Abstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to develop a decision support system that helps school nurses manage health problems they encounter while caring for the elementary and secondary school students, and evaluate usability of it.
Methods
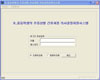
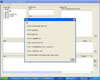
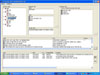
Knowledge was aquired by literatures review and interviews with senior school nurses and was validated by another group of school nurses. The Omaha System was used as a standardized nursing terminology to describe nursing diagnoses and interventions. The system was developed under the Windows environment. C++ was used as a program language and MS Structured Query Language as a database. To investigate usability of the system, 30 school nurses in elementary and secondary schools were recruited and asked to apply it to nursing problems they encountered in actual students care setting.
Results
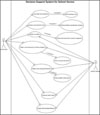
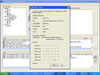
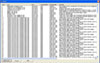
The decision support system with seven major signs and symptoms was developed. It automatically makes a nursing diagnosis based on the input data, and also provides nursing interventions with evidence. It was proven that the system was very useful for school nurses to manage students' health problems.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Kim HJ, Yun SN, June KJ. School health and nursing. 1999. 3rd. Seoul: Sumoon.
2. Hwang MJ. A study on health teachers' status [dissertation]. 2005. Cheungju: Chunbuk National University.
3. Lee EO, Song MS, Kim MK, Park HA. Development of a nursing diagnosis systemusing a neural networkmodel. J Kor Acad Nurs. 1996. 26(4):37–50.
4. Choi YH, Lee HY, Kim HS, Park HK. Computerized nursing process - Nursing diagnosis and intervention. 1999. 1st. Seoul: Hyunmoon.
5. Lee EJ, Lee SS. Development ofmultimedia contents and web-based EPSS for the application of scientific nursing processes and training. Korean Association for Educational Information and Media. 2004. 10(2):135–158.
6. Oh JJ, Kim EJ. A Study on the Utilization of a High School Health Clinic in Seoul. Journal of Korea community health nursing academic society. 1992. 6(6):50–57.
7. Han HM, Choi SH, Doh BN. The Utilization of the health office and Health Problems of the High School Student. The Kyungpook University medical journal. 1995. 37(2):263–271.
8. Moon JS. The Present Status and theAssociated Factors with the Utilization on the School Health Room of the Student in aMiddle and High School in Kwang-ju Area [dissertation]. 2001. Kwang-ju: Chosun University.
9. Park MY. A Study on the Stress and Health Problem in Some Primary School Children. The Chosun University medical journal. 2002. 27(2):57–67.
10. Jung YS, Lee CY, Lee GY. School Health. 2004. 3rd. Seoul: Hyunmoon.
11. Kyonggi Province Office of Education. 2005 School Health Manual. 2005. 3. Suwon: Kyonggi Province Office of Education;92–162.
12. Seoul National University. 2005 in-service education for qualification of school health nurses. 2005. Seoul: College of Nursing, Seoul National University.
13. Hong KJ, Moon YI, Paik SN, Ahn CS, Lee KJ, Lim HK, et al. Pediatric Nursing I,II. 2002. Seoul: Sumoon.
14. Study group for infants and young children's health. Health care for children Topic Approach. 2003. Seoul: Hyunmoon.
15. Seoul national university. New emergency treatment-Diagnosis and treatment. 2005. Seoul: College of Medicine, Seoul National University.
16. Doll WJ, Torkzadeh G. The measurement of end user computing satisfaction. MIS Quarterly. 1988. 12(2):257–274.
17. Ahn SK. Astudy on the user's satisfaction of agriculture information system [dissertation]. 1999. Seoul: Seoul National University.
18. Bridgeman T., Flores M., Rosenbluth J., Pierog J. One emergency department's experience: Clinical algorithms and documentation. J Emerg Nurs. 1997. 23(4):316–325.

19. Yang JJ. Development and Application of the Algorithm for Emergency Nursing Care of Dyspneic Patients [dissertation]. 2005. Kwang-ju: Chonnam University.
20. Kim AR. Development and Evaluation of a Web-based Ostomy Self-care Education Program [dissertation]. 2004. Seoul: Seoul National University.
21. Kang YM. Development of stroke care website and it's effets [dissertation]. 2003. Seoul: Seoul National University.
22. Bong MR. The Development and Evaluation of a Web-based Information Programfor Patients undergoing Spinal Fusion [dissertation]. 2005. Seoul: Seoul National University.
23. Degoulet Patrice, et al. Introduction to clinical medical informatics. 1997. Seoul: Korea medical book publisher.
24. Kim AS. First aid. 2000. Accessed July 30, 2006. Available at:
http://www.1004bang.net.
25. Lim HK. First aid. 2005. Accessed July 30, 2006. Available at:
http://www.narara.org.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download