Abstract
Figures and Tables
Table 1
In vitro antibacterial activity against aerobic bacteria reported in several studies performed in Korea
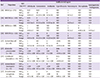
| Ref | Organism |
MIC (µg/mL) |
Antibacterial agent | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arbekacin | Gentamicin | Amikacin | Ciprofloxacin | Vancomycin | Teicoplanin | Quinupristin/Dalfopristin | |||
| [16] | MSSA (n = 271) | MIC50 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 2 | ND | 1 | ND | ND |
| MIC90 | 0.5 | 32 | 4 | ND | 1 | ND | ND | ||
| Range | 0.06 to 2 | 0.125 to 256 | 0.5 to 32 | ND | 0.5 to 2 | ND | ND | ||
| [16] | MSCNS (n = 129) | MIC50 | 0.25 | 2 | 2 | ND | 1 | ND | ND |
| MIC90 | 0.5 | 32 | 8 | ND | 2 | ND | ND | ||
| Range | 0.015 to 2 | 0.125 to256 | 0.125 to 16 | ND | 0.25 to 2 | ND | ND | ||
| [18] | MRSA (n = 328) | MIC50 | 1 | ND | ND | ND | 1 | 4 | 1 |
| MIC90 | 1 | ND | ND | ND | 2 | 8 | 1 | ||
| Range | 0.06 to 2 | ND | ND | ND | 0.5 to 2 | 0.06 to 16 | 0.25 to 1 | ||
| [16] | MRCNS (n = 122) | MIC50 | 0.5 | 32 | 8 | ND | 1 | ND | ND |
| MIC90 | 2 | 256 | 128 | ND | 2 | ND | ND | ||
| Range | 0.03 to 32 | 0.125 to 256 | 0.125 to 256 | ND | 0.25 to 2 | ND | ND | ||
| [17] | Escherichia coli (n = 30) | MIC50 | 1 | 0.5 | 2 | <0.03 | ND | ND | ND |
| MIC90 | 1 | 16 | 4 | 32 | ND | ND | ND | ||
| Range | 0.25 to 16 | <0.12 to 64 | 0.5 to 32 | <0.03 to 64 | ND | ND | ND | ||
| [17] | Klebsiella pneumoniae (n = 30) | MIC50 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 0.06 | ND | ND | ND |
| MIC90 | >128 | >128 | 128 | 32 | ND | ND | ND | ||
| Range | 0.5 to >128 | 0.5 to >128 | 1 to 128 | <0.03 to 128 | ND | ND | ND | ||
| [17] | Citrobacter freundii (n = 15) | MIC50 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0.12 | ND | ND | ND |
| MIC90 | 16 | 128 | 32 | 4 | ND | ND | ND | ||
| Range | 0.5 to >128 | 0.5 to >128 | 1 to >128 | <0.03 to 8 | ND | ND | ND | ||
| [17] | Acinetobacter baumannii (n = 15) | MIC50 | 1 | 2 | 8 | 0.25 | ND | ND | ND |
| MIC90 | >128 | >128 | >128 | 128 | ND | ND | ND | ||
| Range | 0.5 to >128 | 0.5 to >128 | 0.5 to >128 | 0.06 to >128 | ND | ND | ND | ||
| [17] | Pseudomonas aeruginosa (n = 29) | MIC50 | 2 | 2 | 8 | 0.25 | ND | ND | ND |
| MIC90 | 64 | >128 | >128 | 32 | ND | ND | ND | ||
| Range | 0.5 to 64 | 0.5 to >128 | 1 to >128 | 0.06 to >128 | ND | ND | ND | ||
ND, not done; MSSA, methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus; MSCNS, methicillin-susceptible coagulase negative Staphylococcus species; MRSA, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; MRCNS, methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative Staphylococcus species; MIC50, minimal inhibitory concentration for 50% of the organisms; MIC90, minimal inhibitory concentration for 90% of the organisms.
Table 2
Clinical efficacy and safety of arbekacin sulfate in patients with MRSA

| Ref | Year | Sex | Clinical status | Organisms detected | Clinical efficacy rate | Microbiologic efficacy rate | Adverse reactions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [9] | 1994 | NA | Pneumonia (n = 37) | MRSA (n = 85) | Total 85% | Total 83% | NA |
| Enterocolitis (n = 22) | Pneumonia 84% | Pneumonia 87% | |||||
| UTI (n = 1) | Intra-abdominal infection 79% | Intra-abdominal infection 79% | |||||
| Intra-abdominal infection (n = 14) | UTI 100% | ||||||
| Wound infection (n = 6) | Enterocolitis 82% | ||||||
| Biliary tract infection (n = 5) | Wound infection 100% | ||||||
| Hepatobiliary infection 100% | |||||||
| [10] | 2003 | 29 infants | Sepsis (n = 4) | MRSA (n = 27) | Totalc 79.3% | None | NA |
| Pneumonia (n = 17) | MRCNS (n = 2) | Sepsis 75.0% | |||||
| NEC (n = 3) | Othersb | Pneumonia 82.4% | |||||
| Othersa (n = 4) | Others 75.0% | ||||||
| [11]d | 2008 | M/F; 15/4 | Pneumonia (n = 14) | MRSA (N = 14) | Total 71.4% | Total 46.2% | Subjective symptoms 15.8% |
| Abnormal laboratory finding 36.8% | |||||||
| [31] | 2012 | M/F; 64/39 | SST (n = 66) | MRSA (n = 78) | Total 67.4% | None | NA |
| OM (n = 14) | MRSE (n = 13) | ||||||
| Sepsis (n = 8) | MRSC (n = 4) | ||||||
| Pneumonia (n = 5) | |||||||
| Others (n = 10) | |||||||
| [12] | 2012 | M/F; 10/3 | Sepsis (n = 3) | MRSA | Total 66.7% | Total 62.5% | Total 38.5% |
| Pneumonia (n = 10) | Sepsis 66.7% | Sepsis 50.0% | |||||
| Pneumonia 66.7% | Pneumonia 66.7% | ||||||
| [26] | 2013 | M/F; 16/13 | Sepsis (n = 8) | MRSA (n = 22) | Total 89.7% | MRSA 69.2% | <5 mg/kg; 33.3% |
| Pneumonia (n = 21) | MRSA/PAE (n = 4) | <5 mg/kg; 77.8% | P. aeruginosa 100% | ≥5 to <6; 12.5% | |||
| MRSA/ABA (n = 2) | ≥5 to <6; 87.5% | ≥6; 8.3% | |||||
| MRSA/PAE/ABA (n = 1) | ≥6; 100% |
MRSA, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; NA, not applicable; UTI, urinary tract infection; MRCNS, methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative Staphylococcus species; SST, skin and soft tissue infection; OM, osteomyelitis; MRSE, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis; MRSC, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus capitis; PAE, Pseudomonas aeruginosa; ABA, Acinetobacter baumannii.
aVentriculitis (n = 1), cellulitis (n = 1), submandibular glanditis (n = 1), funisitis (n = 1), staphylococcal exanthematous disease (n = 1).
b3 coagulase-negative staphylococcus, 2 Enterococcus faecalis, 3 P. aeruginosa, 1 Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Serratia, Acinetobacter.
c6 cases of ABK only, 23 combinations (ampicillin/sulbactam 100% vs. other combination 64.3%, P < 0.05).
dClinical/bacteriologic analysis (n = 14), adverse reactions (n = 19).
Table 3
Comparative study of arbekacin with glycopeptide in patients with MRSA infection

| Ref | Year | Sex (ABK vs GLY) | CA | Clinical status | Clinical efficacy rate | Microbiological efficacy rate | Adverse reactions (ABK vs. GLY) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [33] | 2003 | ABK 479, VAN 93, TEI 24 | VAN, TEI | Sepsis (n = 33) | ABK/VAN/TEI, 74.7%/64.3%/30.8% | ABK/VAN/TEI, 43.8%/35.1%/45.5% | ABK/VAN/TEI, 5.3%/5.8%/13.0% |
| Pneumonia (n = 196) | |||||||
| Others (n = 86) | |||||||
| [13] | 2011 | M/F; 43/30 vs. 43/30 | VAN | Sepsis (n = 5) | ABK/VAN, 65.3%/76.1% (P = 0.157) | ABK/VAN, 71.2%/79.5% (P = 0.249) | 15.1% vs 32.9% (P = 0.019) |
| WC related (n = 45) | |||||||
| Othersb | |||||||
| [14] | 2013 | M/F; 42/21 vs. 36/23 | VAN | SSTI | ABK/VAN; 67.2%/78.0% (P = 0.265) | ABK/VAN, 73.0%/83.1% (P = 0.264) | 15.9% vs 49.2% (P = 0.001) |
| [34] | 2015 | M/F; 9/11 vs. 15/21 | VAN | CSOMc | ABK/VAN, 90.0%/97.2% (P = 0.288) | ABK/VAN, 85.0%/97.2% (P = 0.125) | 5.0% vs 33.3% (P = 0.020) |
| [15]a | 2016 | M/F; 43/28 vs. 49/22 | TEI | SST (n = 43) | ABK/TEI, 59.4%/69.1% (P = 0.257) | ABK/TEI, 72.9%/70.3% (P = 0.835) | 18.3% vs 36.6% (P = 0.003) |
| Pneumonia (n = 10) | |||||||
| Otitis media (n = 8) | |||||||
| Sepsis (n = 7) | |||||||
| Others (n = 3) |
aSkin and soft tissue infection (ABK vs. TEI; 60.6% vs. 63.5%), pneumonia (ABK vs. TEI; 14.1% vs. 16.9%), otitis media (ABK vs. TEI; 11.3% vs. 0%), sepsis (ABK vs. TEI; 9.8% vs. 14.1%), others (ABK vs. TEI; 4.2% vs. 5.6%).
MRSA, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; ABK, arbekacin; GLY, glycopeptide; CA, comparative antibiotics; VAN, vancomycin; TEI, teicoplanin; WC, wound-and catheter-related infection; SSTI, skin and soft tissue infection; CSOM, chronic suppurative otitis media.
bOtitis media; n = 13, meningitis; n = 6, pneumonia; n = 29, peritonitis; n = 6, urinary tract infection, cellulitis, neutropenic fever; 1.
cChronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM) without cholesteatoma (arbekacin vs. vancomycin 70.0% vs. 75.0%), CSOM with cholesteatoma (arbekacin vs. vancomycin 30.0% vs. 25.0%).
Table 4
Adverse reactions after use of arbekacin

| Clinical adverse reactions |
Yamamoto 2012 [12] (n = 13) |
Hwang 2012 [31] (n = 0) |
Shimizu 2003 [33] (n = 470) |
Hwang 2012 [13] (n = 73) |
Hwang 2013 [14] (n = 63) |
Hwang 2015 [34] (n = 20) |
Hwang 2016 [15] (n = 71) |
Miura 2015 [32] (n = 54) |
Matsumoto 2013 [26] (n = 29) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nephrotoxicity | 23.1% | 7.8% | 4.26% | 6.8% | 3.2% | 0.0% | 5.6% | 11.1% | 6.9% |
| Acute renal failure | 1.91% | ||||||||
| Renal function decreased | 1.28% | ||||||||
| Nephropathy | 0.64% | ||||||||
| Creatinine increased | 0.21% | ||||||||
| BUN increased | 0.21% | ||||||||
| Hepatotoxicity | 7.7% | 7.8% | 0.85% | 4.1% | 6.3% | 5.0% | 8.5% | 6.9% | |
| Gastrointestinal symptoms | |||||||||
| PMC | 3.7% | ||||||||
| Diarrhea | 3.7% | ||||||||
| Nausea | 1.9% | ||||||||
| Ileus | 1.9% | ||||||||
| Constipation | 3.5% | ||||||||
| Leukopenia | 5.5% | 3.2% | 0.0% | 4.2% | 3.7% | ||||
| Thrombocytopenia | 0.21% | ||||||||
| Skin rash | 0.21% | 0.0% | 3.2% | 0.0% | 1.4% | 9.3% | |||
| Drug fever | 1.4% | ||||||||
| EIP | 7.7% | ||||||||
| Eighth nerve lesion | 0.21% |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download