Abstract
Prosthetic decision-making is complex because of various factors, and involves a combination of the individual dentist's interpretation of the objective clinical data and his or her interaction with the patient. Increasing therapeutic options and emerging outcome data demand the constant re-evaluation of our decision-making process. In this case, fixed prosthetic restorations were selected as a treatment method to reconstruct the occlusal plane of a patient with disharmonious occlusal plane. And the occlusal plane was re-established by establishing a treatment plan through diagnostic wax-up. Provisional restorations obtained by continuous re-evaluation for a sufficient period of time was replicated to definitive restorations using CAD/CAM technology. The results were satisfactory when they were observed through clinical follow-up for 3 months after the end of treatment. (J Korean Acad Prosthodont 2017;55:444-50)
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.Gross M. The science and art of occlusion and oral rehabilitation. Quintessence Publishing;2015.
2.Romeo G., Bresciano M. Diagnostic and technical approach to esthetic rehabilitations. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2003. 15:204–16.

3.Turner KA., Missirlian DM. Restoration of the extremely worn dentition. J Prosthet Dent. 1984. 52:467–74.

4.Willis FM. Features of the face involved in full denture prosthesis. Dent Cosmos. 1935. 77:851–4.
5.Kwon KR., Woo YH., Choi DG. The study of relationship between sagittal condylar guide angle and incisal guide angle during mandibular protrusion in normal Korean. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 1989. 27:11–36.
Go to : 
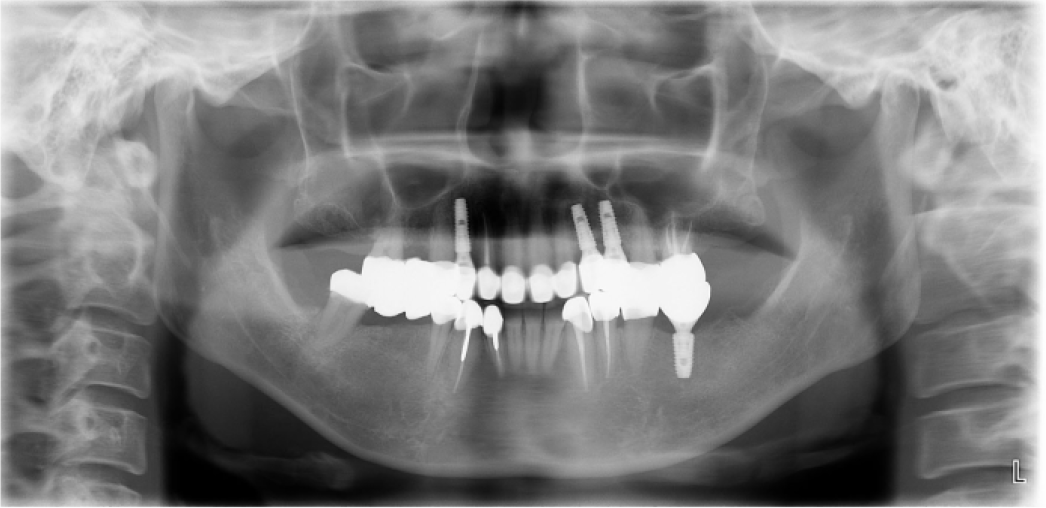
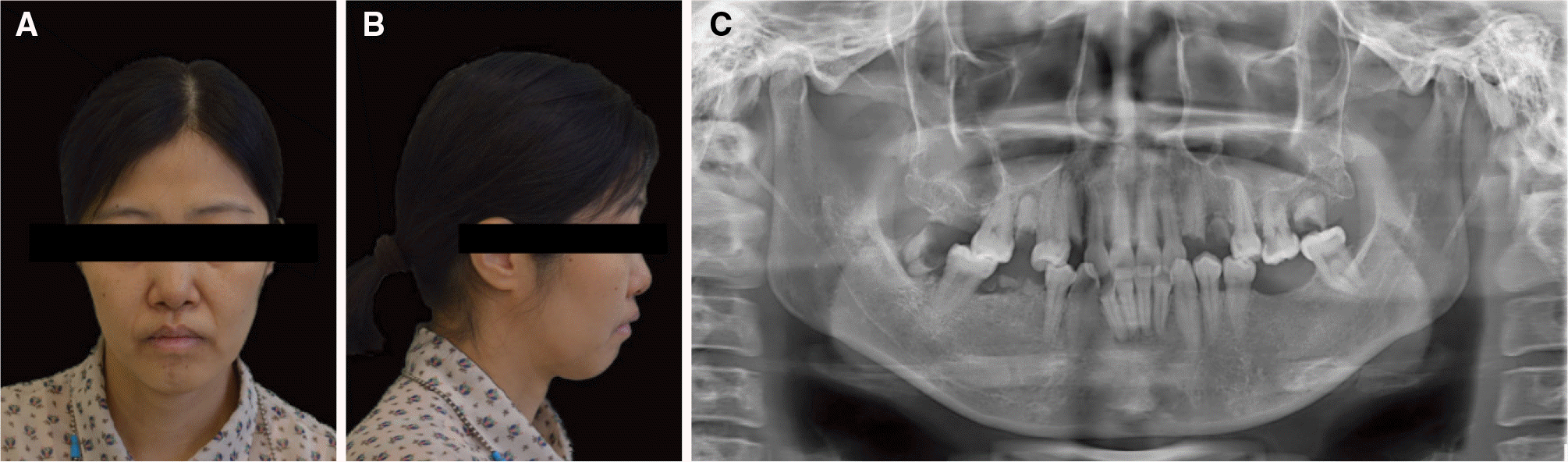 | Fig. 1.Preoperative extraoral photograph and panoramic view. (A) Frontal view, (B) Lateral view (right side), (C) Panoramic view. |
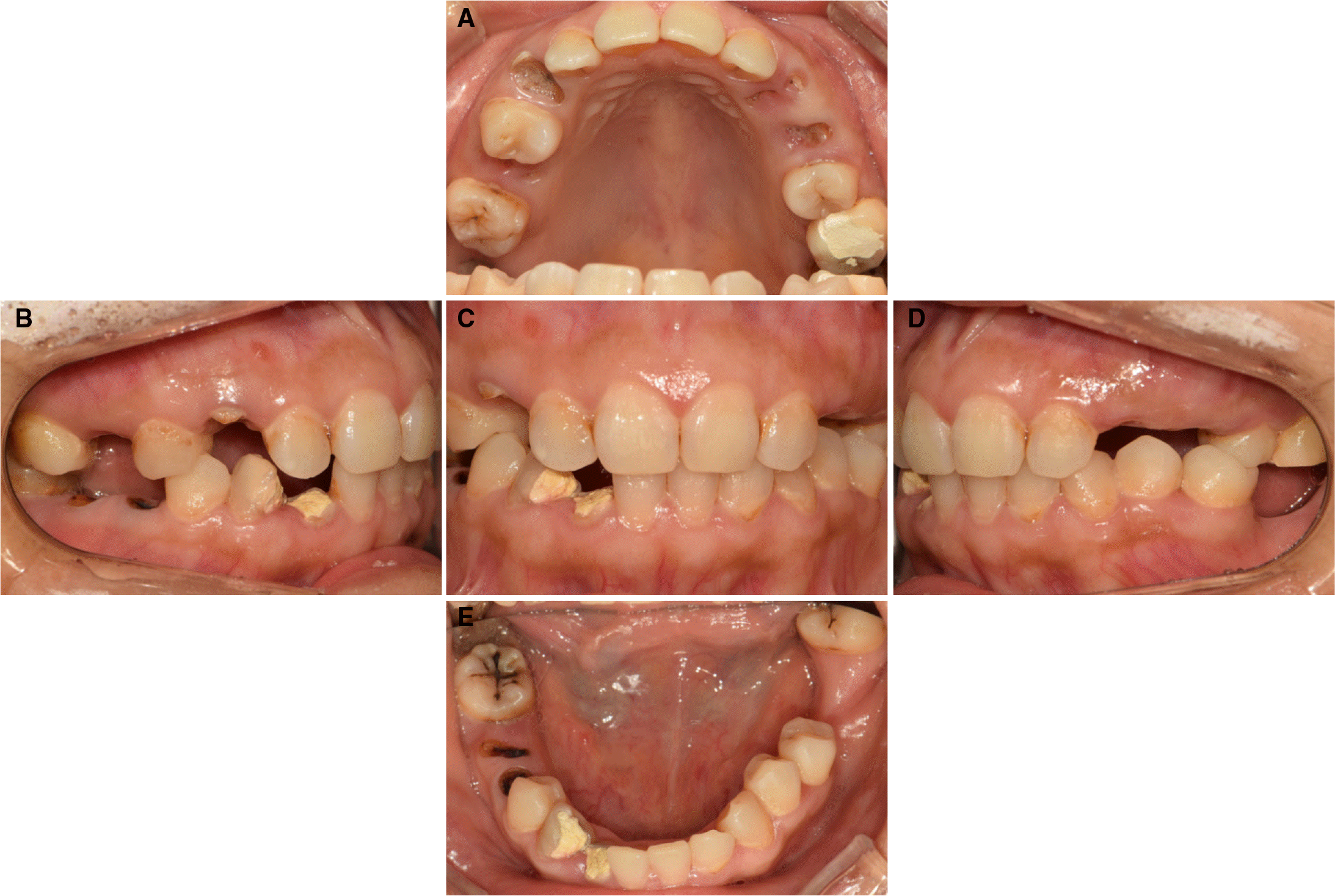 | Fig. 2.Preoperative intraoral view showing uneven occlusal plane. (A) Occlusal view of maxilla, (B) Lateral view (right side), (C) Frontal view, (D) Lateral view (left side). Extrusion of left lower premolar, (E) Occlusal view of mandible. |
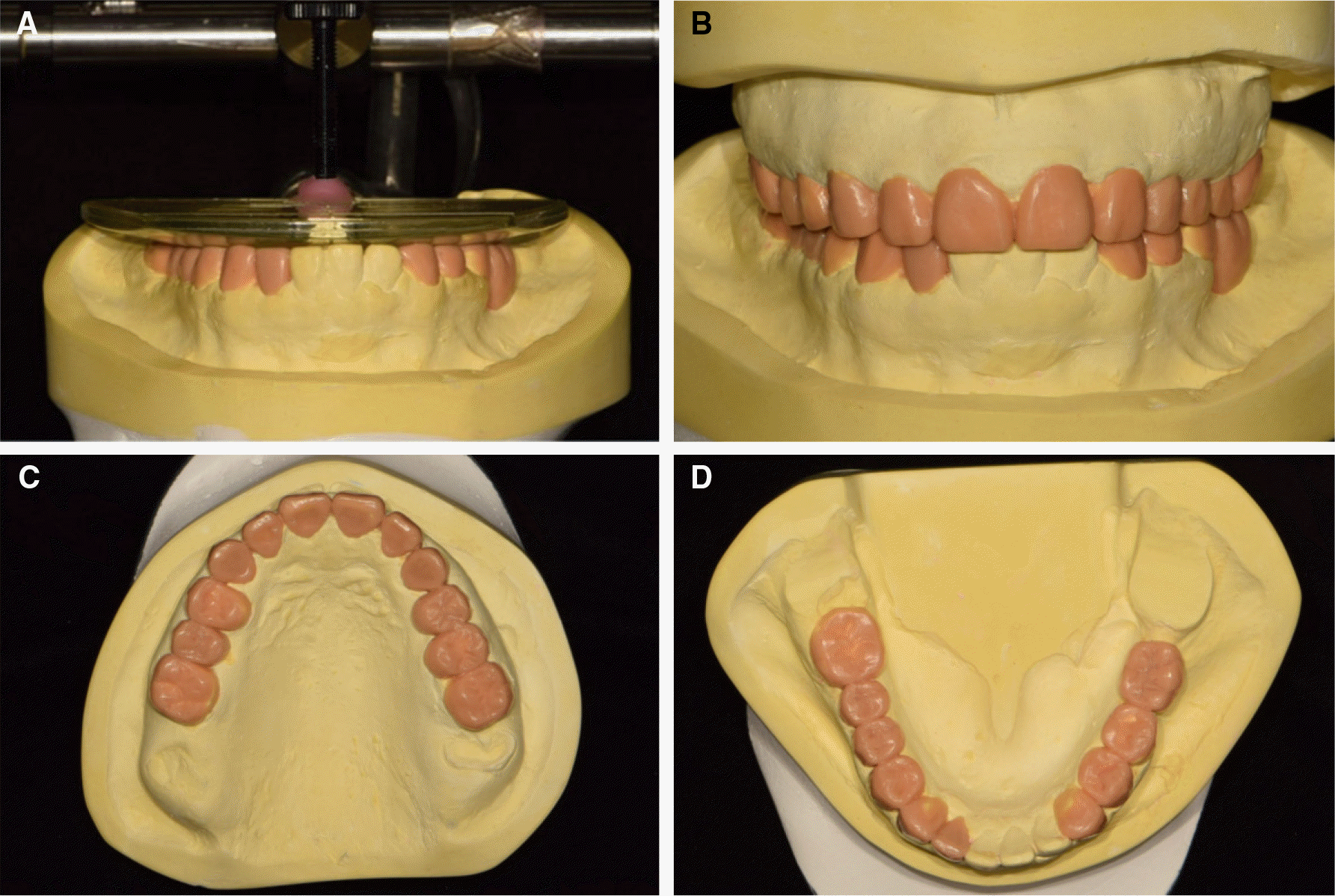 | Fig. 3.Diagnostic wax-up. (A) Diagnostic wax-up using template system, (B) Frontal view, (C) Occlusal view of maxilla, (D) Occlusal view of mandible. |
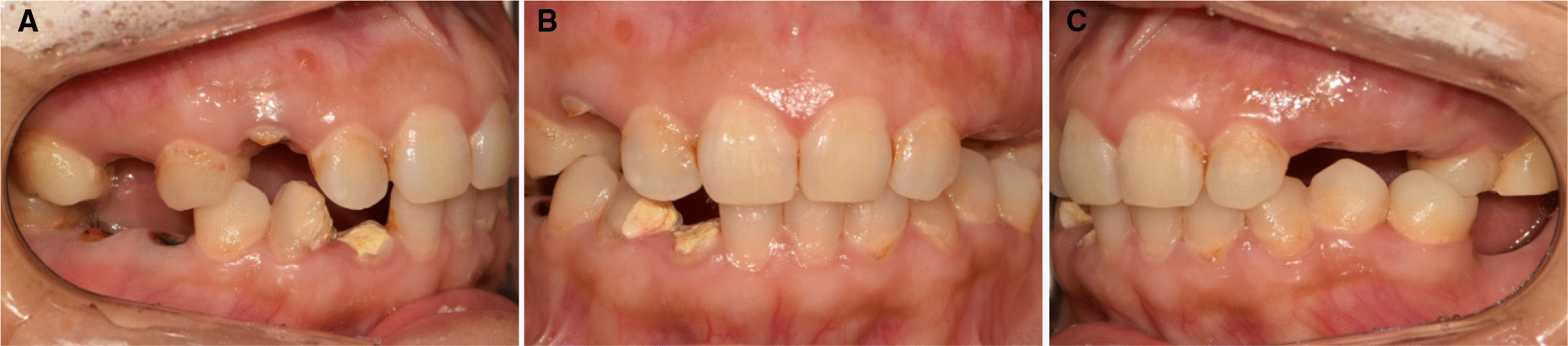 | Fig. 4.Provisional restoration. (A) Frontal view, (B) Occlusal view of maxilla, (C) Occlusal view of mandible. |
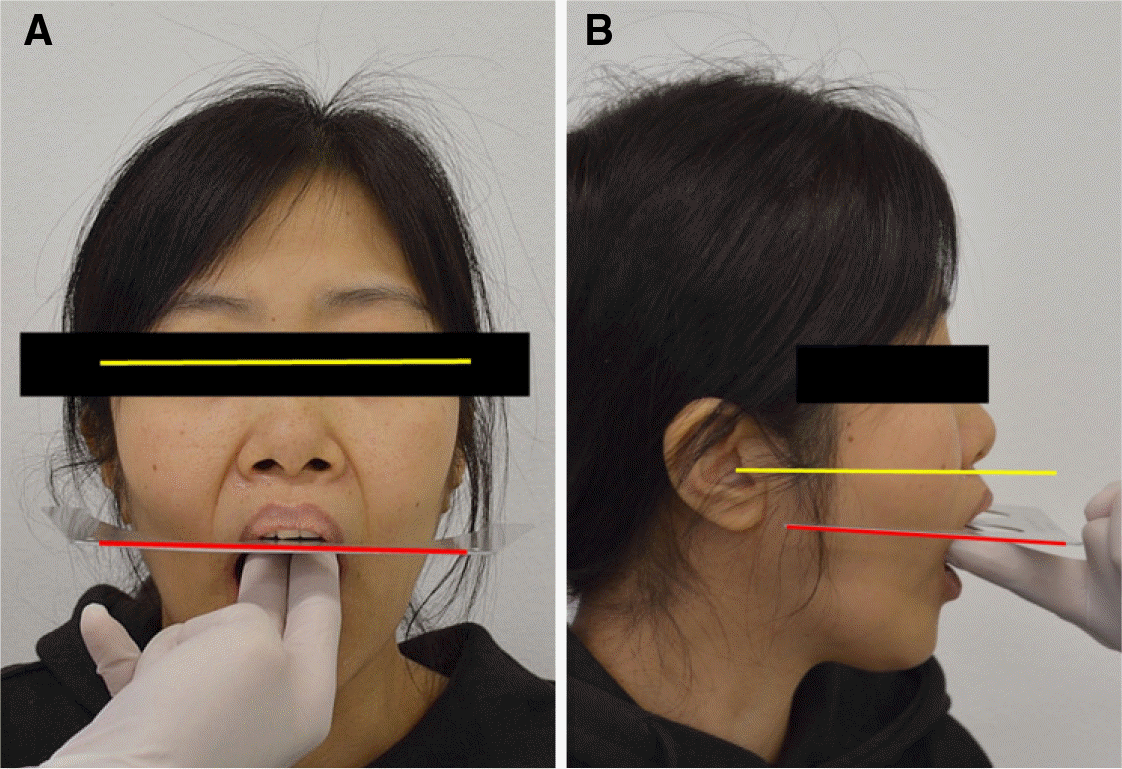 | Fig. 5.Assessment of provisional restoration (occlusal plane). (A) Frontal view, (B) Lateral view (right side). |
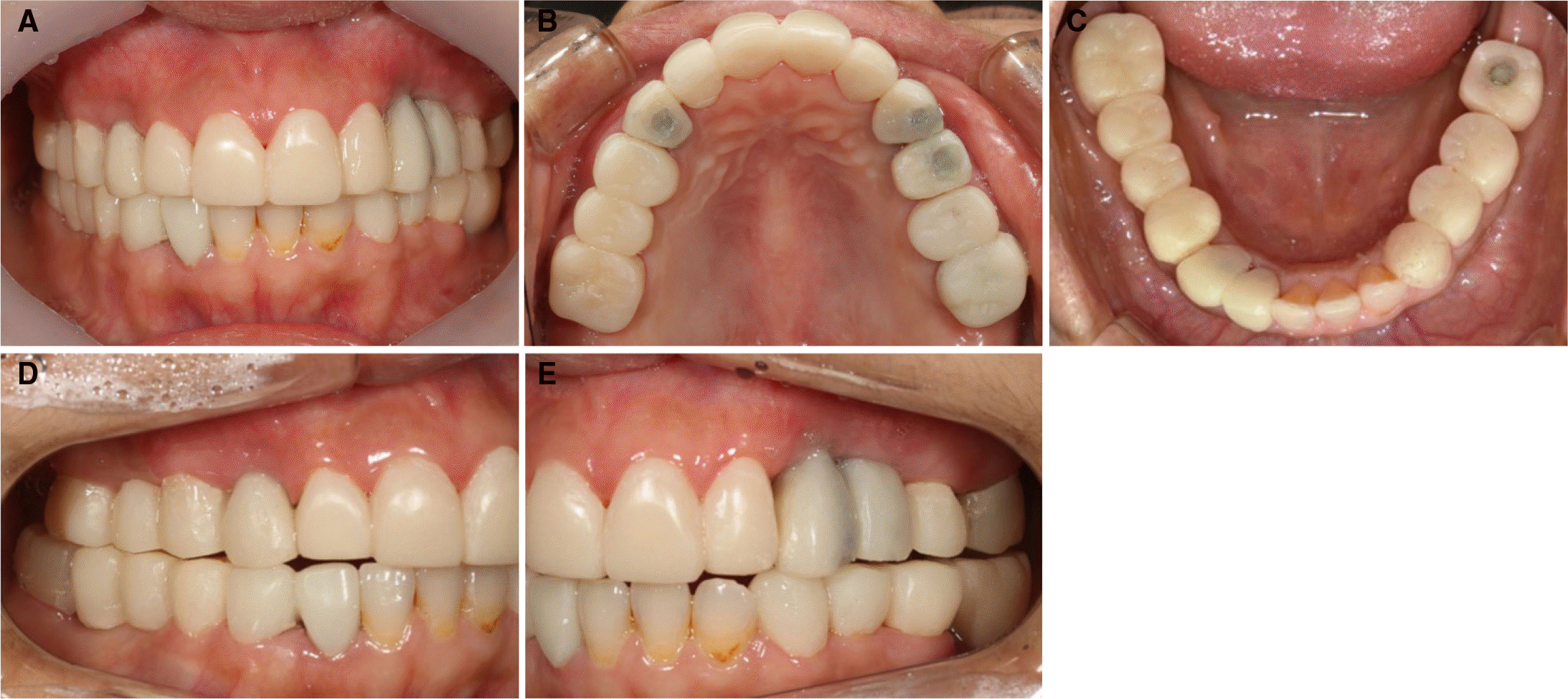 | Fig. 6.Provisional restoration after modification. (A) Frontal view, (B) Occlusal view of maxilla, (C) Occlusal view of mandible, (D) Lateral view (eccentric position, left side) (E) Lateral view (eccentric position, right side). |
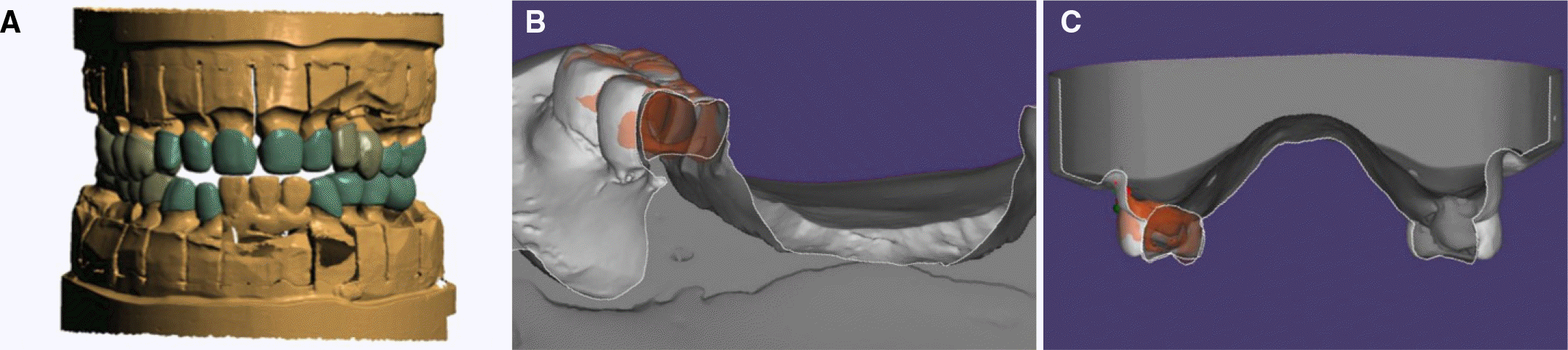 | Fig. 7.Computer-aided design. (A) Computer-aided design of prostheses, (B) Superimposition of mandibular provisional restoration and definitive restoration, (C) Superimposition of maxillary provisional restoration and definitive restoration. |
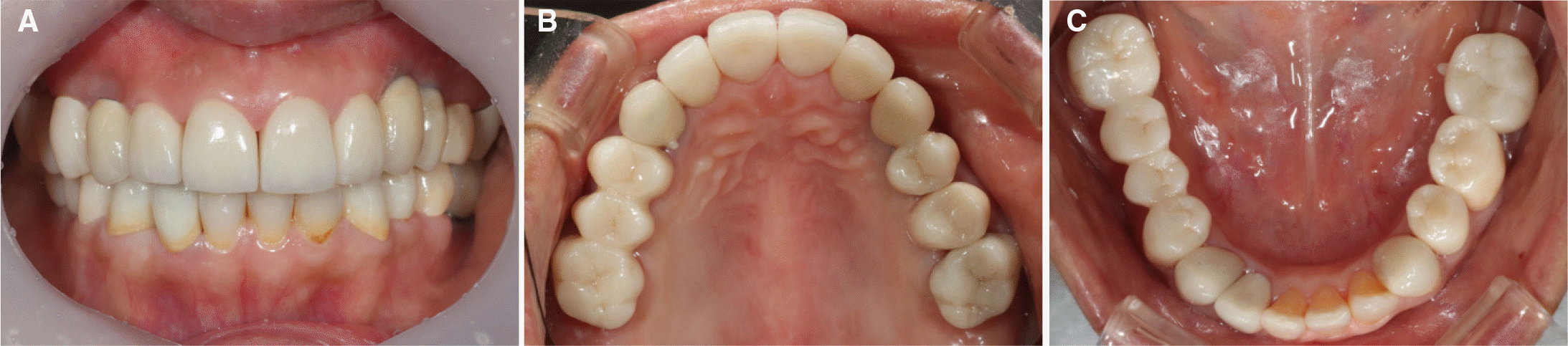 | Fig. 8.Definitive restoration. (A) Frontal view, (B) Occlusal view of maxilla, (C) Occlusal view of mandible. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download