Abstract
Objectives
To discuss pyogenic infections of the facet joints and paraspinal intramuscular abscess that developed after a steroid injection into the facet joint of the lower back.
Material and Methods
A 39- year- old man who received a steroid injection to the facet joint, 3 weeks prior to admission, expe-rienced increasing lower back pain and a high fever.
Results
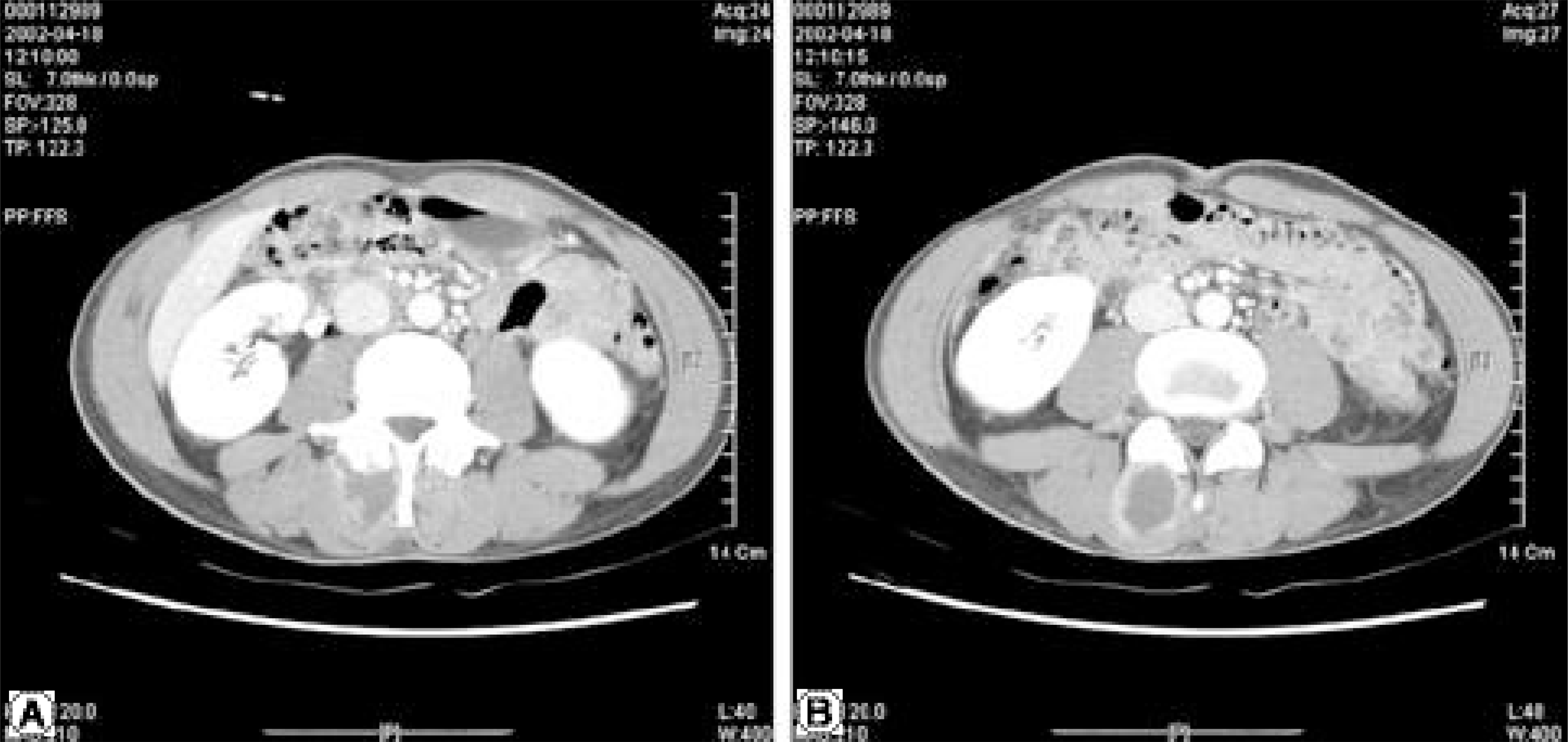
Plain radiographs of the lumbar spine showed osteolytic erosion of the articular process at the L3- 4 facet joint. On a CT scan, the destructed facet joint was connected to a paraspinal intramuscular abscess. MR images also showed a paraspinal intramuscular abscess on multiplane views. In the operative field, the paraspinal abscess, which extended from 2nd to 5th lumbar vertebrae, was found on the right side, with the L3- 4 facet destructed and directly connected to the abscess. Some chalky material, considered to be steroid crystals, was found at the L3- 4 facet joint. Drainage, debridement and irrigation were per-formed. Staphylococcus aureus was isolated from the culture. A fter surgery, intravenous antibiotics were administered, and the patients’ symptoms quickly resolved.
Conclusions
A posterior facet joint injection has its own risks of developing a pyogenic infection of the facet joint. Pyogenic facet joint infections may progress to a paraspinal intramuscular abscess. Surgical drainage is mandatory in cases resistant to antibiotic treatment, with evidence of pus formation on imaging studies.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Baker A., Ojemann R., Swartz ., Richardson E. Spinal epidural abscess. N Engl J Med,. 293:463–468. 1975.

2). Baltz M., Tate D., Glaser J. Lumbar facet joint infection associated with epidural and paraspinal abscess. Clin Orthop,. 339:109–112. 1997.

3). Chevalier X., Marty M., Larget-Piet BJ. Klebsiella pneumonia septic arthritis of a lumbar facet joint. J Rheumatol,. 19:1817–1819. 1992.
4). Cook NJ., Hanrahan P., Song S. Paraspinal abscess following facet joint infection. Clin Rheumatol,. 18:52–53. 1999.
5). Crenshaw AH. Campbell' s Operative Orethopedics. 8th ed.Mosby Year Book;1992.
6). Halpin DS., and Gibson RD. Septic arthritis of a lumbar facet joint. J Bone Joint Surg, 69B-. 3:457–460. 1987.

7). Heenan SD., and Britton J. Septic arthritis in a lumbar facet joint: a rare cause of an epidural abxcess. Neurora -diol,. 37:462–464. 1995.
8). Magee M., Kannangara S., Dennien B, et al. Paraspinal abscess complicating facet joint infection. Clin Nucl Med. 25:71–73. 2000.
9). Muffoletto AJ., Ketonen LM., Mader JT, et al. H ematoge -nous pyogenic facet joint infection. Spine,. 26:1570–1576. 2001.
10). Peris P., Brancos MA., Gratacos J, et al. Septic arthritis of spinal apophyseal joint. Spine, 17-. 12:1514–16. 1992.

11). Roberts W. Pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis of a lumbar facet joint with associated epidural abscess. Spine,. 13:948–952. 1988.

12). Sapico FL., Montgomerie JZ. Pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis; Report of nine cases and review of the liter -ature. Rev Infect Dis. 1:754–776. 1979.
13). Weinstein JN., Wiesel SW. The Lumbar Spine. W. B. Saunders Company;1990.
Go to : 
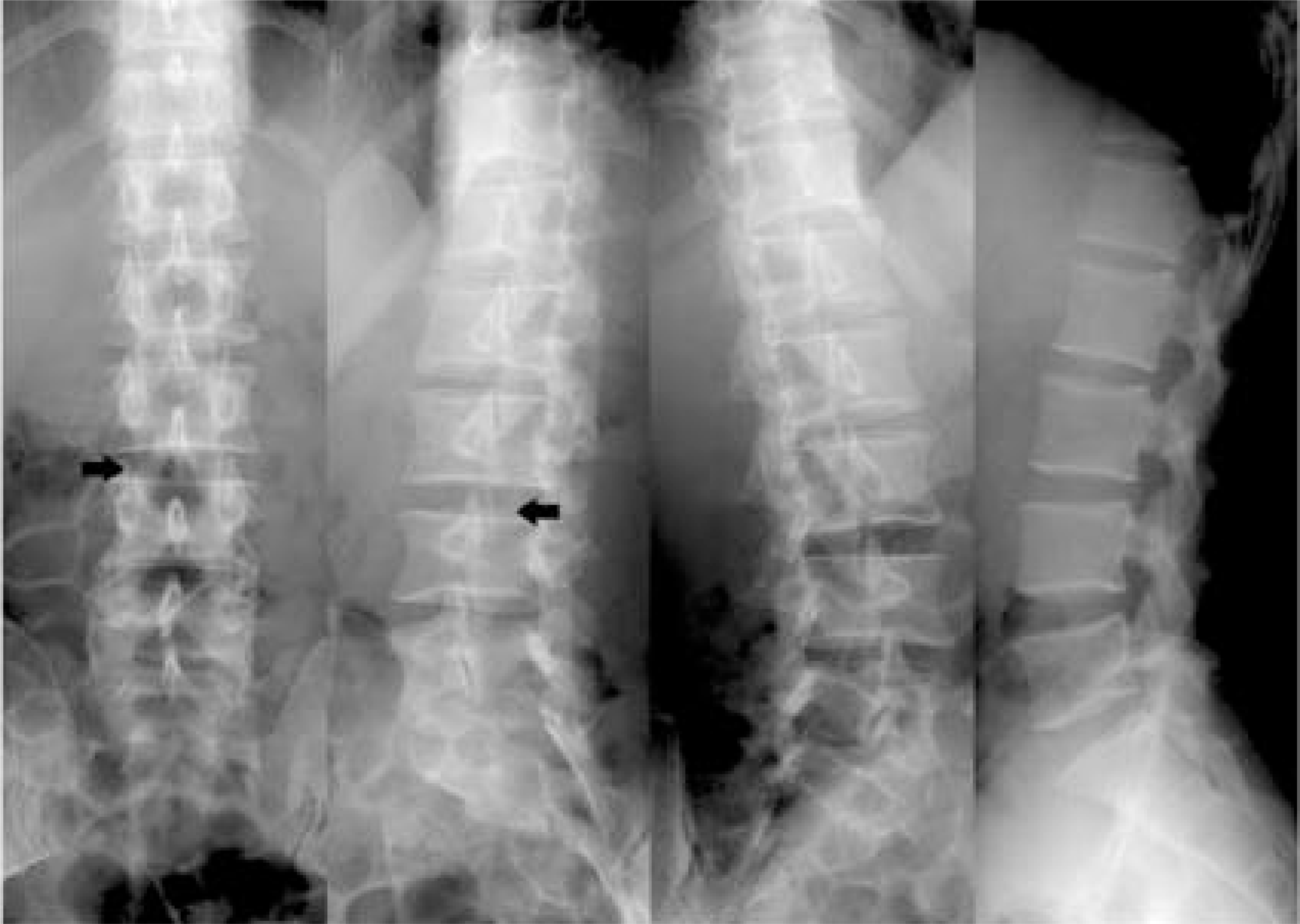 | Fig. 1.Preoperative plain radiographs Arrow points to the erosion of inferior articular process and narrowing of L3-4 facet joint. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download