Abstract
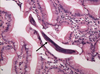
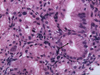
Gastrointestinal strongyloidiasis and Cytomegalovirus infection mostly occur in patients receiving cancer chemotherapy, undergoing immunosuppressive therapy after organ transplantation, and suffering from acquired immune deficiency syndrome. A 56-year-old man was admitted to the hospital because of abdominal pain and constipation. He had a 10-year history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and has been treated intermittently with systemic steroid. The gastroduodenoscopic examination showed a single ulcer on the duodenal bulb and microscopic finding of the biopsy specimens from the ulcer revealed Strongyloides stercoralis and cytomegalovirus immunohistochemical stain positive intranuclear inclusion body on the mucosal surface. The patient was successfully treated with albendazole and ganciclovir.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Choi SI, Hong SW, Lee KG. Hyperinfection syndrome with Strongyloides stercoralis: report of a case. Korean J Pathol. 1989. 23:359–364.
2. Kim J, Joo HS, Kim DH, Lim H, Kang YH, Kim MS. A case of gastric stronglyoidiasis in a Korean patient. Korean J Parasitol. 2003. 41:63–67.

3. Hwang IR, Kim JH, Lee KJ, Shin YJ, Yoo BM, Kim YS, Hahm KB, Cho SW. Two cases of CMV esophagitis and proctitis. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 1998. 18:763–768.
4. Song IS, Choi KW, Kim CY, Jung HC, Kim TH, Kim YS, Kim JS, Lee CH. Efficacy of the treatment with antiviral agent in the cytomegalovirus infection of the gastrointestinal tract. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1998. 32:184–195.
5. Wang BY, Krishnan S, Isenberg HD. Mortality associated with concurrent strongyloidosis and cytomegalovirus infection in a patient on steroid therapy. Mt Sinai J Med. 1999. 66:128–132.
6. Gupta S, Jain A, Fanning TV, Couriel DR, Jimenez CA, Eapen GA. An unusual cause of alveolar hemorrhage post hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a case report. BMC Cancer. 2006. 6:87.

7. Keiser PB, Nutman TB. Strongyloides stercoralis in the immunocompromised population. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2004. 17:208–217.

8. Yoon DH, Yang SJ, Kim JS, Hong ST, Chai JY, Lee SH, Chi JG. A case of fatal malabsorption syndrome caused by strongyloidiasis complicated with isosporiasis and human cytomegalovirus infection. Korean J Parasitol. 1992. 30:53–58.

9. Tsai HC, Lee SS, Liu YC, Lin WR, Huang CK, Chen YS, Wann SR, Tsai TH, Lin HH, Yen MY, Yen CM, Chen ER. Clinical manifestations of strongyloidiasis in southern Taiwan. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2002. 35:29–36.
10. Rhee JC, Choi KW, Lee HY, Koh KC, Paik SW, Lee JK, Lee KT, Lee JH, Lee SH, Kang IK, Hyun JG, Rhee PL, Kim JJ, Oh YR, Chae JI. A case of gastric strongyloidiasis diagnosed by endoscopic biopsy. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 1999. 19:249–253.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download