Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study is to compare the accuracy of the CT guided implant template that was produced by using an intraoral scanner according to the edentulous distance.
Materials and methods
Five maxillary casts were fabricated using radiopaque acrylic resin with the second premolars, first molars, and second molars missing. Then a virtual cast was acquired by scanning each resin cast. Implant treatment was planned on the missing sites by superimposing the presurgical CT DICOM file and the virtual cast. Then the implants were placed using a surgical template followed by postsurgical CT scan. The distance and angle of the platform and apex between the presurgical implant and postsurgical implant were measured using the X, Y, and Z axis of the superimposed presurgical CT and postsurgical CT via software followed by statistical analysis using Kruskall-Wallis test and Mann-Whitney test.
Results
The implant placement angle error increased towards the second molars but there was no statistically significant difference. The implant placement distance error at the platform and apex also increased towards the second molars and there was a statistically significant error at the second molars.
Conclusion
Although the placement angle had no statistically significant difference between the presurgical implant and postsurgical implant, the placement distance at the platform and apex showed a larger error and a statistically significant difference at the second molar implant. (J Korean Acad Prosthodont 2017;55:1-8)
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.Park C., Raigrodski AJ., Rosen J., Spiekerman C., London RM. Accuracy of implant placement using precision surgical guides with varying occlusogingival heights: an in vitro study. J Prosthet Dent. 2009. 101:372–81.

2.Noharet R., Pettersson A., Bourgeois D. Accuracy of implant placement in the posterior maxilla as related to 2 types of surgical guides: a pilot study in the human cadaver. J Prosthet Dent. 2014. 112:526–32.
4.Ganz SD. Presurgical planning with CT-derived fabrication of surgical guides. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005. 63:59–71.

5.Güth JF., Keul C., Stimmelmayr M., Beuer F., Edelhoff D. Accuracy of digital models obtained by direct and indirect data capturing. Clin Oral Investig. 2013. 17:1201–8.

6.Reyes A., Turkyilmaz I., Prihoda TJ. Accuracy of surgical guides made from conventional and a combination of digital scanning and rapid prototyping techniques. J Prosthet Dent. 2015. 113:295–303.

7.Turbush SK., Turkyilmaz I. Accuracy of three different types of stereolithographic surgical guide in implant placement: an in vitro study. J Prosthet Dent. 2012. 108:181–8.

8.van Steenberghe D., Naert I., Andersson M., Brajnovic I., Van Cleynenbreugel J., Suetens P. A custom template and definitive prosthesis allowing immediate implant loading in the maxilla: a clinical report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2002. 17:663–70.
9.Van Assche N., van Steenberghe D., Guerrero ME., Hirsch E., Schutyser F., Quirynen M., Jacobs R. Accuracy of implant placement based on presurgical planning of three-dimensional conebeam images: a pilot study. J Clin Periodontol. 2007. 34:816–21.

10.Villa R. A technique for the presurgical simulation of the position of computer-assisted, template-based, planned implants: a clinical report. J Prosthet Dent. 2014. 112:1030–4.

11.Di Giacomo GA., Cury PR., de Araujo NS., Sendyk WR., Sendyk CL. Clinical application of stereolithographic surgical guides for implant placement: preliminary results. J Periodontol. 2005. 76:503–7.
12.Pettersson A., Kero T., Gillot L., Cannas B., Fäldt J., Söderberg R., Näsström K. Accuracy of CAD/CAM-guided surgical template implant surgery on human cadavers: Part I. J Prosthet Dent. 2010. 103:334–42.

13.Ruppin J., Popovic A., Strauss M., Spüntrup E., Steiner A., Stoll C. Evaluation of the accuracy of three different computer-aided surgery systems in dental implantology: optical tracking vs. stereolith-ographic splint systems. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2008. 19:709–16.

Go to : 
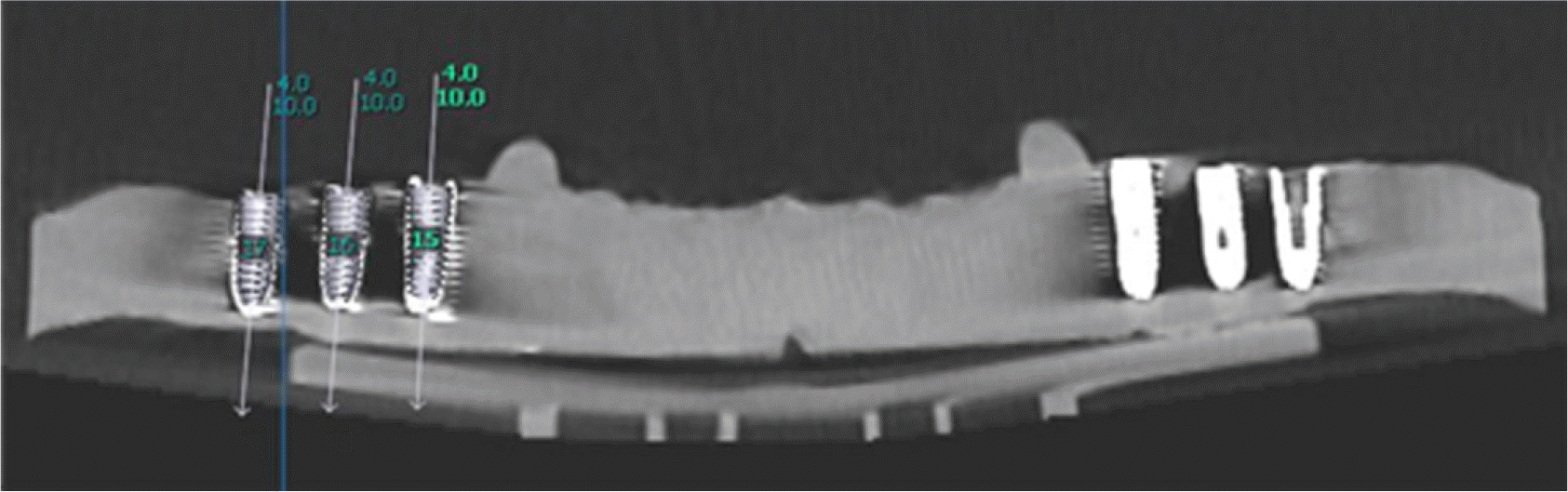
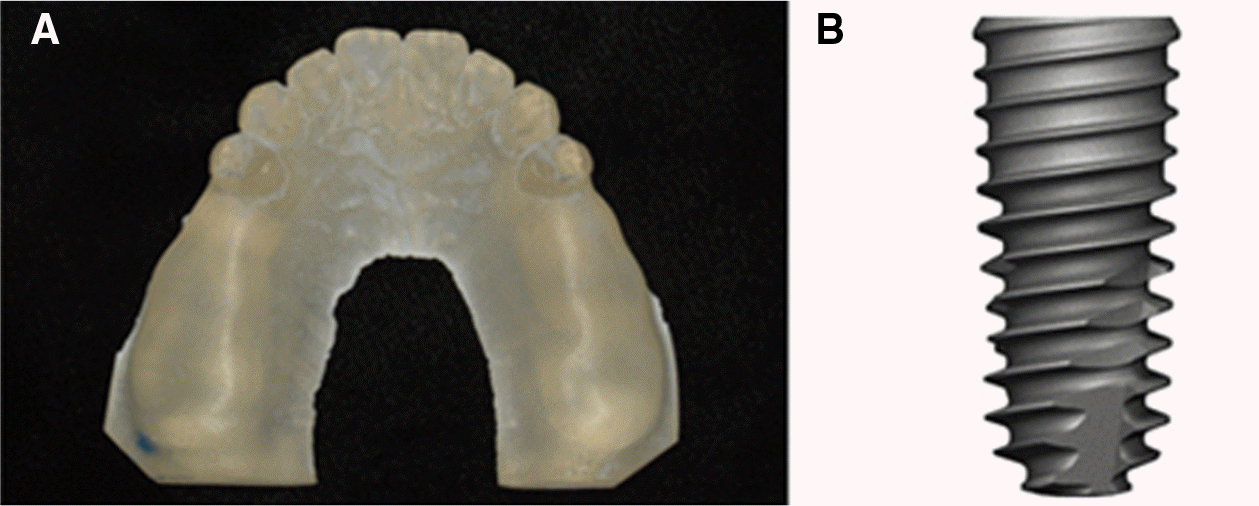 | Fig. 1.Resin model and implant uesd in this study. (A) Resin model made by VisiJet M3 Stoneplast (3DSYSTEMS), (B) TS III SA (Osstem. Co.). |
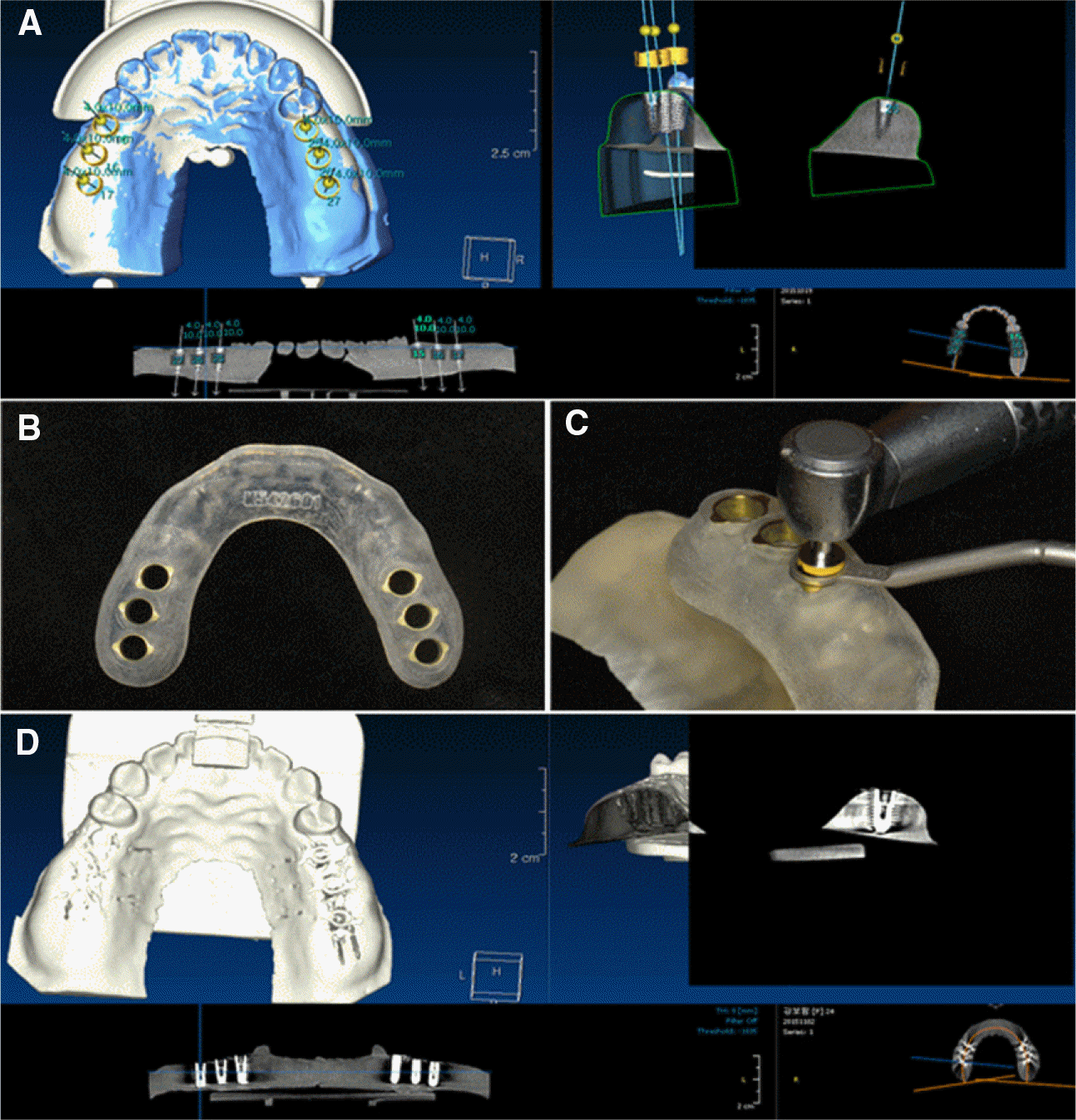 | Fig. 3.Planning and insertion of implant. (A) Planning on position and angulation of the implant, (B) CT guided implant template, (C) Drilling through the implant template with a drill, (D) Post-surgical cone beam-CT image. |
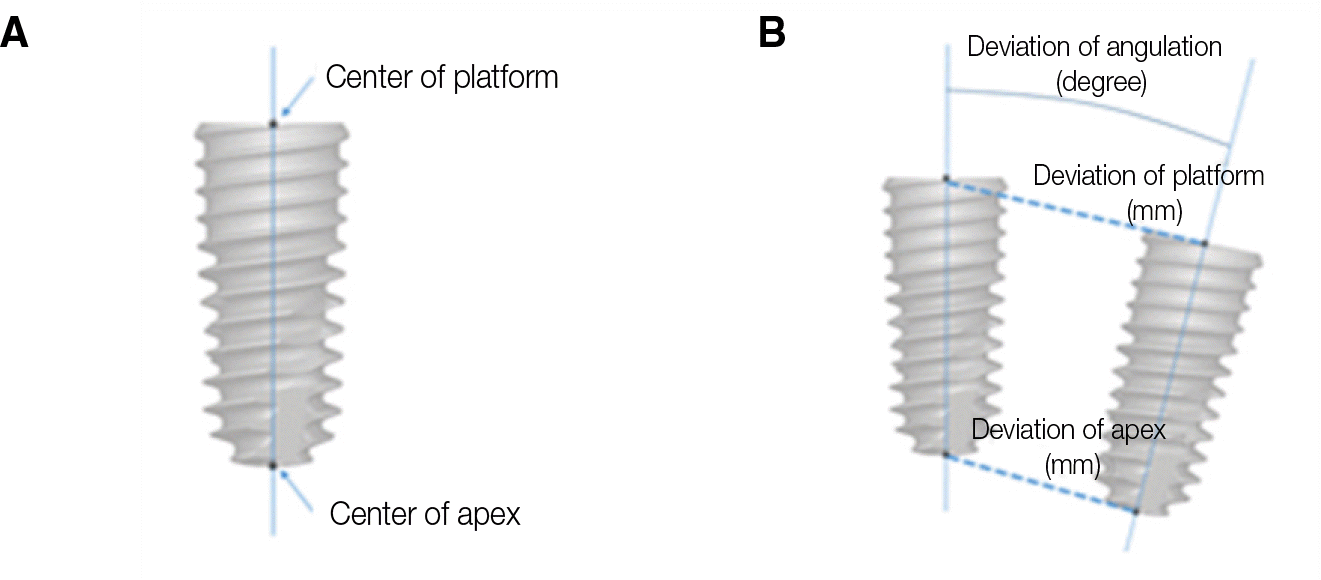 | Fig. 5.Deviation between virtually planned and actually placed implant. (A) Center of prosthetic platform of implant, and apex refers to center of tip of implant, (B) Deviation between virtually planned and actually placed implant is illustrated for platform, apex, and angulation. |
Table 1.
Variation of platform of implant
| Variation of platform of implant | Kruskall-Wallis Mean ± SD (mm) | Mann-Whitney | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #5 | #6 | #7 | ||
| #5 | 0.230 ± 0.06 | 0.289 | < 0.05† | |
| #6 | 0.270 ± 0.09 | < 0.05† | ||
| #7 | 0.480 ± 0.12 | |||
| All | 0.325 ± 0.14 | |||
| P-value | < .05∗ | |||
Table 2.
Variation of apex of implant
| Variation of apex of implant | Kruskall-Wallis Mean ± SD (mm) | Mann-Whitney | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #5 | #6 | #7 | ||
| #5 | 0.390 ± 0.06 | 0.198 | < 0.05† | |
| #6 | 0.430 ± 0.06 | < 0.05† | ||
| #7 | 0.640 ± 0.07 | |||
| All | 0.486 ± 0.13 | |||
| P-value | < .05∗ | |||




 ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download