Abstract
Background
The objective of this study was to evaluate protective immunity against diphtheria and tetanus in the Korean population.
Materials and Methods
Healthy subjects were enrolled at four university hospitals in Korea. Subjects were assigned to seven age groups (every 10 years). Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits were used for measurement of diphtheria or tetanus anti-toxoid antibodies in sera, and geometric mean concentrations (GMC) of antibodies were determined. Subjects with antibody titers <0.1 IU/mL would require a booster vaccination.
Results
A total of 1,605 subjects participated in this study. In analysis of antibody against diphtheria, subjects in the age group <11 yr showed the highest GMC (1.31 IU/mL) while the lowest GMC was observed in subjects in the 31-40 yr age group (0.17 IU/mL). With regard to tetanus, subjects in the age group <11 yr also showed the highest GMC (1.81 IU/mL). Among subjects ≥11 yr (600 subjects), 363 (60.5%) would require a diphtheria booster, and 422 (70.4%) would require a tetanus booster.
Conclusions
GMC of antibodies against diphtheria and tetanus of adolescents and adults were relatively low, while those of children in Korea were satisfactory. Approximately two-thirds of Korean adolescent and adult subjects in this study would require a booster vaccination in order to maintain long-term protective immunity against diphtheria and tetanus.
Figures and Tables
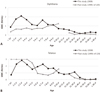 | Figure 1Geometric mean concentrations (GMC) of subjects are shown by age group. (A) Diphtheria anti-toxoid antibodies. (B) Tetanus anti-toxoid antibodies. |
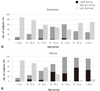 | Figure 2Number (%) of subjects with different antibody concentrations (<0.01 IU/mL, 0.01-0.1 IU/mL, or ≥0.1 IU/mL) are shown by age group. The subjects with antibody titers <0.1 IU/mL would require a booster vaccination while those with ≥0.1 IU/mL are considered as seroprotective against (A) Diphtheria, or (B) Tetanus. |
References
1. Vetter RT, Johnson GM. Vaccination update. Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, mumps, rubella, measles. Postgrad Med. 1995. 98:133–137. 141–142. 144–145.
2. Prevots R, Sutter RW, Strebel PM, Cochi SL, Hadler S. Tetanus surveillance--United States, 1989-1990. MMWR CDC Surveill Summ. 1992. 41:1–9.
3. Gergen PJ, McQuillan GM, Kiely M, Ezzati-Rice TM, Sutter RW, Virella G. A population-based serologic survey of immunity to tetanus in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1995. 332:761–766.

4. . Expanded programme on immunization. Outbreak of diphtheria, update. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 1993. 68:134–140.
5. Hardy IR, Dittmann S, Sutter RW. Current situation and control strategies for resurgence of diphtheria in newly independent states of the former Soviet Union. Lancet. 1996. 347:1739–1744.

6. The Korean Pediatric Society. Lee HJ, editor. Diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus vaccines. Immunization guideline. 2008. 6th ed. Seoul: The Korean Pediatric Society;75–90.
7. Maple PA, Efstratiou A, George RC, Andrews NJ, Sesardic D. Diphtheria immunity in UK blood donors. Lancet. 1995. 345:963–965.

8. IPSEN J Jr. Immunization of adults against diphtheria and tetanus. N Engl J Med. 1954. 251:459–466.

9. Galazka AM, Robertson SE. Immunization against diphtheria with special emphasis on immunization of adults. Vaccine. 1996. 14:845–857.

10. Sesardic D, Corbel MJ. Testing for neutralising potential of serum antibodies to tetanus and diphtheria toxin. Lancet. 1992. 340:737–738.

11. Christenson B, Böttiger M. Serological immunity to diphtheria in Sweden in 1978 and 1984. Scand J Infect Dis. 1986. 18:227–233.

12. Khuri-Bulos N, Hamzah Y, Sammerrai SM, Shehabi A, Hamed R, Arnaout MA, Turk J, Qubain H. The changing epidemiology of diphtheria in Jordan. Bull World Health Organ. 1988. 66:65–68.
13. Cellesi C, Zanchi A, Michelangeli C, Giovannoni F, Sansoni A, Rossolini GM. Immunity to diphtheria in a sample of adult population from central Italy. Vaccine. 1989. 7:417–420.

14. Vitek CR, Wharton M. Plotkin SA, Orenstein WA, Offit PA, editors. Diphtheria toxoid. Vaccines. 2008. 5th ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co.;139–156.

15. Wassilak SGF, Roper MH, Kretsinger K, Orenstein WA. Plotkin SA, Orenstein WA, Offit PA, editors. Tetanus toxoid. Vaccines. 2008. 5th ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co.;805–840.

16. Gergen PJ, McQuillan GM, Kiely M, Ezzati-Rice TM, Sutter RW, Virella G. A population-based serologic survey of immunity to tetanus in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1995. 332:761–766.

17. Stark K, Schönfeld C, Barg J, Molz B, Vornwald A, Bienzle U. Seroprevalence and determinants of diphtheria, tetanus and poliomyelitis antibodies among adults in Berlin, Germany. Vaccine. 1999. 17:844–850.

18. Reported tetanus in Korea. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (KCDC). Accessed 10 December 2011. Available at: http://cdc.go.kr/kcdchome/jsp/observation/stat/tot/STATTOT0902List.jsp.
19. Kang JH, Hur JK, Kim JH, Lee KI, Park SE, Ma SH, Lee MS, Ban SJ, Hong SH, Cho DH, Lee SH. Age related serosurvey of immunity to tetanus in Korean populations. Korean J Infect Dis. 2001. 33:104–111.
20. Kang JH, Hur JK, Kim JH, Lee KI, Park SE, Ma SH, Lee MS, Baek SY, Hong SH, Min HK. Age related seroepidemiological study of diphtheria among Koreans. Korean J Infect Dis. 2000. 32:1–7.
21. Lee BK, Park JK, Yoo JI, Shin KH, Sohn YM, Park KD, Lee CG, Kim JS. Serological immunity to diphtheria among Korean population. Korean J Infect Dis. 1998. 30:278–283.
22. Christenson B, Böttiger M. Serological immunity to diphtheria in Sweden in 1978 and 1984. Scand J Infect Dis. 1986. 18:227–233.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download