Abstract
Bell's palsy is an acute-onset unilateral peripheral facial neuropathy. For patients with sequelae of facial paresis, the successful rehabilitation of fully edentulous arches is challenging. This case report described the treatment procedures and clinical considerations to fabricate complete dentures of a patient who showed unilateral displacement of mandible, unilateral chewing pattern and parafunctional jaw movement due to sequelae of Bell's palsy. Gothic arch tracing was used to record reproducible centric relation and lingualized occlusion was performed to provide freedom to move between centric relation and the patient's habitual functional area in fabricating satisfactory dentures in terms of function and esthetics. (J Korean Acad Prosthodont 2017;55:451-7)
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.Eviston TJ., Croxson GR., Kennedy PG., Hadlock T., Krishnan AV. Bell's palsy: aetiology, clinical features and multidisciplinary care. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2015. 86:1356–61.

2.Dawson PE. Centric relation. Its effect on occluso-muscle harmony. Dent Clin North Am. 1979. 23:169–80.
3.Payne SH. A posterior set-up to meet individual requirements. Dent Digest. 1941. 47:20–2.
6.Carlsson GE. Symptoms of mandibular dysfunction in complete denture wearers. J Dent. 1976. 4:265–70.

7.Mercado MD., Faulkner KD. The prevalence of craniomandibular disorders in completely edentulous denture-wearing subjects. J Oral Rehabil. 1991. 18:231–42.

8.Chen CK., Tang YB. Myectomy and botulinum toxin for paralysis of the marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve: a series of 76 cases. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007. 120:1859–64.

9.Yurkstas AA., Kapur KK. Factors influencing centric relation records in edentulous mouths. 1964. J Prosthet Dent. 2005. 93:305–10.
10.Smith HF Jr. A comparison of empirical centric relation records with location of terminal hinge axis and apex of the gothic arch tracing. J Prosthet Dent. 1975. 33:511–20.

11.Myers M., Dziejma R., Goldberg J., Ross R., Sharry J. Relation of Gothic arch apex to dentist-assisted centric relation. J Prosthet Dent. 1980. 44:78–81.

12.Utz KH., Müller F., Bernard N., Hültenschmidt R., Kurbel R. Comparative studies on check-bite and central-bearing-point method for the remounting of complete dentures. J Oral Rehabil. 1995. 22:717–26.

13.Linsen SS., Stark H., Samai A. The influence of different registration techniques on condyle displacement and electromyographic activity in stomatognathically healthy subjects: a prospective study. J Prosthet Dent. 2012. 107:47–54.

14.Becker CM., Swoope CC., Guckes AD. Lingualized occlusion for removable prosthodontics. J Prosthet Dent. 1977. 38:601–8.

16.Inoue S., Kawano F., Nagao K., Matsumoto N. An in vitro study of the influence of occlusal scheme on the pressure distribution of complete denture supporting tissues. Int J Prosthodont. 1996. 9:179–87.
Go to : 
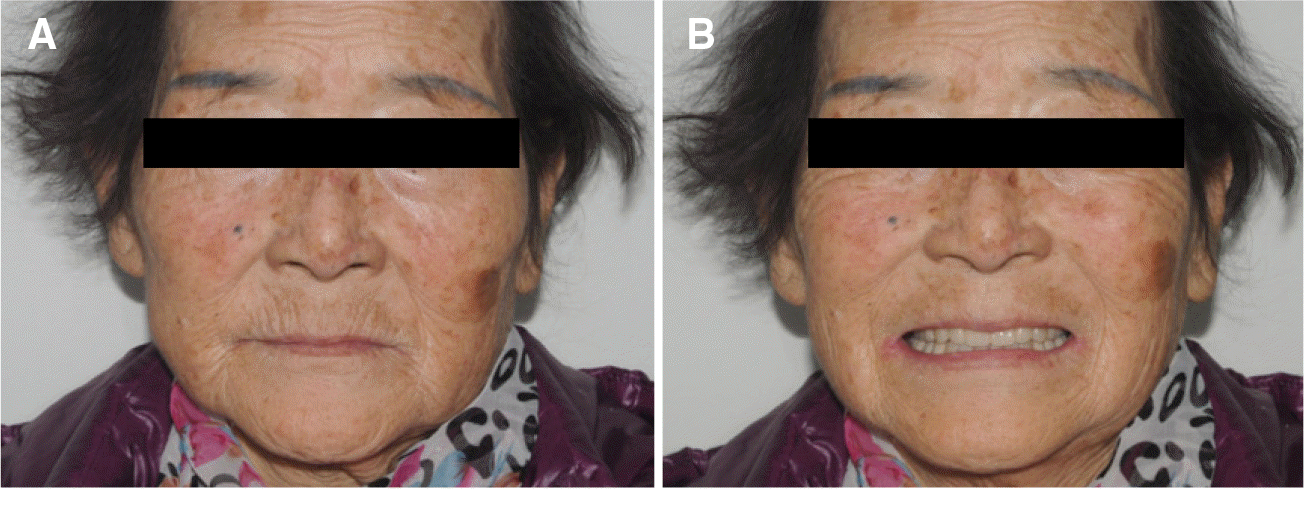
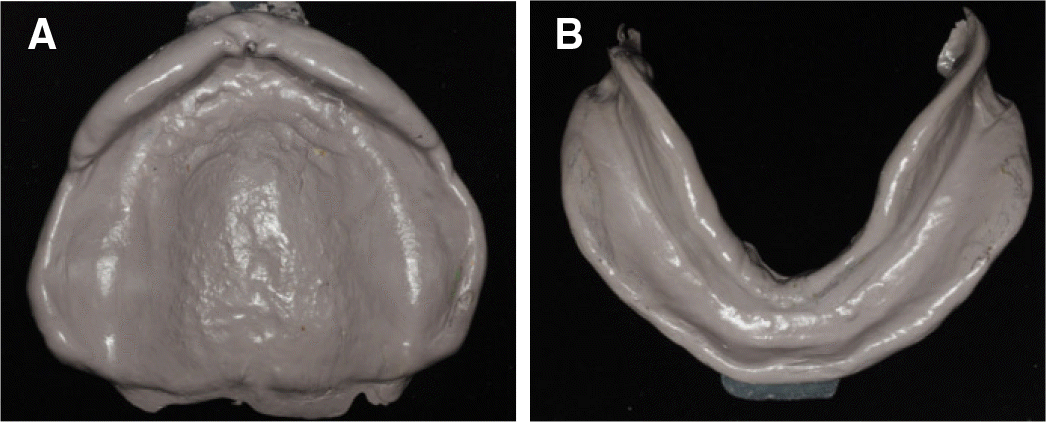 | Fig. 1.Initial intraoral photograph. (A) Lateral view (right), (B) Frontal view, (C) Lateral view (left). |
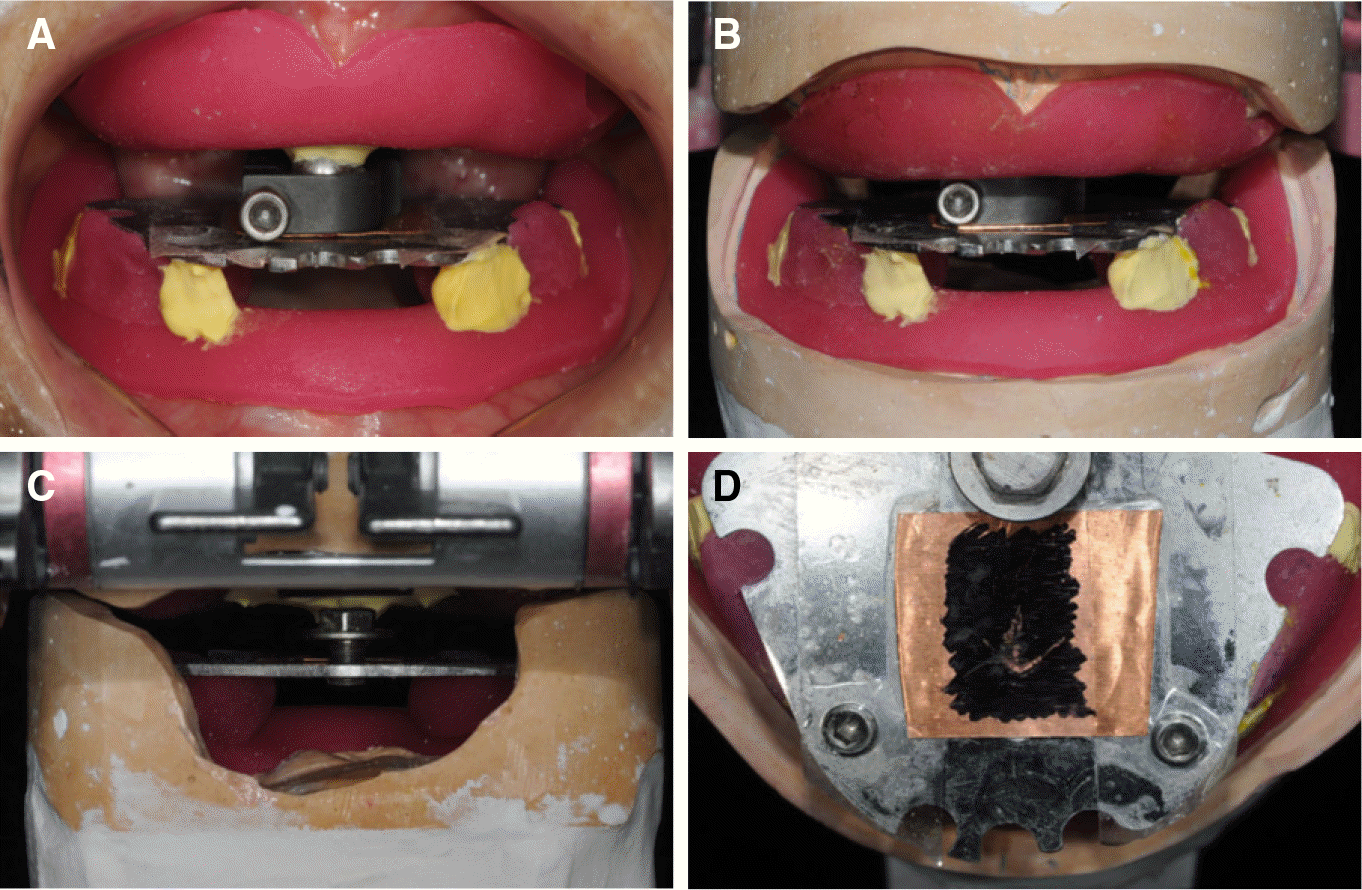 | Fig. 3.Registration of centric relation using an intraoral gothic arch tracer. (A) Intraoral photograph wearing the gothic arch tracer, (B) Frontal view and (C) Posterior view of mounted master casts using the gothic arch tracer, (D) Gothic arch tracing. |
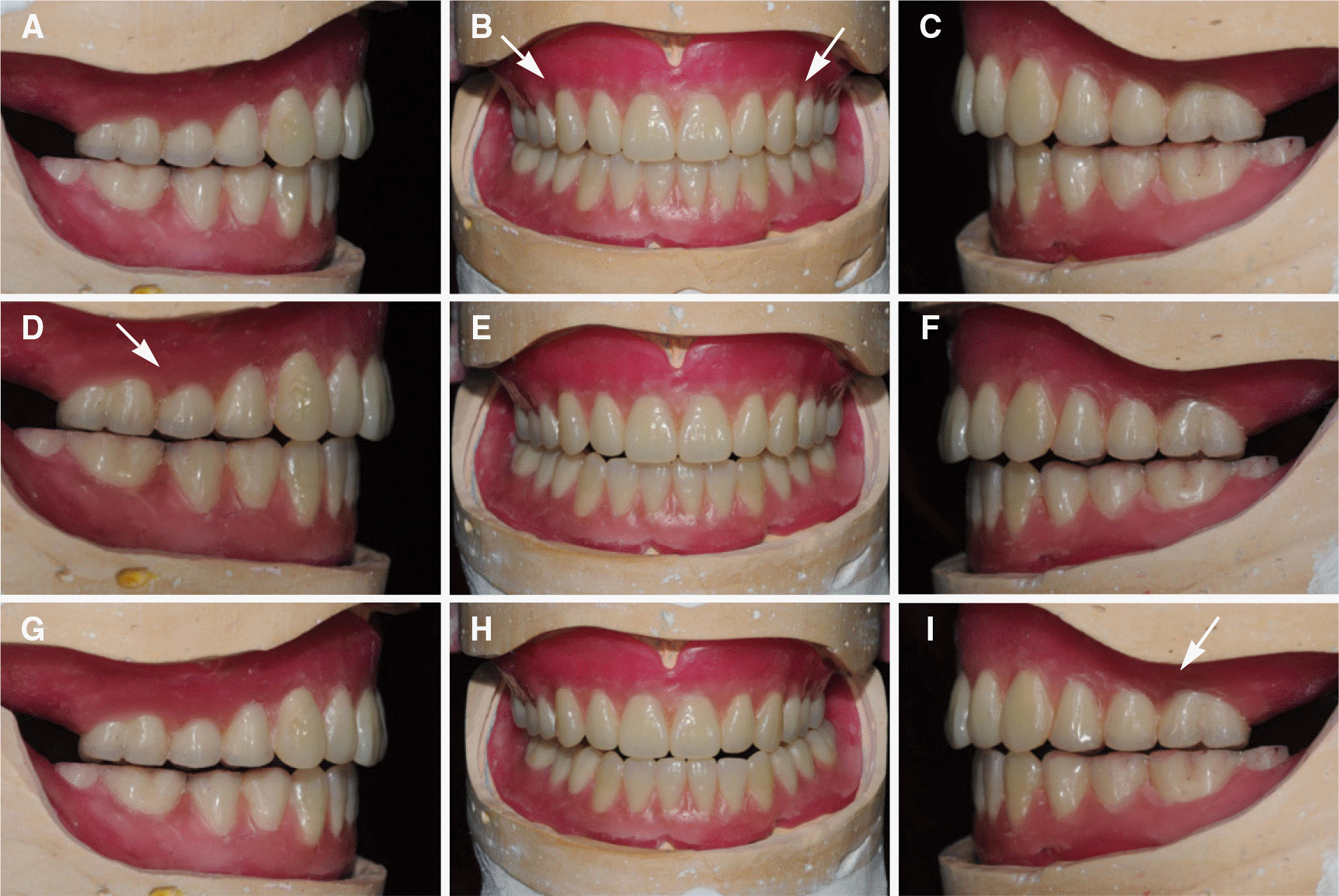 | Fig. 4.(A) Lateral view (right), (B) frontal view, maxillary posterior teeth are rotated slightly to avoid all contact of the buccal cusp (arrows). and (C) lateral view (left) of wax denture at centric relation, (D) Lateral view (right), working side contact is limited to maxillary lingual cusp (arrow), (E) frontal view, and (F) lateral view (left) at eccentric position to right side, (G) Lateral view (right), (H) frontal view, and (I) lateral view (left) at eccentric position to left side, working side contact is limited to maxillary lingual cusp (arrow). |
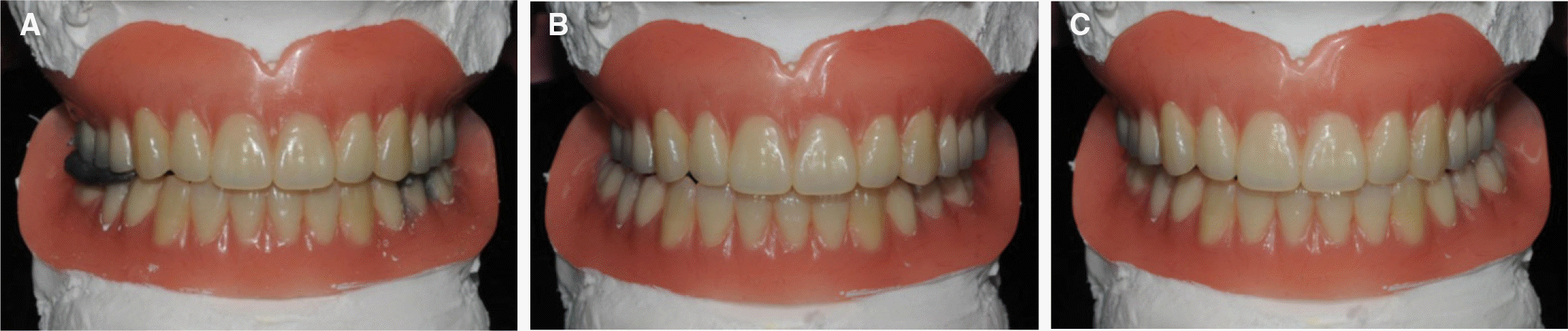 | Fig. 5.Clinical remounting of definitive dentures at (A) centric relation, (B) eccentric position to right side, and (C) eccentric position to left side. |
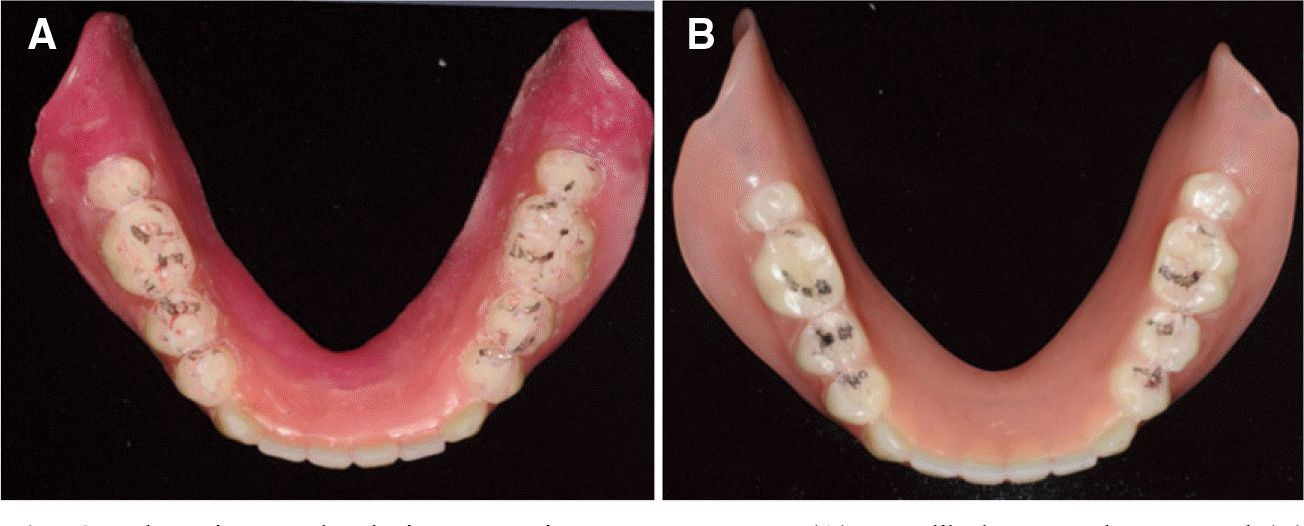 | Fig. 6.Indentation marks during excursive movements on (A) mandibular wax denture and (B) mandibular denture after selective grinding. |
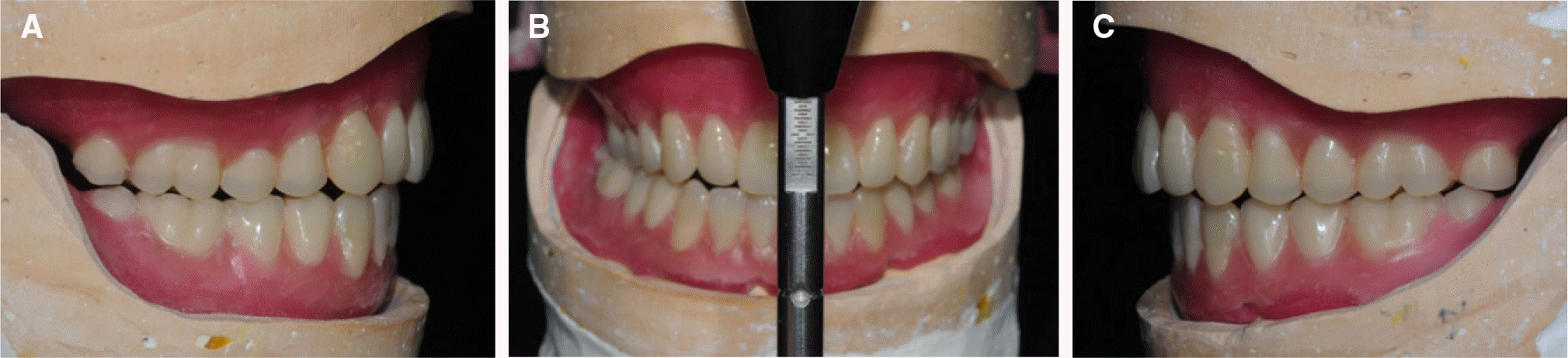 | Fig. 9.Discrepancy between two registration methods, gothic arch tracing and chin point guidance. Displacement of lower cast in chin point guidance compared to gothic arch tracing generates premature contact on right side. (A) Lateral view (right), (B) Frontal view, (C) Lateral view (left). |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download