Abstract
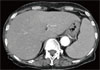
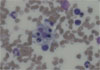
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) is a rare disease with a high mortality rate. It is associated with a variety of bacterial, viral, fungal, and parasitic infections. In the literature, there are several cases of HLH associated with scrub typhus in adults, all of which were successfully treated with antibiotic therapy for scrub typhus. This report describes a case of HLH accompanied by scrub typhus in an 81-year-old woman, in whom the disease progressed despite doxycyclin therapy. The patient refused to receive immunosuppressive chemotherapy for HLH and died 5 weeks after admission due to multi-organ failure. To our knowledge, this is the first case of death due to scrub typhus-associated HLH in an adult.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Lee HG, Min SK, Kong SJ, Lee SJ, Song HH, Yoon JW, Lee MG, Shin DH, Kang SH, Lee JY, Park YI, Choi MG. Clinical features of tsutsugamushi disease in Chuncheon. Korean J Med. 2005. 69:190–196.
2. Varghese GM, Abraham OC, Mathai D, Thomas K, Aaron R, Kavitha ML, Mathai E. Scrub typhus among hospitalised patients with febrile illness in South India: magnitude and clinical predictors. J Infect. 2006. 52:56–60.

3. Janka G, Imashuku S, Elinder G, Schneider M, Henter JI. Infection- and malignancy-associated hemophagocytic syndromes. Secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1998. 12:435–444.
5. Kobayashi T, Takizawa H, Hiroshima K, Uruma T, Enokihara H, Okuyama A. [A case of new type scrub typhus (tsutsugamushi disease) presenting with acute respiratory failure and hemophagocytic syndrome]. Nihon Kyobu Shikkan Gakkai Zasshi. 1992. 30:447–452. Japanese.
6. Iwasaki H, Hashimoto K, Takada N, Nakayama T, Ueda T, Nakamura T. Fulminant Rickettsia tsutsugamushi infection associated with haemophagocytic syndrome. Lancet. 1994. 343:1236.

7. Takami A, Yamauchi H, Asakura H, Ishiyama K, Nakao S. Tsutsugamushi disease (scrub typhus)-associated hemophagocytic syndrome. Int J Hematol. 2002. 75:337–338.

8. Miyakawa K, Ohsugi K, Sugahara S, Kuriyama C, Kikuchi A, Ohta M. [Tsutsugamushi disease with hemophagocytosis complicated by Parvovirus B19 infection]. Nippon Naika Gakkai Zasshi. 2006. 95:2544–2546. Japanese.

9. Premaratna R, Williams HS, Chandrasena TG, Rajapakse RP, Kularatna SA, de Silva HJ. Unusual pancytopenia secondary to haemophagocytosis syndrome in rickettsioses. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2009. 103:961–963.

10. Yang SH, Ho YH, Chu CH, Chu SY. Childhood scrub typhus in eastern Taiwan: ten-year experience from a medical center. Acta Paediatr Taiwan. 2007. 48:332–336.
11. Diagnosis of Tsutsugamushi disease. Korea Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed 18 May 2010. Available at: http://cdc.go.kr/kcdchome/jsp/diseasedic/dic/DISEDIC0001Detail.jsp?menuid=510535&contentid=8150&boardid=null&appid=kcdcdz01&pageNum=null&sub=null&tabinx=1&q_had01=A&q_had02=2010&idxType=0&idxNum=9.
12. Blacksell SD, Bryant NJ, Paris DH, Doust JA, Sakoda Y, Day NP. Scrub typhus serologic testing with the indirect immunofluorescence method as a diagnostic gold standard: a lack of consensus leads to a lot of confusion. Clin Infect Dis. 2007. 44:391–401.

13. Henter JI, Horne A, Aricó M, Egeler RM, Filipovich AH, Imashuku S, Ladisch S, McClain K, Webb D, Winiarski J, Janka G. HLH-2004: Diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2007. 48:124–131.

14. Ishii E, Ohga S, Aoki T, Yamada S, Sako M, Tasaka H, Kuwano A, Sasaki M, Tsunematsu Y, Ueda K. Prognosis of children with virus-associated hemophagocytic syndrome and malignant histiocytosis: correlation with levels of serum interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor. Acta Haematol. 1991. 85:93–99.

15. Imashuku S, Hibi S, Fujiwara F, Ikushima S, Todo S. Haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, interferon-gammanaemia and Epstein-Barr virus involvement. Br J Haematol. 1994. 88:656–658.

16. Imashuku S, Hibi S, Sako M, Ishida Y, Mugishima H, Chen J, Tsunematsu Y. Soluble interleukin-2 receptor: a useful prognostic factor for patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Blood. 1995. 86:4706–4707.

17. Iwasaki H, Takada N, Nakamura T, Ueda T. Increased levels of macrophage colony-stimulating factor, gamma interferon, and tumor necrosis factor alpha in sera of patients with Orientia tsutsugamushi infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1997. 35:3320–3322.

18. Kaito K, Kobayashi M, Katayama T, Otsubo H, Ogasawara Y, Sekita T, Saeki A, Sakamoto M, Nishiwaki K, Masuoka H, Shimada T, Yoshida M, Hosoya T. Prognostic factors of hemophagocytic syndrome in adults: analysis of 34 cases. Eur J Haematol. 1997. 59:247–253.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download