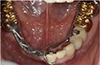
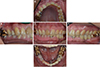
|
|
| 1. |
Eggbeer D, Bibb R, Williams R. The computer-aided design and rapid prototyping fabrication of removable partial denture frameworks. Proc Inst Mech Eng H 2005;219:195–202.
|
|
| 2. |
Bibb RJ, Eggbeer D, Williams RJ, Woodward A. Trial fitting of a removable partial denture framework made using computer-aided design and rapid prototyping techniques. Proc Inst Mech Eng H 2006;220:793–797.
|
|
| 3. |
Wu J, Wang X, Zhao X, Zhang C, Gao B. A study on the fabrication method of removable partial denture framework by computer-aided design and rapid prototyping. Rapid Prototyp J 2012;18:318–323.
|
|
| 4. |
Kattadiyil MT, Mursic Z, AlRumaih H, Goodacre CJ. Intraoral scanning of hard and soft tissues for partial removable dental prosthesis fabrication. J Prosthet Dent 2014;112:444–448.
|
|
| 5. |
Hong YS, Park EJ, Kim SK, Koak JY, Heo SJ, Park JM. Surveyed restoration and RPD framework design utilizing electronic surveying. J Korean Acad Prosthodont 2011;49:354–361.
|
|
| 6. |
Ormianer Z, Gross M. A 2-year follow-up of mandibular posture following an increase in occlusal vertical dimension beyond the clinical rest position with fixed restorations. J Oral Rehabil 1998;25:877–883.
|
|
| 7. |
Ormianer Z, Palty A. Altered vertical dimension of occlusion: a comparative retrospective pilot study of tooth- and implantsupported restorations. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2009;24:497–501.
|
|
| 8. |
Abduo J, Lyons K. Clinical considerations for increasing occlusal vertical dimension: a review. Aust Dent J 2012;57:2–10.
|
|
| 9. |
Kanazawa M, Iwaki M, Minakuchi S, Nomura N. Fabrication of titanium alloy frameworks for complete dentures by selective laser melting. J Prosthet Dent 2014;112:1441–1447.
|
|
| 10. |
Koutsoukis T, Zinelis S, Eliades G, Al-Wazzan K, Rifaiy MA, Al Jabbari YS. Selective laser melting technique of Co-Cr dental alloys: A review of structure and properties and comparative analysis with other available techniques. J Prosthodont 2015;24:303–312.
|
|




 ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print