc and neural foramen and width changes of the neural foramen after anterior lumbar interbody fusion and posterior fixation in the lumbar spine.
Summary of Literature Review
A nterior lumbar interbody fusion distracts the height of the intervertebral disc and neural foramen and the width of the neural foramen.
Materials and Methods
Minimal anterior lumbar interbody fusion and posterior fixation were performed in 20 cases from January 1999 to January 2001. The measuring factors were the height of the anterior and posterior discs, and the height and width of the neural foramen, measured with a caliper in 1mm reconstructive, computed tomography, sagittal images before and 6 months after anterior lumbar interbody fusion. The factors were independently measured by three different persons.
Results
The height of the anterior and posterior discs was increased by mean 32.2% and 40.5%, respectively. The height of the right and left neural foramen was increased by mean 15.7% and 18.3%, respectively. The width of the superior, middle and inferior neural foramen was increased by mean 20.6%, 30.3% and 38.6%, respectively. There were significant increases in all measuring factors after minimal anterior lumbar interbody fusion.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Kirkaldy-Willis WH, McIVor G. Lumbar spinal stenosis-editorial comment. Clin Orthop. 1976; 115:2–3.
2). Vernon-Roberts B, Pirie C. Degenerative change in the intervertebral discs of the lumbar spine and their seque -lae. Rheumatology and Rehabilitation. 1977; 16:13–21.
3). Chen D, Fay LA, Lok F, Yuan P, Edwards WT, Yuan HA. Increasing neuroforaminal volume by anterior interbody distraction in degenerative lumbar spine. Spine. 1995; 20:74–79.

4). Giles L, Kaveri M. Some osseous and soft tissue causes of human intervertebral canal (foramen)stenosis. J Rheumatol. 1990; 17:1474–1481.
5). Panjabi M, Takata K, Goel V. Kinematics of lumbar intervertebral foramen. Spine. 1983; 8:348–357.

6). Kirkaldy-Willis WH. The relationship of structural pathology to the nerve root. Spine. 1984; 9(1):49–52.

7). An HS, Glover JM. Lumbar spinal stenosis: Historical perspective, classification, and pathoanatomy. Semin Spine Surg. 1994; 67-77.
8). Crock HV. Normal and pathological anatomy of the lumbar spinal nerve root canals. J. Bone and Joint Surg. 1981; 63-B(4):437–490.
9). Vanderlinden RG. Subarticular entrapment of the dorsal root ganglion as a cause of sciatic pain. Spine. 1984; 9:19–22.

10). Hasegawa T, An HS, Haughton VM, Nowicki BH. Lumbar foraminal stenosis: Critical heights of the intervertebral discs and foramina: A cryomicrotome study in cadavera. J Bone Joint Surg[Am]. 1995; 77:32–38.
11). Stephens MM, Evans JH, OBrien JPK. Lumbar intervertebral foramens: An in vitro study of their shape in relation to intervertebral disc pathology. Spine. 1991; 16:525–529.
12). Yoo JU, Zou D, Edwards W, Bayley J, Yuan H. Effect of cervical spine motion on the neuroforaminal dimensions of human cervical spine. Spine. 1992; 17(10):1131–1136.

13). Mayoux-Benhamou MA, Aaron C, Chomette G, Amor B. A morphometric study of the lumbar foramen. Influence of flexion-extension movements and of isolated disc collapse. Surg. and Radiol. Anat. 1989; 11:97–102.
14). Dennis S, Watkins R, Landaker S, Dillin W, Springer D. Comparison of Disc Space Heights after Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion. Spine. 1989; 14(8):876–878.

15). Inufusa A, An HS, Glover JM, McGrady L, Lim TH, Riley LH. The Ideal Amount of Lumbar Foraminal Distraction for Pedicle Screw Instrumentation, Spine. 1996; 21(19):2218–2223.
16). Hoyland JA, Freemont AJ, Jason MIV. Interve rtebral foramen venous obstruction: A cause of periadicular fibrosis? Spine. 1989; 14(6):558–568.
17). Bernhardt M, Bridwell KH. Segmental analysis of the sagittal plane alignment of the normal thoracic and lumbar spines and thoracolumbar junction. Spine. 1989; 14:717–721.

18). Bolender N, Schonstrom NS, Spengler D. Role of computed tomography and myelography in the diagnosis of central spinal stenosis. J Bone Joint Surg[Am]. 1985; 67(2):240–246.

19). Shirado O, Zdeblick TA, McAfee PC, Warden AK. Biomechnical evaluation of methods of posterior stabilization of the spine and posterior lumbar interbody arthrodesis for lumbosacral isthmic spondylolisthesis: A calf-spine model. J Bone Joint Surg[Am]. 1991; 73:518–526.
Go to : 
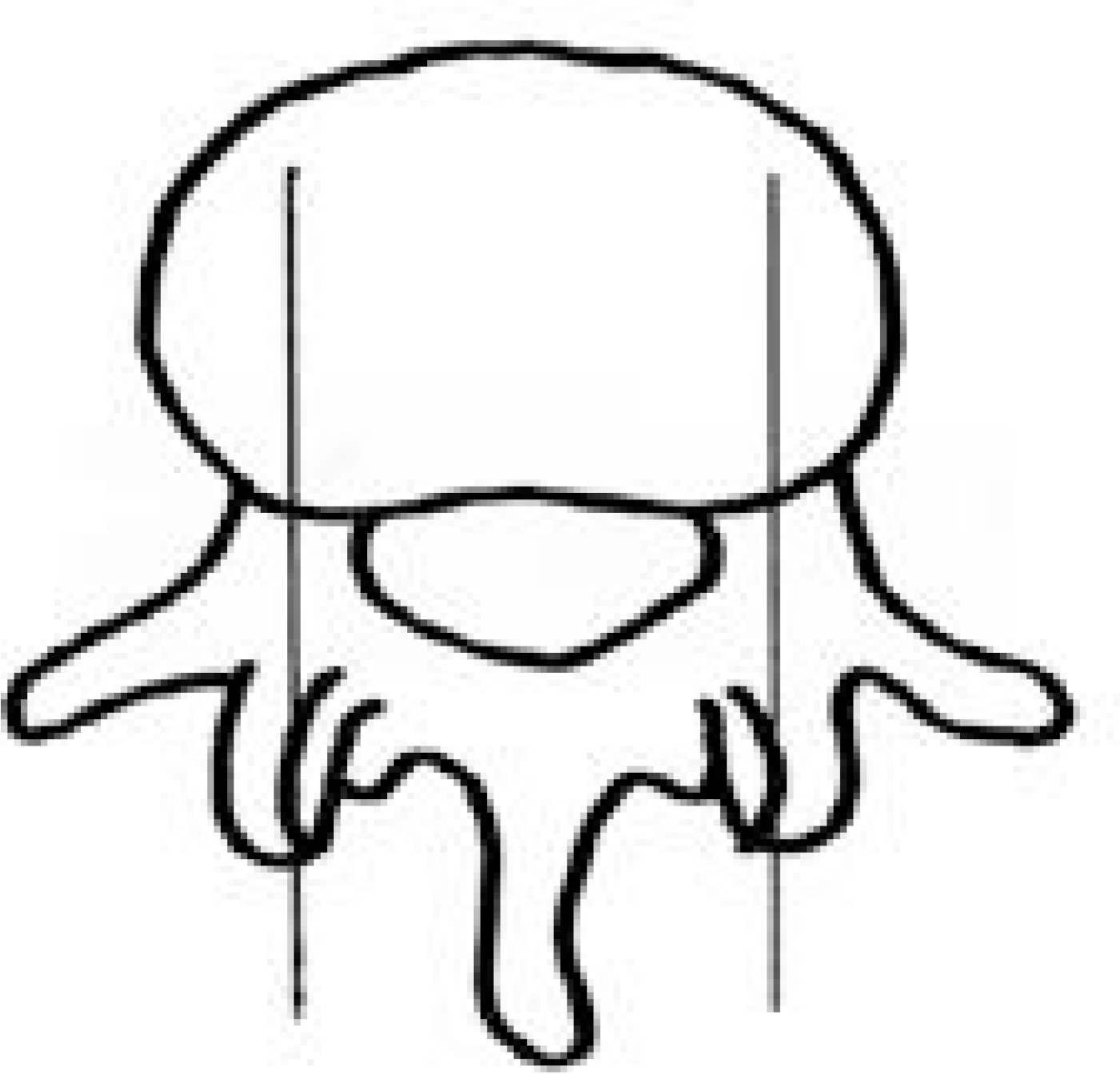 | Fig. 1.Schematic picture for CT measurement were done via sagittal reconstruction at the level of the mid pedicle on axial CT cut |
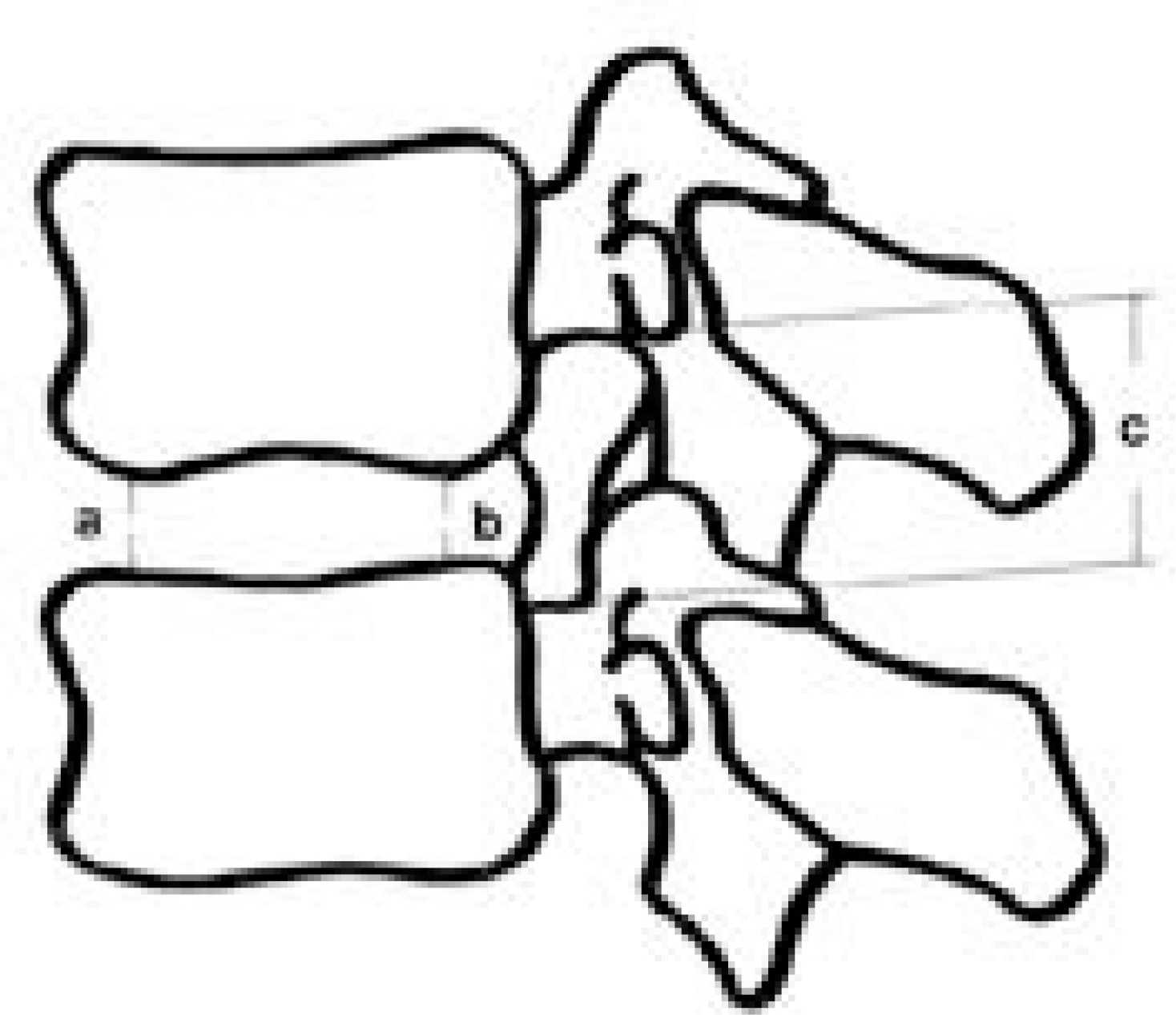 | Fig. 2.Diagram showing the measurements made on the discs and neuroforamina. a: anterior disc height, b: posterior disc height, c: foraminal height |
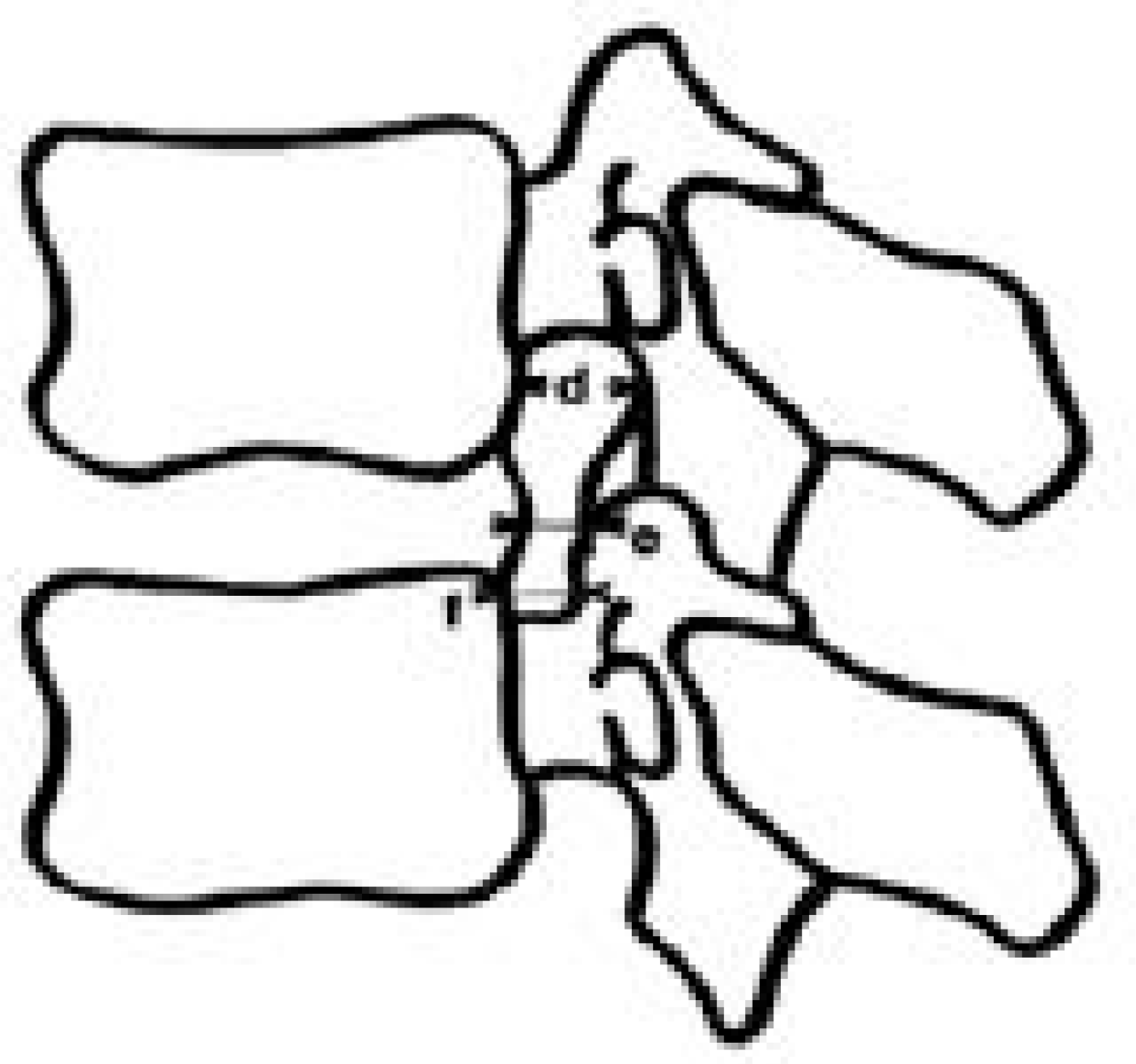 | Fig. 3.Diagram showing the mesurements made on the neuro-foramina for the width of neuroforamen. d: superior foraminal width, e: middle foraminal width, f: inferior foraminal width. |
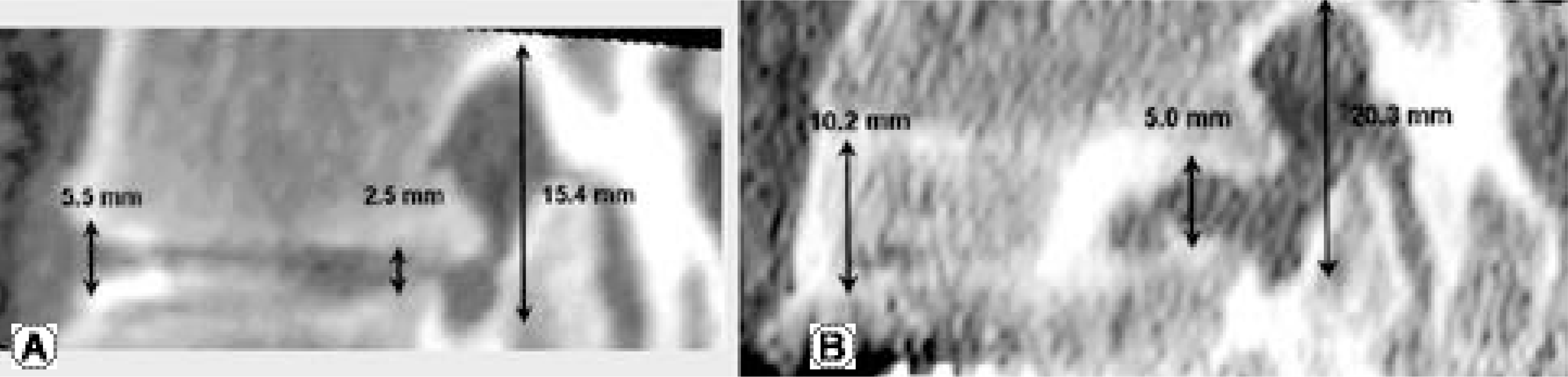 | Fig. 4.A 34-year-old woman with spinal stenosis on L4-5 Fig. 4. (A) Left side sagittal reconstruction image of preoperative CT scan Fig. 4. (B) Left side sagittal reconstruction image of seven-month postoperative CT scan shows marked increase of the anterior disc height, the posterior disc height and the height of neural foramen. |
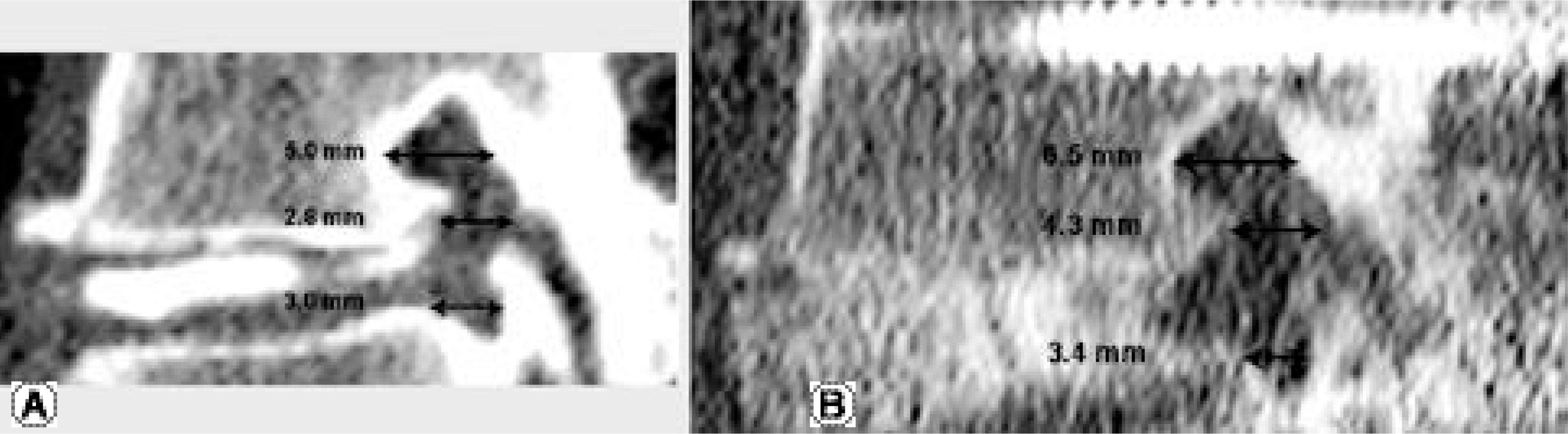 | Fig. 5.A 55-year-old woman with spinal stenosis on L4-5 and instability Fig. 4. (A) Left side sagittal reconstruction image of preoperative CT scan Fig. 4. (B) Left side sagittal reconstruction image of six-month postoperative CT scan shows slight increase of the superior, middle and inferior foraminal width. |
Table 1.
The changes of value in CT mesurement
Table 2.
The changes of the height of intervertebral disc in CT mesurement.
| Pre-op (mm) | Post-op (mm) | % increase (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anterior disc | 7.6 | 9.5 | 32.3 |
| Posterior disc | 5.6 | 7.1 | 40.5 |
Table 3.
The changes of the height of neural foramen in CT mesurement.
| Pre-op (mm) | Post-op (mm) | % increase (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Right | 18.1 | 21.0 | 15.7 |
| Left | 17.7 | 20.9 | 18.3 |
Table 4.
The changes of the width of neural foramen in CT mesurement.
| Pre-op (mm) | Post-op (mm) | % increase (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sperior | 5.7 | 6.8 | 20.6 |
| Middle | 4.0 | 5.0 | 40.5 |
| Inferior | 3.5 | 4.6 | 38.6 |
Table 5.
The result of paired t-test in postoperative changes of measuring factors.
| Average | S.D.∗ | S.E.∗∗ | t-score | Degree of freedom | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Height of anterior disc | 2.010 | 1.261 | 0.282 | 7.130 | 19 | < 0.001 |
| Height of posterior disc | 1.495 | 0.841 | 0.188 | 7.952 | 19 | < 0.001 |
| Height of neural foramen | 3.160 | 3.826 | 0.855 | 3.694 | 19 | = 0.002 |
| Width of superior foramen | 1.090 | 0.912 | 0.612 | 1.780 | 19 | < 0.001 |
| Width of middle foramen | 0.950 | 0.919 | 0.482 | 1.971 | 19 | < 0.001 |
| Width of inferior foramen | 1.080 | 1.267 | 0.559 | 1.931 | 19 | = 0.001 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download