Abstract
Background
Patients with malignancy are considered to be at high risk of severe pandemic influenza A/H1N1 2009. This study was conducted to identify the severity of pandemic influenza A/H1N1 2009 among patients with malignancy.
Materials and Methods
Between August 2009 and December 2009, we reviewed clinical data and medical records of 31 patients with malignancy and 63 hospitalized patients without malignancy.
Results
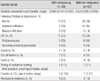
Eighty-three patients with laboratory-confirmed pandemic influenza A/H1N1 2009 were admitted. The rate of ICU admission was higher among patients with malignancy (without malignancy 13% vs with malignancy 35%, P=0.024). The mortality rate was higher among patients with malignancy (without malignancy 6% vs with malignancy 25%, P=0.033). Patients using immunosuppressants showed a higher rate of lower respiratory tract infection (83% vs 24%, P=0.013).
Figures and Tables
Table 1
Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Malignancy Who Were Confirmed to be Infected with Pandemic Influenza A/H1N1 2009
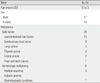
Table 2
Clinical and Laboratory Characteristics of 83 Patients with Laboratory-confirmed Pandemic Influenza A/H1N1 2009: Comparison between Subjects with Malignancy and without Malignancy
References
1. Perez-Padilla R, de la Rosa-Zamboni D, Ponce de Leon S, Hernandez M, Quiñones-Falconi F, Bautista E, Ramirez-Venegas A, Rojas-Serrano J, Ormsby CE, Corrales A, Higuera A, Mondragon E, Cordova-Villalobos JA. INER Working Group on Influenza. Pneumonia and respiratory failure from swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) in Mexico. N Engl J Med. 2009. 361:680–689.

2. Zarocostas J. World Health Organization declares A (H1N1) influenza pandemic. BMJ. 2009. 338:b2425.

3. Walsh EE, Cox C, Falsey AR. Clinical features of influenza A virus infection in older hospitalized persons. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002. 50:1498–1503.

4. Neuzil KM, Maynard C, Griffin MR, Heagerty P. Winter respiratory viruses and health care use: a population-based study in the northwest United States. Clin Infect Dis. 2003. 37:201–207.

5. Yousuf HM, Englund J, Couch R, Rolston K, Luna M, Goodrich J, Lewis V, Mirza NQ, Andreeff M, Koller C, Elting L, Bodey GP, Whimbey E. Influenza among hospitalized adults with leukemia. Clin Infect Dis. 1997. 24:1095–1099.

6. Tai Y, Lee TC, Chang HL, Chen KT. Epidemiology and outcomes of hospitalization of influenza in the cancer population in Taiwan. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2009. 135:1061–1066.

7. Kunisaki KM, Janoff EN. Influenza in immunosuppressed populations: a review of infection frequency, morbidity, mortality, and vaccine responses. Lancet Infect Dis. 2009. 9:493–504.

8. Safdar A, Armstrong D. Infectious morbidity in critically ill patients with cancer. Crit Care Clin. 2001. 17:531–570.

9. Zarychanski R, Stuart TL, Kumar A, Doucette S, Elliott L, Kettner J, Plummer F. Correlates of severe disease in patients with 2009 pandemic influenza (H1N1) virus infection. CMAJ. 2010. 182:257–264.

10. Hajjar LA, Mauad T, Galas FR, Kumar A, da Silva LF, Dolhnikoff M, Trielli T, Almeida JP, Borsato MR, Abdalla E, Pierrot L, Filho RK, Auler JO Jr, Saldiva PH, Hoff PM. Severe novel influenza A (H1N1) infection in cancer patients. Ann Oncol. 2010. 21:2333–2341.

11. Redelman-Sidi G, Sepkowitz KA, Huang CK, Park S, Stiles J, Eagan J, Perlin DS, Pamer EG, Kamboj M. 2009 H1N1 influenza infection in cancer patients and hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. J Infect. 2010. 60:257–263.

12. Venkata C, Sampathkumar P, Afessa B. Hospitalized patients with 2009 H1N1 influenza infection: the Mayo Clinic experience. Mayo Clin Proc. 2010. 85:798–805.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download