Abstract
Study Design
Thirty- eight patients with thoracolumbar spinal tuberculosis were evaluated according to the surgical treatment method, either a one or two stage anterior debridement, with anterior or posterior instrumentation, respectively.
Purpose
The aim of this study was to compare the effects of the one stage anterior debridement, with anterior instrumentation, to the two stage anterior debridement, with posterior instrumentation
Materials and Methods
Thirty- eight patients, with tuberculous spine, were divided into two groups depending on the surgical method. One group consisted of 21patients treated with anterior debridement combined with anterior instrumentation, and the other group consisted of 17 patients treated by a two stage operation of anterior debridement combined with posterior instrumentation. The clinical outcomes were evaluated from the hematological laboratory findings, bone union in radiographs, change of kyphotic angle, duration of hospital stay and the medical cost during hospitalization.
Results
There were no recurrences of infection in either group and bone union was obtained within 6 months of the operation for all cases in both groups. The preoperative, postoperative and final follow-up kyphotic angle in the two groups were 18/20,7/9 and 10/11 degrees, respectively. There was no significant difference in the decrease of the kyphotic angle between the two groups (p>0.05). However, group I was superior to group II in relation to the duration of hospital stay and the medical cost.
Conclusion: We concluded that the one stage operation was the better of the operative methods for the treatment of active tuberculous spondylitis in a thoracolumbar spine.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Albee FH. Transplantation of a portion of the tibia into the spine for Pott's disease. J. A.M.A. 57:885–886. 1911.
2). Bailey HL., Gabriel M., Hodgson AR., Shin JS. Tuberculosis of the spine in children. operative findings and results in one hundred consecutive patients treated by removal of the lesion and anterior grafting. J Bone Joint Surg,. 54-A:1633–1657. 1972.
3). Boachie-Adjei O., Squillante RG. Tuberculosis of the spine. Clin Orthop. North America,. 27:95–103. 1996.
4). Cho DY., Kim EH., Koh ES., Cho KN. A comparative study of anterior interbody fusion with and without anteri -or instrumentation in multi-level tuberculosis of thoracolumbar spine. J Korean Orthop Assoc,. 30:298–306. 1995.
5). Chung YK., Kim SW., Han HM., Lee EJ., Choi SJ., Chang JD. The results of the surgical treatment using posterior spinal instrumentation. J of Korean Spine Surg,. 6:81–88. 1999.
6). Eysel P., Hopf C., Vogel I., Rompe JD. Primary stable anterior instrumentation or dorsoventral spondylodesis in spondylodiscitis? results of a comparative study. Euro -pean Spine J,. 6:152–157. 1997.
7). Fountain SS., Hsu LCS., Yau ACMC., Hodgson AR. Progressive kyphosis following solid anterior spinal fusion in children with tuberculosis of the spine. J Bone Joint Surg,. 57-A:1104–1107. 1975.
8). Girdlestone GR., Somerville FW. Tuberculosis of Bone and Joints. ed. 2. New York: 1952. Oxford University Press.
9). Ha KY., Kim WY., Lee KH., Park JS., Kim ST. Tho -racolumbar tuberculous spondylitis treated with AIF and TSRH. J of Korean Spine Surg,. 3:210–216. 1996.
10). Hibbs RA. An Operation for Pott's Disease of the Spine. J. A.M.A. 65-6:433. 1912.
11). Hibbs RA. Treatment of Vertebral Tuberculosis by Fusion Operation. J. A.M.A. 71:1372. 1918.
12). Hodgson AR., Stock FS. Anterior spinal fusion: A preliminary communication on the radical treatment of Pott's paraplegia. Br J Surg,. 44:266–75. 1956.
13). Ito H., Tsuchiya J., Asami G. A new radical operation for Pott's disease. Report of ten cases. J Bone Joint Surg,. 16:499–515. 1934.
14). Kemp HBS., Jackson JW., Jeremiah JD., Cook J. Anterior fusion of the spine for infective lesions in adults. J Bone Joint Surg,. 55-B:715–734. 1973.

15). Kim KW., Lee JW., Lee KW., Baek GH., Soh SH., Choi DH. Clinical study on progression of kyphosis on spinal tuberculosis treated by anterior arthrodesis. J Korean Orthop Assoc,. 25:1756–1760. 1990.
16). Kim NH., Hahn SB., Kim SS. Changes of kyphotic angle in children and adults after anterior intervertebral fusion in spinal tuberculosis. J Korean Orthop Assoc,. 26:1514–1524. 1991.

17). Korkusuz F., Carl A., Ferron S. Prevention of postop -erative late kyphosis in Pott's disease by anterior decom -pression and intervertebral grafting. World J Surg,. 21:524–528. 1997.
18). Lifeso RM., Weaver P., Harder EH. Tuberculo us spondylitis in adults. J Bone Joint Surg,. 67-A:1405–1413. 1985.
19). Louw JA. Spinal tuberculosis with neurological deficit. Treatment with anterior vascularized rib grafts, posterior osteotomies and fusion. J Bone Joint Surg,. 72-B(4):686–693. 1990.
20). Moon MS., Woo YK., Lee KS., Ha KY., Kim SS., Sun DH. Posterior instrumentation and anterior interbody fusion for tuberculous kyphosis of dorsal and lumbar spines. Spine,. 20:1910–1916. 1995.

21). Moon MS., Woo YK., Ok IY., Lee KS., Kang YK., Ha KY., Kim SS. posterior instrumentation for treatment of active dorsolumbar tuberculosis with kyphosis, J Korean Orthop Assoc,. 24:660–665. 1989.
22). Nussbaum ES., Rockswold GL., Bergman TA., Erickson DL., Seljeskog EL. Spinal tuberculosis: a diagnostic and management challenge. J Neurosurg,. 83:243–247. 1995.

23). Oga M., Arizono T., Takasita M., and Sugioka Y. Evalu -ation of the risk of instrumentation as a foreign body in spinal tuberculosis. Clinical and biologic study. Spine,. 18:1890–1894. 1993.
24). Park JT., Ahn GY., Kim HG., Seong YH. The results of anterior fusion with anterior instrumentation in spinal tuberculosis, J of Korean Spine Surg,. 3:217–224. 1996.
25). Rajasekaran S., Soundarapandian S. Progression of kyphosis in tuberculosis of the spine treated by anterior arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg,. 71-A:1314–1323. 1989.

26). Rose GK., Robert O., Sanderson JM. Transposition of rib with blood supply for the stabilization of a spinal kyphosis. J Bone and Joint Surg.,. 57-B:112. 1975.
27). Wilkinson MC. The management of tuberculosis of the spine by evacuation of the paravertebral abscess and cur -rettage of the vertebral bodies. J Bone Joint Surg,. 37-B:382–391. 1955.
28). Yilmaz C., Hakan YS., Gurkan I., Erdemli B., Korkusuz Z. Anterior instrumentation for the treatment of spinal tuberculosis. J Bone Joint Surg,. 81-A:1261–1267. 1999.

29). Yune SH., Lee KJ., Lee JK., Ahn SR., Moon HS. A clinical study of anterior interbody fusion on tuberculosis of the spine, J Korean Orthop Assoc,. 22:1317–1325. 1987.
Go to : 
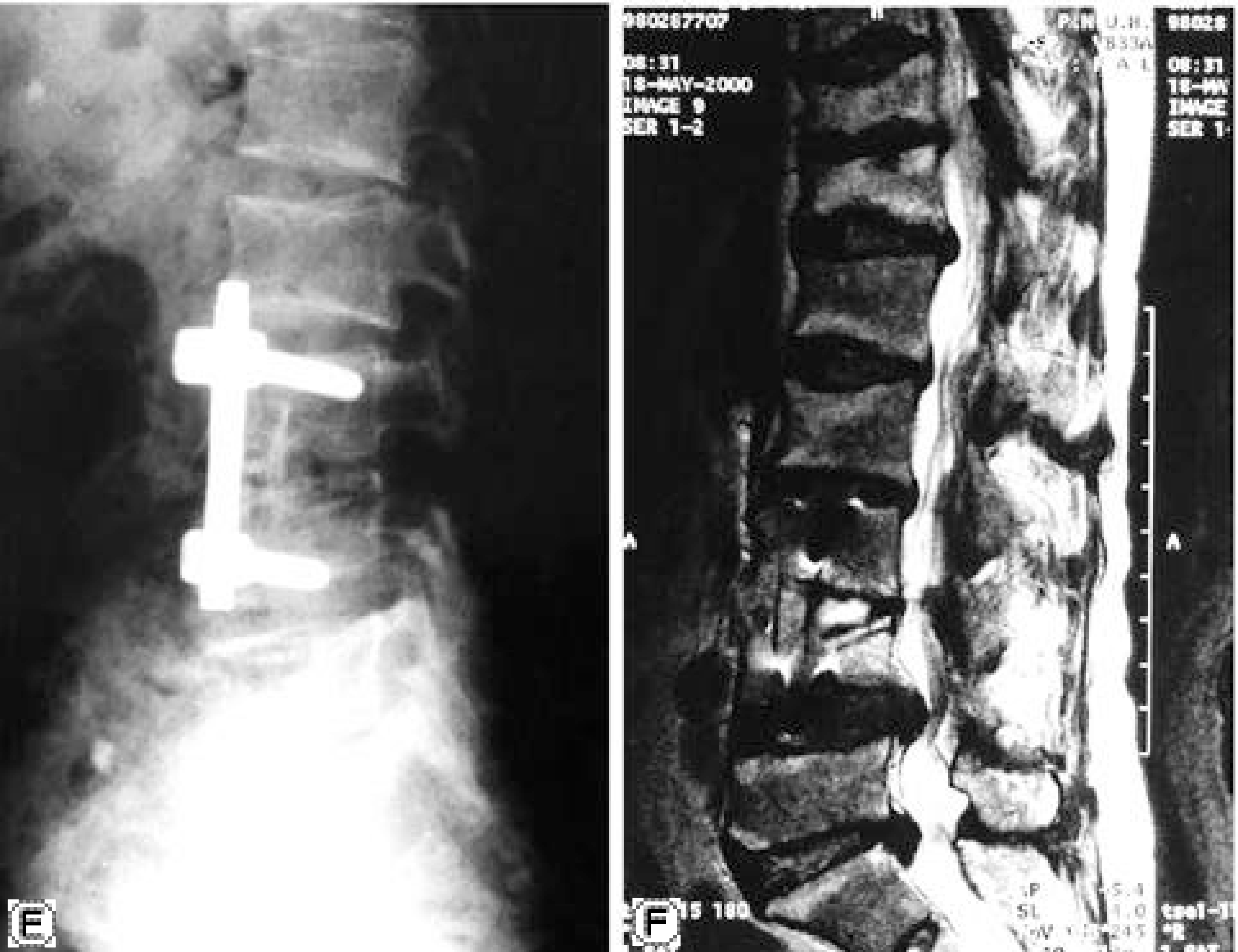 | Fig. 1.
A. Preoperative radiograph of a 55-year-old woman showed L3-4 joint space narrowing and destruction of cartilagenous end plate B & C. Preoperative T2-weighted coronal and sagittal MR image showed L3-4 involvement and both paraspinal psoas abscess. D. Immediate postoperative radiograph after L3-4 anterior decompression and strut bone graft with anterior instrumentation. E & F. At postoperative 13 months, plain radiograph and T2-weighted sagittal MR image showed bony union with satisfacto-ry maintenance of corrective kyphotic angle and didn't show any recurrence of infection. |
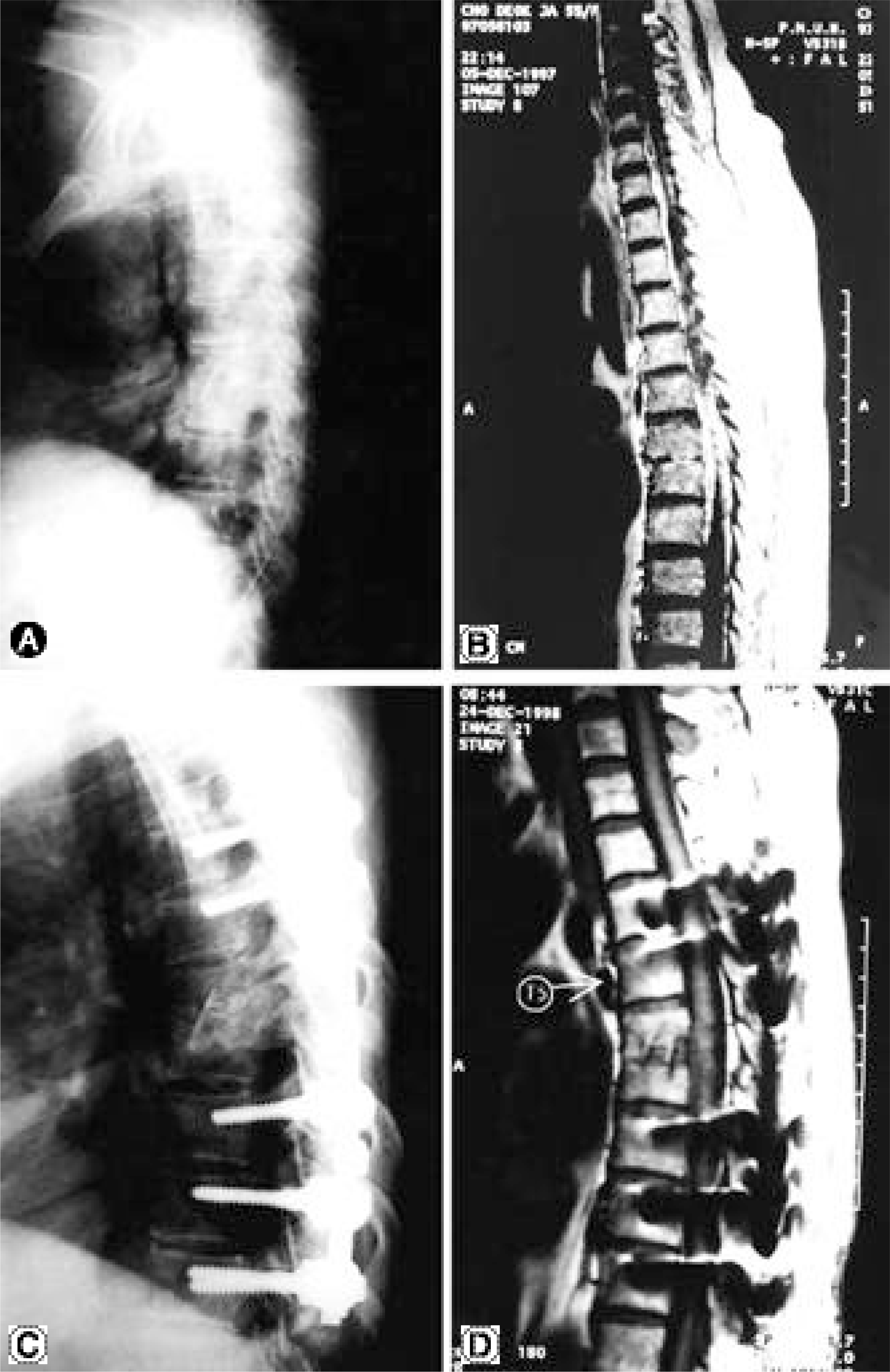 | Fig. 2.
A & B. Preoperative radiograph and T1-weighted sagittal MR image of 55-year-old woman showed T6-7 tuberculous with extended inflammatory discharge into spinal canal. C. Postoperative radiograph after two stage operation-posterior instrumentation following anterior decompression of involved body and anterior interbody fusion. D. At postoperative 12 months, T1-weighted sagittal MR image shows no recurrence of tuberculosis infection. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download