Abstract
The implant-supported fixed dental prosthesis in irradiated maxilla needs meticulous treatment planning due to low bone healing capacity. All-on-4 concept implantation can reduce the number of implants to be placed avoiding bone grafting procedure. Conventionally, prefabricated angled abutments for tilted implants have been used. However, in this case, it was replaced with computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) abutment. This case report described all-on-4 concept implantation and fabrication of CAD/CAM zirconia fixed dental prostheses using CAD/CAM titanium abutments. (J Korean Acad Prosthodont 2017;55:218-24)
REFERENCES
1.Zarb G., Bolender C., Eckert S., Jacob R., Fenton A., Mericske-Stern R. Prosthodontic treatment for edentulous patients. 12th ed.St. Louis: Elsevier Mosby;2004. p. 427.
2.Beumer J III., Curtis TA., Marunick MT. Maxillofacial rehabilitation: prosthodontic and surgical considerations. St. Louis: Ishiyaku Euro America, Inc.;1996. p. 65–70. 85.
3.Malo′ P., Nobre Md., Lopes A. The rehabilitation of completely edentulous maxillae with different degrees of resorption with four or more immediately loaded implants: a 5-year retrospective study and a new classification. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2011. 4:227–43.
4.Malo′ P., de Arau′jo Nobre M., Lopes A., Francischone C., Rigolizzo M. "All-on-4" immediate-function concept for completely edentulous maxillae: a clinical report on the medium (3 years) and longterm (5 years) outcomes. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2012. 14:e139–50.
5.Malo′ P., de Arau′jo Nobre MA., Lopes AV., Rodrigues R. Immediate loading short implants inserted on low bone quantity for the rehabilitation of the edentulous maxilla using an All-on-4 design. J Oral Rehabil. 2015. 42:615–23.

6.Barnea E., Tal H., Nissan J., Tarrasch R., Peleg M., Kolerman R. The Use of Tilted Implant for Posterior Atrophic Maxilla. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2016. 18:788–800.

7.Kim KS., Kim YL., Bae JM., Cho HW. Biomechanical comparison of axial and tilted implants for mandibular full-arch fixed prostheses. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2011. 26:976–84.
8.Abdulmajeed AA., Lim KG., Närhi TO., Cooper LF. Complete-arch implant-supported monolithic zirconia fixed dental prostheses: A systematic review. J Prosthet Dent. 2016. 115:672–7.

9.Papaspyridakos P., Lal K. Computer-assisted design/computer-assisted manufacturing zirconia implant fixed complete prostheses: clinical results and technical complications up to 4 years of function. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2013. 24:659–65.
10.Rojas-Vizcaya F. Full zirconia fixed detachable implant-retained restorations manufactured from monolithic zirconia: clinical report after two years in service. J Prosthodont. 2011. 20:570–6.

11.Pozzi A., Holst S., Fabbri G., Tallarico M. Clinical reliability of CAD/CAM cross-arch zirconia bridges on immediately loaded implants placed with computer-assisted/template-guided surgery: a retrospective study with a follow-up between 3 and 5 years. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2015. 17:e86–96.

12.Kern JS., Kern T., Wolfart S., Heussen N. A systematic review and meta-analysis of removable and fixed implant-supported prostheses in edentulous jaws: post-loading implant loss. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2016. 27:174–95.

13.Tsuge T., Hagiwara Y. Influence of lateral-oblique cyclic loading on abutment screw loosening of internal and external hexagon implants. Dent Mater J. 2009. 28:373–81.

14.Roumanas E., Nishimura R., Beumer J., Moy P., Weinlander M., Lorant J. Craniofacial defects and osseointegrated implants: Six-year follow-up report on the success rates of craniofacial implants at UCLA. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1994. 9:579–85.
15.Chang JS., Ji W., Choi CH., Kim S. Catastrophic failure of a monolithic zirconia prosthesis. J Prosthet Dent. 2015. 113:86–90.

16.Lee DH. CAD/CAM-fabricated template for locating implant abutment screws in cement-retained anatomic zirconia restorations. J Prosthet Dent. 2015. 114:343–5.

17.Heintze SD., Rousson V. Survival of zirconia- and metal-supported fixed dental prostheses: a systematic review. Int J Prosthodont. 2010. 23:493–502.
Fig. 3.
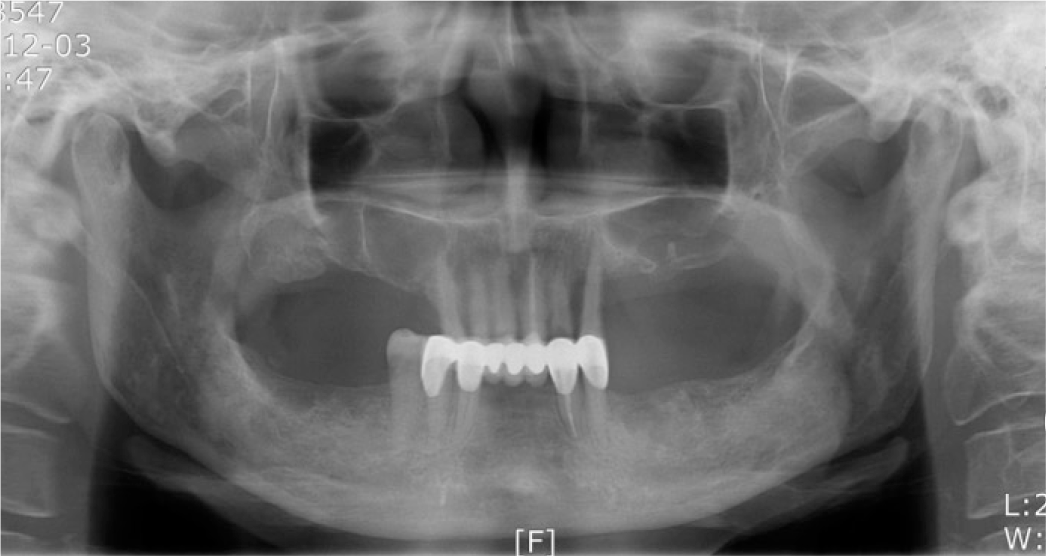
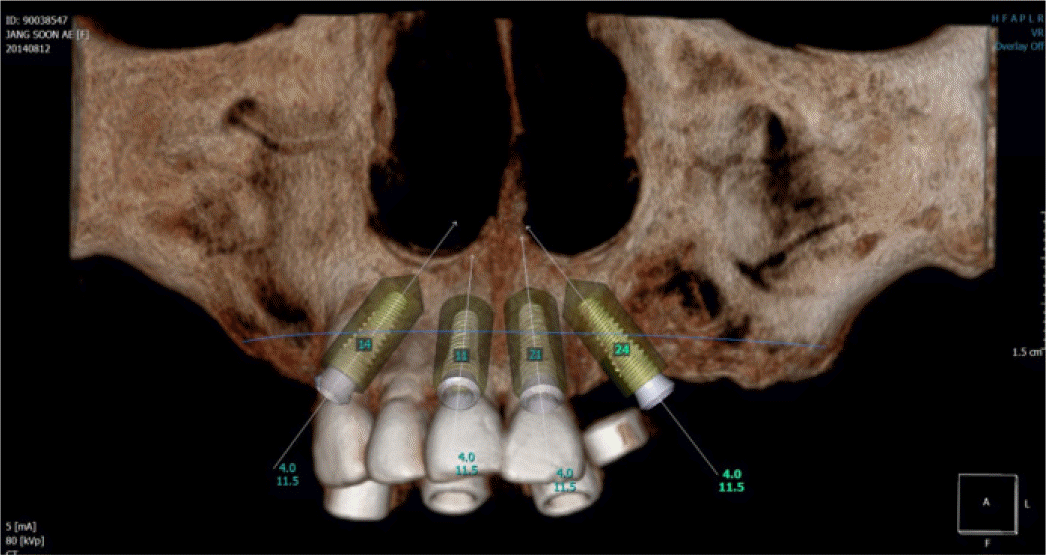
Placement of implants. (A) Intraoral surgery images of implants placed in the maxilla. (B) Panoramic radiograph after all-on-4 implant placement surgery.
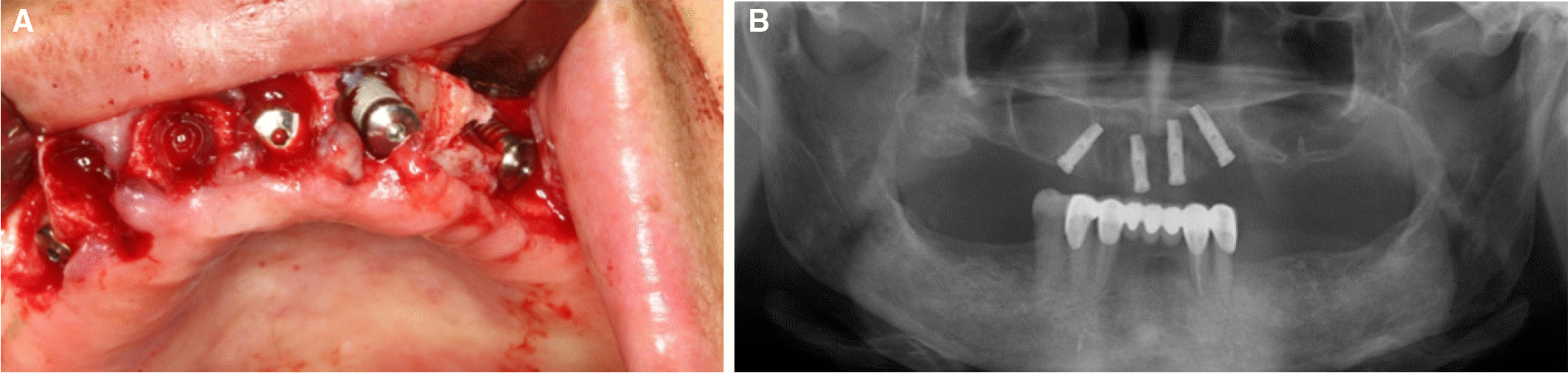
Fig. 4.
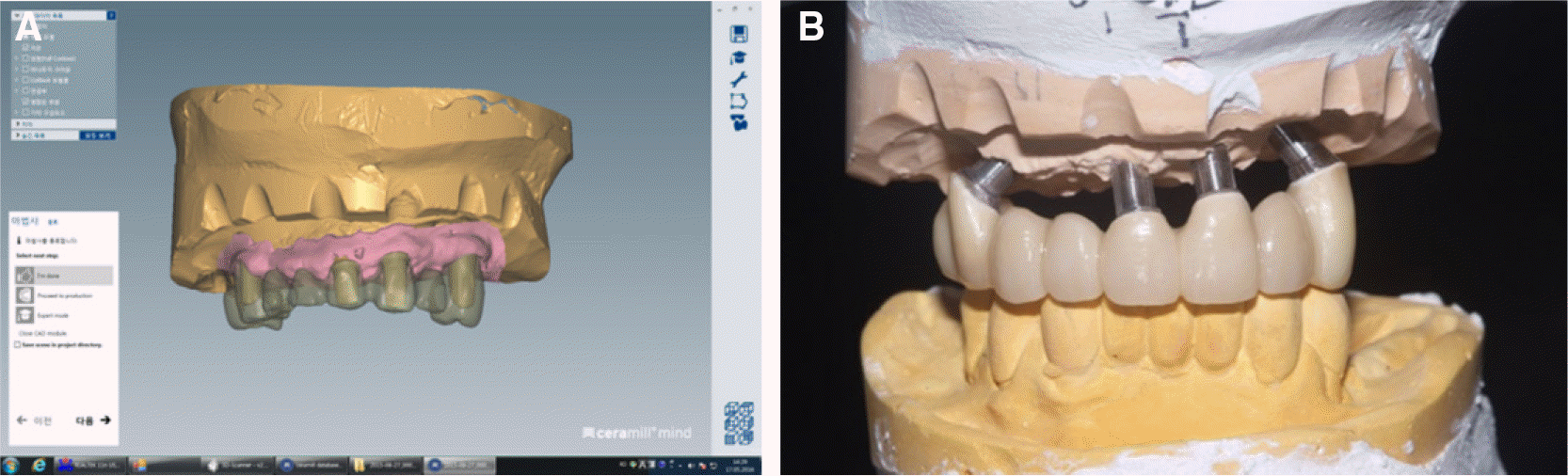
Impression and provisional prosthesis. (A) Splinted impression copings connected to implants, (B) Definitive implant-level cast, (C) Delivery of provisional restorations with temporary abutments.
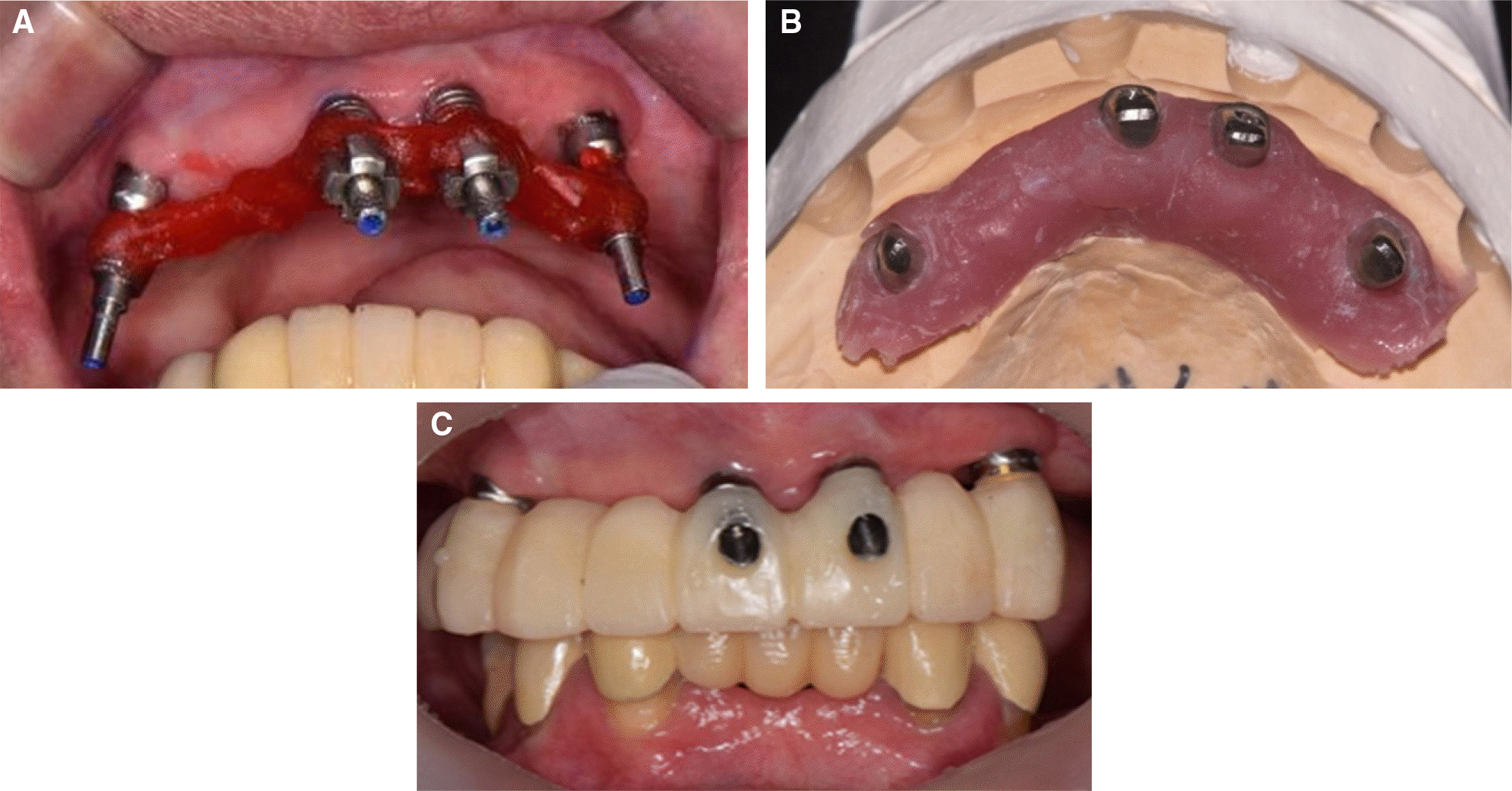
Fig. 5.
Digital design of customized titanium CAD/CAM abutments. (A) frontal view, (B) sagittal view.
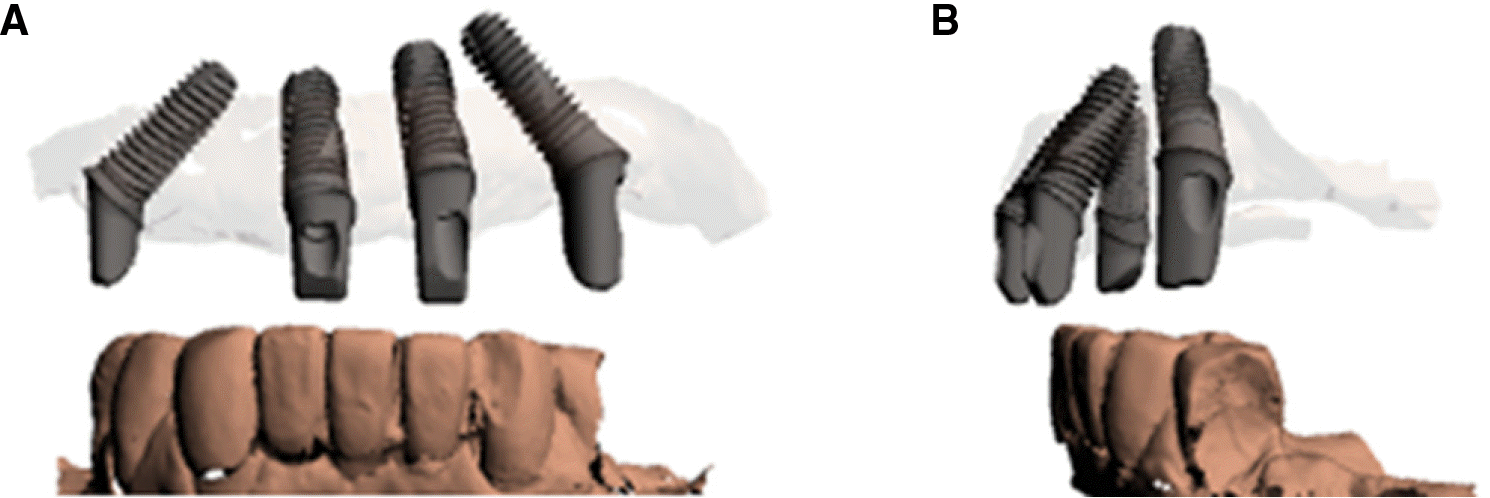
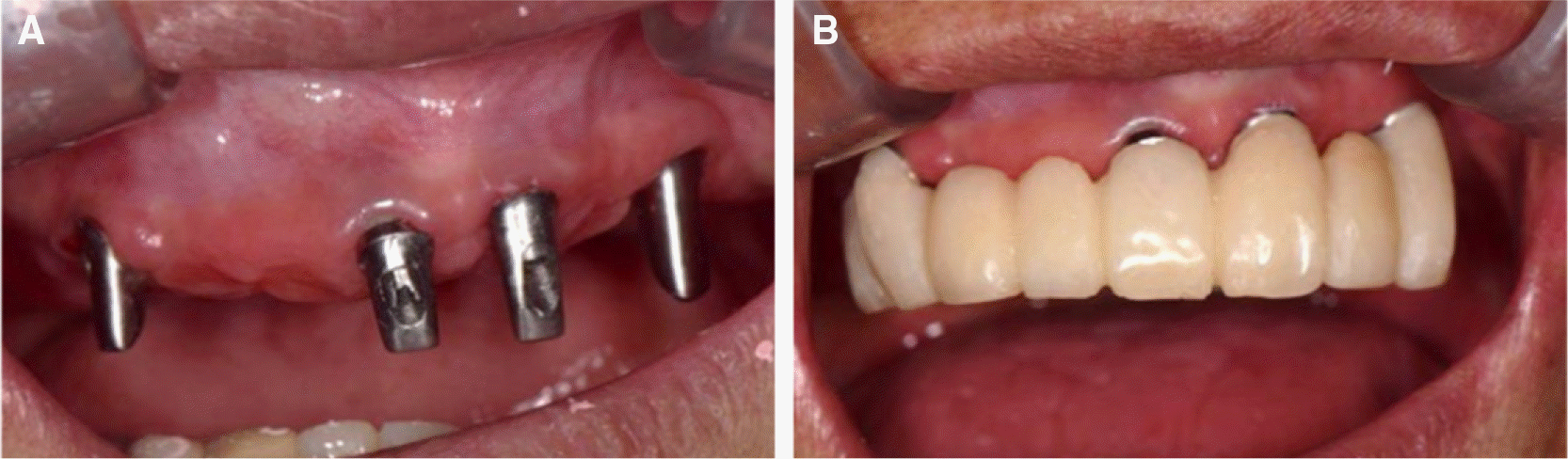
Fig. 6.
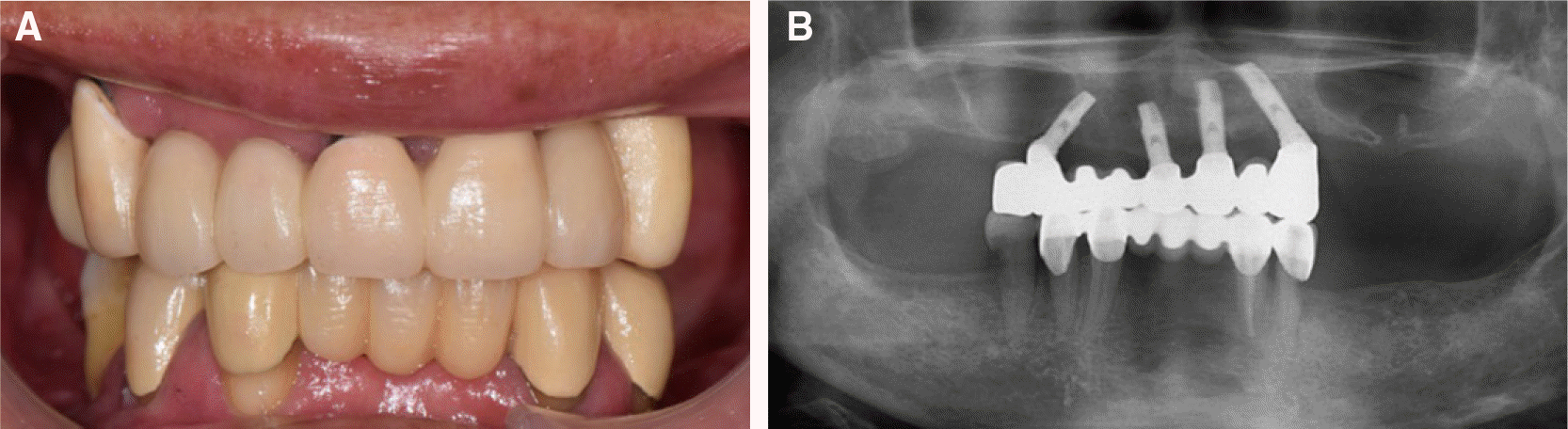
CAD/CAM abutments. (A) Connected customized abutments to implants, (B) Provisional restoration on the CAD/CAM abutments.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download