Abstract
Objective
This study was conducted to measure radiographic joint space width and to estimate erosion in the hands of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. It showed that joint space width, homogeneity, and invariant moments are parameters to discriminate between the normal and the rheumatoid joint.
Methods
In order to measure the joint space width and to estimate erosion in the finger joint, 32 radiographic images were used - 16 images for training and 16 images for testing. The joint space width was measured in order to quantify the joint space narrowing. Also, homogeneity and invariant moments was computed in order to quantify erosion. Finally, artificial neural networks were constructed and tested as a classifier distinguishing between the normal and the rheumatoid joint.
Results
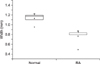
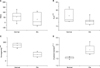
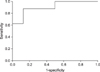
The joint space width of normal was 1.04±0.15 mm and the width of patients with rheumatoid arthritis was 0.94±0.15 mm. The Homogeneity of normal was 16568.83±2669.83 and invariant moments were 6843.45±2937.55. They were statistically difference (p<.05). Using these characteristics, artificial neural networks showed that they discriminate between normal and rheumatoid arthritis (AUC=0.91).
Figures and Tables
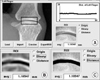
Figure 1
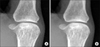
Joint space narrowing and erosive destructions11). An early stage (left), rheumatoid arthritis progression (right)

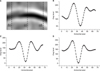
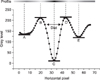
Figure 6
The profiles of ROI. (A) The dot lines are vertical profiles. (B) The profile of the first dot line. (C) The profile of the second dot line. (D) The profile of the third dot line
References
1. Farrant J, Grainger A, O'Connor P. Advanced imaging in rheumatoid arthritis: part 1: synovitis. Skeletal Radiology. 2007. 36(4):269–279.
2. Farrant J, Grainger A, O'Connor P. Advanced imaging in rheumatoid arthritis: part 2: erosion. Skeletal Radiology. 2007. 36(5):381–389.
3. Duryea J, Jiang Y, Zakharevich M. Neural network based algorithm to quantify joint space width in joints of the hand for arthritis assessment. Medical Physics. 2000. 27(5):1185–1194.

4. Sharp J, Gardner J, Bennett E. Computer-based methods for measuring joint space and estimating erosion volume in the finger and wrist joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism. 2000. 43(6):1378–1386.

5. Finckh A, Pablo P, Katz J. Performance of an automated computer-based scoring method to assess joint space narrowing in rheumatoid arthritis: a longitudinal study. Arthritis & Rheumatism. 2006. 54(5):1444–1450.

6. Sharp J, Bluhm G, Brook Al. Reproducibility of multiple-observer scoring of radiologic abnormalities in the hands and wrists of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism. 1985. 28(1):16–24.

7. Goldbach-Mansky R, Mahadevan V, Yao L. The evaluation of bone damage in rheumatoid arthritis with magnetic resonance imaging. Clinical and experimental rheumatology. 2003. 21(5):S50–S53.
8. Peloschek P, Langs G, Weber M. An automatic model-based system for joint space measurements on hand radiographs: initial experience. Radiology. 2007. 245(3):855–862.

9. Langs G, Peloschek P, Bischof H. Determining position and fine shape detail in radiological anatomy. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. 2003. 2781:532–539.

10. Langs G, Peloschek P, Bischof H. Asm driven snakes in rheumatoid arthritis assessment. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. 2003. 2749:454–461.

11. Langs G, Peloschek P, Bischof H. Automatic quantification of joint space narrowing and erosions in rheumatoid arthritis. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging. 2009. 28(1):151–164.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download