Abstract
In case of the insufficient horizontal bone loss, a regular diameter implant is not possible without lateral bone augmentation. In this situation, narrow diameter implants (NDIs) could be the alternative to lateral bone augmentation procedures. However, complication generally expected with the NDI is implant fracture. Recently, the survival rate and success rate of NDI in the posterior region are similar to that of standard-diameter implants (SDIs). These 3 case reports demonstrate the incorporation of NDI to replace missing mandibular posterior teeth. So far, the follow-up examination period was maintained and no unusual complications were presented for more than four years. Long term follow-up clinical data are needed to confirm the excellent clinical performance of these implants. (J Korean Acad Prosthodont 2017;55:212-7)
REFERENCES
1.Tolentino L., Sukekava F., Garcez-Filho J., Tormena M., Lima LA., Arau′jo MG. One-year follow-up of titanium/zirconium alloy X commercially pure titanium narrow-diameter implants placed in the molar region of the mandible: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2016. 27:393–8.

2.Altuna P., Lucas-Taule′ E., Gargallo-Albiol J., Figueras-A′lvarez O., Herna′ndez-Alfaro F., Nart J. Clinical evidence on titanium-zirconium dental implants: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016. 45:842–50.

3.Cehreli MC., Akça K. Narrow-diameter implants as terminal support for occlusal three-unit FPDs: a biomechanical analysis. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2004. 24:513–9.
4.Jensen AT., Jensen SS., Worsaae N. Complications related to bone augmentation procedures of localized defects in the alveolar ridge. A retrospective clinical study. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016. 20:115–22.

5.Chiapasco M., Zaniboni M., Boisco M. Augmentation procedures for the rehabilitation of deficient edentulous ridges with oral implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006. 17:136–59.

6.Klein MO., Schiegnitz E., Al-Nawas B. Systematic review on success of narrow-diameter dental implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2014. 29:43–54.

7.Buser D., von Arx T., ten Bruggenkate C., Weingart D. Basic surgical principles with ITI implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2000. 11:59–68.

8.Romeo E., Lops D., Amorfini L., Chiapasco M., Ghisolfi M., Vogel G. Clinical and radiographic evaluation of small-diameter (3.3-mm) implants followed for 1-7 years: a longitudinal study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006. 17:139–48.

9.Arisan V., Bölükba i N., Ersanli S., Ozdemir T. Evaluation of 316 narrow diameter implants followed for 5-10 years: a clinical and radiographic retrospective study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010. 21:296–307.
10.Malo′ P., de Arau′jo Nobre M. Implants (3.3 mm diameter) for the rehabilitation of edentulous posterior regions: a retrospective clinical study with up to 11 years of follow-up. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2011. 13:95–103.
11.Assaf A., Saad M., Daas M., Abdallah J., Abdallah R. Use of narrow-diameter implants in the posterior jaw: a systematic review. Implant Dent. 2015. 24:294–306.
12.Chiapasco M., Casentini P., Zaniboni M., Corsi E., Anello T. Titanium-zirconium alloy narrow-diameter implants (Straumann Roxolid(�)) for the rehabilitation of horizontally deficient edentulous ridges: prospective study on 18 consecutive patients. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012. 23:1136–41.
13.Allum SR., Tomlinson RA., Joshi R. The impact of loads on standard diameter, small diameter and mini implants: a comparative laboratory study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2008. 19:553–9.

14.Javed F., Romanos GE. Role of implant diameter on long-term survival of dental implants placed in posterior maxilla: a systematic review. Clin Oral Investig. 2015. 19:1–10.

15.Lee JS., Kim HM., Kim CS., Choi SH., Chai JK., Jung UW. Long-term retrospective study of narrow implants for fixed dental prostheses. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2013. 24:847–52.

16.Misch CE. Implant design considerations for the posterior regions of the mouth. Implant Dent. 1999. 8:376–86.

17.Zinsli B., Sägesser T., Mericske E., Mericske-Stern R. Clinical evaluation of small-diameter ITI implants: a prospective study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2004. 19:92–9.
19.Grandin HM., Berner S., Dard M. A review of titanium zirconium (TiZr) Alloys for use in endosseous dental implants. Materials. 2012. 5:1348–60.

20.Sista S., Wen C., Hodgson PD., Pande G. The influence of surface energy of titanium-zirconium alloy on osteoblast cell functions in vitro. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2011. 97:27–36.

21.Thoma DS., Jones AA., Dard M., Grize L., Obrecht M., Cochran DL. Tissue integration of a new titanium-zirconium dental implant: a comparative histologic and radiographic study in the canine. J Periodontol. 2011. 82:1453–61.

22.Geckili O., Munncu E., Bilhan H. Radiographic Evaluation of Narrow-Diameter Implants After 5 Years of Clinical Function: A Retrospective Study. Journal of Oral Implantology. 2013. 39:273–9.

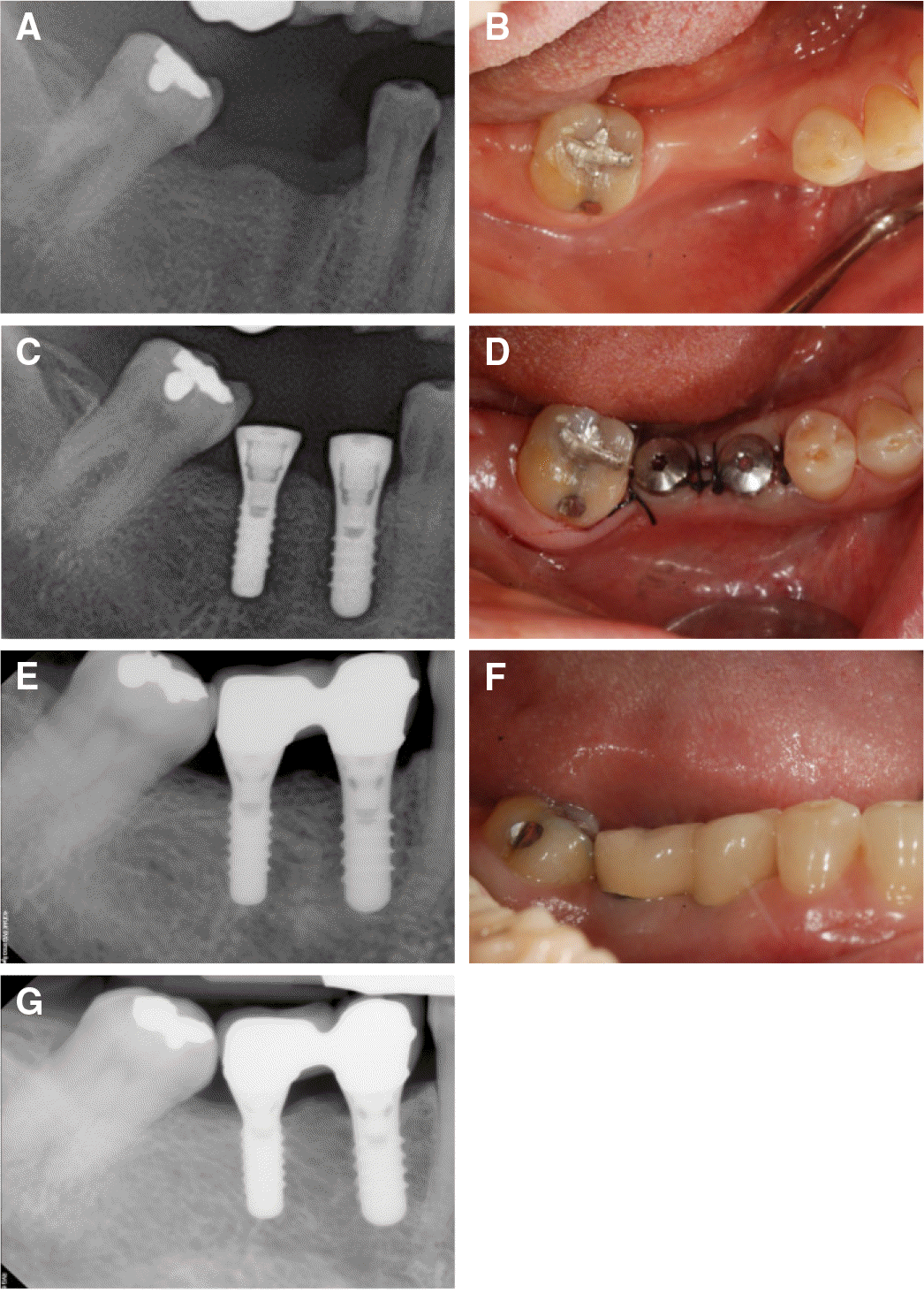
Fig. 1.
Clinical pictures of case 1. (A), (B) after tooth extraction, (C), (D) implant surgery, (E), (F) the placement of definitive prosthesis, (G) 51-months follow up after the placement of definitive prosthesis placement.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download