Abstract
Objective
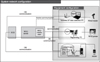
A system for reinforcing the patient safety has been established based on RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology in order to minimize a variety of potential medical errors which can take place in hospitals. The system is intended to prevent simple errors or misunderstandings attributed to manifold surgery, transfusion, and medication errors.
Methods
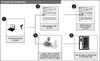
The RFID system was developed and established in one general hospital. The system was applied to managing the patient in the run-up to surgery during anesthesia preparation, transfusion, and anticancer medications, of which procedure information and the patient information are rechecked for assurance, respectively.
Results
With regard to the technological aspects, the system used 13.56 MHz of spectrum bandwidth and tags complying with ISO 15693 standard. The tag readers varied with the work, PDAs in the intensive care unit, and laptop computers in the anesthesiology department and on the general wards. After applying the system, we surveyed user's usage and satisfaction.
Conclusion
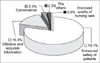
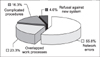
The results of our survey indicated a high level of satisfaction with the RFID system in terms of reinforcing the patient's safety in medical environments. Respondents stated that patients were likely to wear an electronic bracelet, even if inconvenient, with their information revealed on the wrist and while going through extended medical procedures. Nurses had intentions to utilize the RFID system for managing hospital assets and tracking patients. A revitalization of the RFID system would be network stability, including the network environment, as well as quantitative effectiveness analysis.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Ahluwalia J, Marott L. Critical incident reporting systems [abstract]. Seminars in Fetal and Neonatal Medicine. 2004. 10:31–37.
2. Kohn LT, Corrigan JM, Donaldson MS. To err is human: building a safer health system. 1999. Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
3. Sheldon T. Dutch study shows that 40% of adverse incidents in hospital are avoidable. BMJ. 2007. 334(7600):925.

4. Park DK, Jung E, Jeong K. Status of RFID/USN Application in Health Care. KICS. 2008. 25:1–8.
5. Min DK, Kim EJ, Lee EJ, Seol TR. Research on an application model of RFID technology for Patient safety: a case of Y Hospital. EJIT. 2006. 5:91–103.
6. Korea Internet & Security agency. Report of Policy & Technology for RFID. 2006. 10.
7. Park DK. Strategies for application of ubiquitous technology. The Official Journal of the IHF. 2009. 45:8–11.
8. Kim DS, Kim JC, Kim SH, Yoo SK. A study on the patient location monitoring system based on RFID-RSSI. JKSMI. 2009. 15:41–48.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print











 XML Download
XML Download